Bankruptcy offers a legal process to eliminate most debts but severely impacts credit scores and remains on credit reports for up to ten years. Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often resulting in less damage to credit but may require large lump-sum payments. Choosing between bankruptcy and debt settlement depends on the individual's financial situation, debt amount, and long-term credit goals.
Table of Comparison
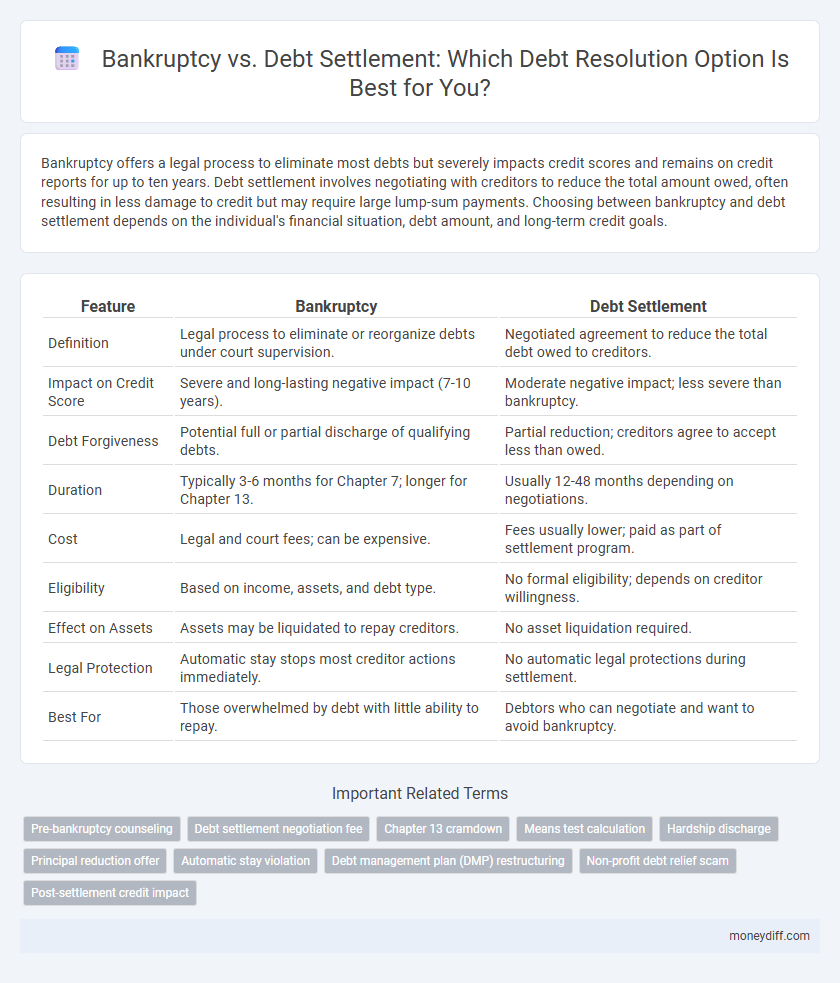
| Feature | Bankruptcy | Debt Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to eliminate or reorganize debts under court supervision. | Negotiated agreement to reduce the total debt owed to creditors. |
| Impact on Credit Score | Severe and long-lasting negative impact (7-10 years). | Moderate negative impact; less severe than bankruptcy. |
| Debt Forgiveness | Potential full or partial discharge of qualifying debts. | Partial reduction; creditors agree to accept less than owed. |
| Duration | Typically 3-6 months for Chapter 7; longer for Chapter 13. | Usually 12-48 months depending on negotiations. |
| Cost | Legal and court fees; can be expensive. | Fees usually lower; paid as part of settlement program. |
| Eligibility | Based on income, assets, and debt type. | No formal eligibility; depends on creditor willingness. |
| Effect on Assets | Assets may be liquidated to repay creditors. | No asset liquidation required. |
| Legal Protection | Automatic stay stops most creditor actions immediately. | No automatic legal protections during settlement. |
| Best For | Those overwhelmed by debt with little ability to repay. | Debtors who can negotiate and want to avoid bankruptcy. |
Understanding Bankruptcy: An Overview
Bankruptcy is a legal process designed to help individuals or businesses eliminate or repay debts under the protection of the bankruptcy court. It provides a structured framework to discharge unsecured debts like credit card balances or medical bills, typically through Chapter 7 or reorganize obligations under Chapter 13. Understanding bankruptcy involves recognizing its impact on credit scores, the potential for asset liquidation, and eligibility requirements based on income and debt levels.
What Is Debt Settlement? Key Concepts
Debt settlement is a negotiated agreement between a debtor and creditors to pay a reduced balance as full payment, typically used as an alternative to bankruptcy. This process involves working with creditors or a third-party company to reduce the overall debt amount, avoiding court involvement and potentially minimizing credit damage. Key concepts include understanding the impact on credit scores, potential tax implications, and the risk of creditor litigation during negotiations.
Bankruptcy vs Debt Settlement: Core Differences
Bankruptcy is a legal process that provides debt relief by discharging most or all debts, often resulting in a significant impact on credit scores for up to 10 years, whereas debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to pay a reduced lump-sum amount without legal intervention. Bankruptcy offers a structured and court-supervised resolution ideal for overwhelming debt situations, while debt settlement can be less costly but may lead to tax consequences and does not guarantee creditor agreement. Understanding the core differences in long-term credit effects, legal implications, and eligibility criteria is crucial for selecting the best debt resolution strategy.
Eligibility Criteria for Bankruptcy and Debt Settlement
Eligibility criteria for bankruptcy typically require individuals to demonstrate an inability to repay debts, often meeting specific income thresholds and asset disclosures under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 filings. Debt settlement eligibility depends on creditors' willingness to negotiate and the debtor's capacity to make lump-sum or installment payments, without statutory restrictions but influenced by the amount of outstanding unsecured debt. Understanding these criteria helps determine whether bankruptcy protection or a negotiated debt settlement offers a more viable solution for debt resolution.
How Each Process Affects Your Credit Score
Bankruptcy typically causes a significant and long-lasting negative impact on your credit score, remaining on your credit report for up to 10 years, which can hinder your ability to obtain new credit or favorable interest rates. Debt settlement may also lower your credit score, but the effect is often less severe and shorter-lived, as it involves negotiating with creditors to pay less than the full amount owed without the formal legal consequences of bankruptcy. Both options can damage credit, but debt settlement generally offers a less drastic credit impact while still providing a pathway to debt resolution.
Legal Implications of Bankruptcy and Debt Settlement
Bankruptcy involves a court-supervised process that legally discharges or restructures debts, significantly impacting credit scores and potentially resulting in asset liquidation depending on the chapter filed. Debt settlement, by contrast, is a negotiated agreement between debtor and creditor that reduces the total debt amount but often requires a lump-sum payment and may lead to tax consequences for forgiven debt. Both options carry distinct legal implications: bankruptcy provides automatic protection from creditor lawsuits, while debt settlement lacks formal legal protection, possibly leaving debtors vulnerable to collection actions.
Pros and Cons: Bankruptcy vs Debt Settlement
Bankruptcy offers a legal resolution by discharging most unsecured debts but severely impacts credit scores for 7-10 years, while debt settlement negotiates reduced payoffs, preserving credit history but may result in tax liabilities on forgiven amounts. Bankruptcy provides immediate debt relief and protection from creditors, yet involves court procedures and potential asset liquidation. Debt settlement avoids court involvement and can be less damaging to credit but often requires upfront negotiation fees and risks creditor lawsuits during the process.
Financial Impact: Costs and Fees Compared
Bankruptcy typically involves court fees and legal costs that can significantly affect one's credit profile for up to 10 years, while debt settlement usually incurs negotiation fees that may range from 15% to 25% of the settled debt amount. Although bankruptcy provides a more comprehensive debt discharge, it has a longer-lasting impact on future credit opportunities compared to debt settlement, which may allow for faster credit rebuilding but with potential tax consequences on forgiven amounts. Evaluating both options requires considering immediate out-of-pocket expenses against long-term financial recovery and creditworthiness.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Debt Situation
Bankruptcy provides legal protection by discharging certain debts but significantly impacts credit scores and may involve asset liquidation. Debt settlement negotiates reduced balances with creditors, preserving more credit value but risks fees and potential tax consequences on forgiven debt. Evaluate your financial status, credit goals, and long-term impact to select between bankruptcy or debt settlement for effective debt resolution.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bankruptcy and Debt Settlement
Bankruptcy offers legal protection from creditors and can discharge most unsecured debts but severely impacts credit scores for up to 10 years. Debt settlement involves negotiating reduced balances with creditors, which can damage credit scores temporarily and may result in tax liabilities from forgiven debt. Choosing between bankruptcy and debt settlement depends on factors like debt type, financial situation, and long-term credit goals, making it essential to consult with a qualified debt resolution expert.
Related Important Terms
Pre-bankruptcy counseling
Pre-bankruptcy counseling provides essential financial education and a personalized assessment to help debtors explore alternatives such as debt settlement or bankruptcy, potentially reducing debt burden without court involvement. This counseling is a mandatory step under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, ensuring informed decisions and improving outcomes in debt resolution strategies.
Debt settlement negotiation fee
Debt settlement negotiation fees typically range from 15% to 25% of the total debt enrolled, which can significantly impact the overall savings during debt resolution compared to bankruptcy, where court and attorney fees vary widely. Choosing debt settlement allows negotiators to reduce principal balances, but elevated negotiation fees may reduce net benefits, whereas bankruptcy may discharge most debts outright but involves distinct costs and credit implications.
Chapter 13 cramdown
Chapter 13 bankruptcy cramdown offers a structured debt resolution by reducing secured debt to the collateral's current market value, enabling lower monthly payments over a 3 to 5-year repayment plan. This option preserves credit better than bankruptcy liquidation and provides protection from creditor lawsuits while restructuring affordable debt repayment terms.
Means test calculation
The Means Test calculation assesses monthly income and expenses to determine eligibility for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, often comparing current income against the state median to establish repayment capability. In contrast, debt settlement does not require a Means Test but involves negotiating with creditors to reduce outstanding balances without court oversight.
Hardship discharge
Hardship discharge allows individuals to eliminate certain debts through bankruptcy when financial hardship makes repayment impossible, providing legal relief that debt settlement cannot guarantee. Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total owed but may adversely impact credit scores and does not provide the automatic protection against collections that hardship discharge offers.
Principal reduction offer
Bankruptcy typically results in the liquidation or reorganization of debt, often eliminating unsecured debts entirely, while debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to achieve a principal reduction offer, allowing borrowers to pay less than the full amount owed. A well-structured principal reduction can significantly lower debt balances, providing a more manageable repayment plan without the severe credit impact associated with bankruptcy.
Automatic stay violation
Bankruptcy provides an automatic stay that legally halts creditor actions, whereas debt settlement lacks this immediate protective injunction, potentially leading to automatic stay violations if creditors continue collection efforts during settlement negotiations. Violating the bankruptcy automatic stay can result in severe penalties and legal consequences for creditors, emphasizing the importance of understanding these protections in debt resolution.
Debt management plan (DMP) restructuring
Debt management plan (DMP) restructuring offers a strategic alternative to bankruptcy by consolidating unsecured debts into a manageable monthly payment, often lowering interest rates and fees while protecting credit scores. Unlike bankruptcy, DMPs emphasize negotiated repayment terms tailored to individual financial situations, enabling debtors to resolve obligations without asset liquidation or court involvement.
Non-profit debt relief scam
Non-profit debt relief scams exploit consumers by falsely promising debt settlement or bankruptcy alternatives with upfront fees and no real assistance, targeting vulnerable individuals seeking debt resolution. Understanding the differences between legitimate bankruptcy filings and debt settlement options is crucial to avoid fraud and ensure effective, lawful debt relief.
Post-settlement credit impact
Bankruptcy typically causes a more severe and prolonged negative impact on credit scores, remaining on credit reports for up to 10 years, while debt settlement may lower credit scores temporarily but usually stays on reports for only 7 years. Post-settlement, borrowers often face reduced credit limits and higher interest rates, requiring careful financial management to rebuild creditworthiness.
Bankruptcy vs debt settlement for debt resolution. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com