Secured debt offers lenders collateral protection, reducing risk and often resulting in lower interest rates, making it a traditional choice for debt structuring. Carbon-neutral debt integrates environmental sustainability by funding projects that offset carbon emissions, attracting investors focused on green finance and enhancing corporate social responsibility. Balancing secured debt with carbon-neutral debt strategies enables companies to optimize financial stability while advancing climate goals.
Table of Comparison
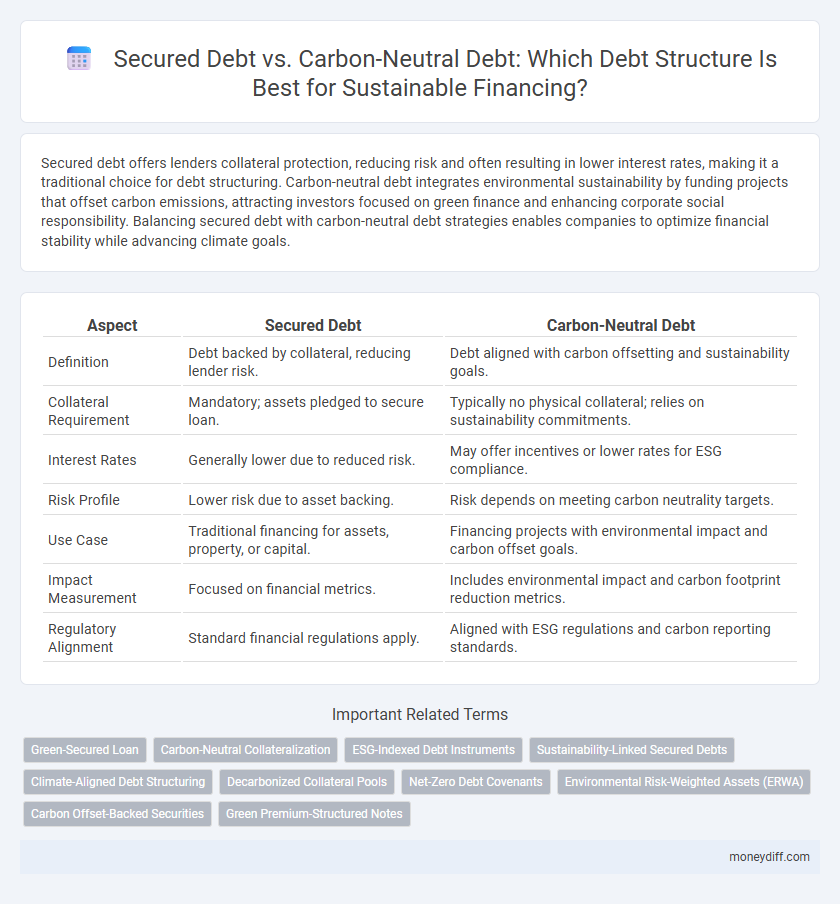
| Aspect | Secured Debt | Carbon-Neutral Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debt backed by collateral, reducing lender risk. | Debt aligned with carbon offsetting and sustainability goals. |
| Collateral Requirement | Mandatory; assets pledged to secure loan. | Typically no physical collateral; relies on sustainability commitments. |
| Interest Rates | Generally lower due to reduced risk. | May offer incentives or lower rates for ESG compliance. |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk due to asset backing. | Risk depends on meeting carbon neutrality targets. |
| Use Case | Traditional financing for assets, property, or capital. | Financing projects with environmental impact and carbon offset goals. |
| Impact Measurement | Focused on financial metrics. | Includes environmental impact and carbon footprint reduction metrics. |
| Regulatory Alignment | Standard financial regulations apply. | Aligned with ESG regulations and carbon reporting standards. |
Understanding Secured Debt: Definition and Key Features
Secured debt is a type of borrowing backed by collateral, which reduces the lender's risk and often results in lower interest rates. Key features include specific asset pledges, priority claims in case of default, and detailed legal agreements outlining rights and obligations. Unlike carbon-neutral debt that emphasizes environmental impact, secured debt primarily focuses on enhancing credit security through tangible asset guarantees.
Carbon-Neutral Debt: What It Means in Modern Finance
Carbon-neutral debt represents a transformative approach in modern finance by offsetting the carbon emissions associated with borrowing activities, aligning debt structuring with global sustainability goals. This type of debt integrates environmental impact assessments and carbon offset mechanisms, enabling companies to finance projects while minimizing their carbon footprint. Secured debt, traditionally backed by collateral, contrasts with carbon-neutral debt by emphasizing environmental responsibility over asset guarantees in risk management.
Comparing Risk Profiles: Secured vs Carbon-Neutral Debt
Secured debt typically carries lower risk due to collateral backing, which reduces lender exposure in default scenarios, while carbon-neutral debt often incorporates environmental impact assessments that can influence risk through regulatory incentives or potential penalties. The creditworthiness in secured debt is primarily driven by asset valuation and liquidity, whereas carbon-neutral debt risk profiles hinge on the issuer's sustainability practices and compliance with evolving climate policies. Investors must balance traditional financial security against emerging environmental risks and opportunities when structuring debt portfolios.
Collateral Requirements: Traditional Debt vs Sustainable Alternatives
Secured debt typically demands tangible collateral such as property or equipment to mitigate lender risk, ensuring priority claims in default scenarios. Carbon-neutral debt, often classified as sustainable finance instruments, may involve less conventional or intangible collateral like carbon credits or sustainability-linked assets, reflecting evolving market acceptance. This shift in collateral requirements influences debt structuring by integrating environmental criteria, potentially unlocking new funding avenues while complicating asset valuation processes.
Interest Rates: How Green Initiatives Affect Borrowing Costs
Secured debt typically offers lower interest rates due to collateral backing, reducing lender risk and improving borrowing costs for organizations. Carbon-neutral debt, often linked to green initiatives and sustainability goals, can attract preferential rates and incentives from investors focused on environmental impact. These green financing options influence debt structuring by potentially lowering interest expenses while aligning capital strategy with corporate environmental responsibility targets.
Environmental Impact of Debt Structuring Choices
Secured debt typically prioritizes collateral value and lender protection, often leading to investments in traditional, high-carbon industries with significant environmental footprints. Carbon-neutral debt, by contrast, integrates environmental impact into the structuring process, promoting funding for renewable energy projects and sustainable assets that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing carbon-neutral debt over secured debt can significantly lower an organization's carbon footprint and align financial strategies with climate goals.
Investor Preferences: Secured vs ESG-Focused Debt Instruments
Investors show a strong preference for secured debt due to its collateral backing, which reduces risk and enhances creditworthiness. In contrast, ESG-focused carbon-neutral debt appeals to investors prioritizing sustainability and long-term environmental impact, often accepting lower yields for positive social outcomes. Debt structuring increasingly balances these preferences by integrating secured debt's risk mitigation with the growing demand for ESG-aligned, carbon-neutral investment opportunities.
Regulatory Landscape for Secured and Carbon-Neutral Debts
Regulatory frameworks for secured debt emphasize collateral requirements and risk mitigation, ensuring creditor protection and contractual enforcement. Carbon-neutral debt faces evolving regulations focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, including mandatory disclosure of carbon offsets and alignment with international climate agreements such as the Paris Accord. Compliance with these distinct regulatory landscapes shapes debt structuring strategies, balancing financial security with sustainability commitments.
Long-Term Financial Stability: Traditional vs Green Debt Approaches
Secured debt offers long-term financial stability by providing lenders with collateral, reducing risk and often resulting in lower interest rates, which supports predictable repayment structures. Carbon-neutral debt, as part of green financing, promotes sustainable investments that align with environmental goals while potentially attracting ESG-focused investors seeking long-term value. Integrating carbon-neutral debt into debt structuring can enhance corporate reputation and access to innovative funding sources, balancing financial stability with environmental responsibility.
Choosing the Right Debt Structure: Factors for Businesses to Consider
Businesses should evaluate risk tolerance, collateral availability, and environmental goals when choosing between secured debt and carbon-neutral debt for debt structuring. Secured debt offers lower interest rates by leveraging assets, while carbon-neutral debt aligns with sustainability commitments and can enhance corporate climate reputation. Financial stability, regulatory incentives, and investor expectations are critical factors influencing the optimal debt structure selection.
Related Important Terms
Green-Secured Loan
Green-secured loans integrate environmental sustainability with traditional secured debt by using assets as collateral to lower interest rates while funding projects that reduce carbon emissions. This innovative debt structuring approach enhances credit risk management and supports carbon-neutral objectives, appealing to investors prioritizing both financial security and environmental impact.
Carbon-Neutral Collateralization
Carbon-neutral collateralization integrates environmental sustainability into debt structuring by securing loans with assets or projects that reduce or offset carbon emissions, enhancing green financing appeal. Unlike traditional secured debt relying solely on tangible assets, carbon-neutral debt leverages ecological impact as collateral, attracting investors committed to environmental responsibility and fostering sustainable economic growth.
ESG-Indexed Debt Instruments
Secured debt provides lenders with collateral-backed protection, enhancing credit quality and lowering borrowing costs, while carbon-neutral debt integrates environmental impact metrics, promoting sustainability-linked financing aligned with ESG goals. ESG-indexed debt instruments uniquely combine credit security with carbon neutrality targets, enabling issuers to access capital markets that prioritize ecological responsibility and risk mitigation simultaneously.
Sustainability-Linked Secured Debts
Sustainability-linked secured debts combine traditional secured debt structures with performance-based sustainability targets, enabling borrowers to lower interest rates by meeting predefined environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This innovative debt structuring promotes carbon neutrality by incentivizing companies to enhance their sustainability metrics while maintaining creditor protections through asset-backed guarantees.
Climate-Aligned Debt Structuring
Secured debt provides lenders with collateral protection, reducing risk and often lowering interest rates, while carbon-neutral debt integrates environmental impact considerations to align financing with climate goals. Climate-aligned debt structuring prioritizes sustainable investments by combining secured debt mechanisms with carbon offset strategies, enabling organizations to fund projects that support decarbonization and regulatory compliance.
Decarbonized Collateral Pools
Decarbonized collateral pools enhance secured debt structuring by incorporating carbon-neutral assets that reduce environmental risk and align with sustainability goals. This integration improves creditworthiness while supporting green finance initiatives and advancing corporate decarbonization efforts.
Net-Zero Debt Covenants
Net-zero debt covenants in debt structuring integrate carbon reduction targets directly into secured debt agreements, enhancing environmental accountability while maintaining creditor protections. Secured debt backed by tangible assets offers lower risk and cost, whereas carbon-neutral debt aligns financial incentives with sustainability goals, promoting long-term environmental and economic resilience.
Environmental Risk-Weighted Assets (ERWA)
Secured debt prioritizes collateral to mitigate credit risk, often overlooking environmental factors, whereas carbon-neutral debt incorporates Environmental Risk-Weighted Assets (ERWA) to directly address ecological impact and climate-related financial risks. Integrating ERWA in debt structuring enables more accurate risk assessment, promoting sustainability by incentivizing investments that reduce carbon footprints and enhance environmental performance.
Carbon Offset-Backed Securities
Secured debt is backed by tangible assets, offering lenders collateral protection, whereas carbon offset-backed securities represent carbon-neutral debt instruments where repayments are linked to verified carbon offset projects, integrating climate impact mitigation with financial returns. Implementing carbon offset-backed securities in debt structuring aligns investment goals with sustainability targets, attracting environmentally conscious investors and supporting global carbon reduction commitments.
Green Premium-Structured Notes
Green Premium-Structured Notes combine the credit security of traditional secured debt with sustainability-linked benefits, offering lower interest rates by incentivizing carbon-neutral project outcomes. This hybrid debt structuring mechanism optimizes capital costs and aligns investor interests with environmental impact goals, enhancing portfolio resilience through ESG-driven credit enhancements.
Secured debt vs carbon-neutral debt for debt structuring. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com