Debt settlement involves agreeing to pay a reduced lump sum to creditors to resolve the debt, often impacting credit scores negatively. Debt negotiation covers a broader range of strategies, including payment plans and interest rate reductions, aiming to make repayment more manageable without necessarily lowering the total amount owed. Choosing between the two depends on individual financial situations and goals for credit recovery.
Table of Comparison
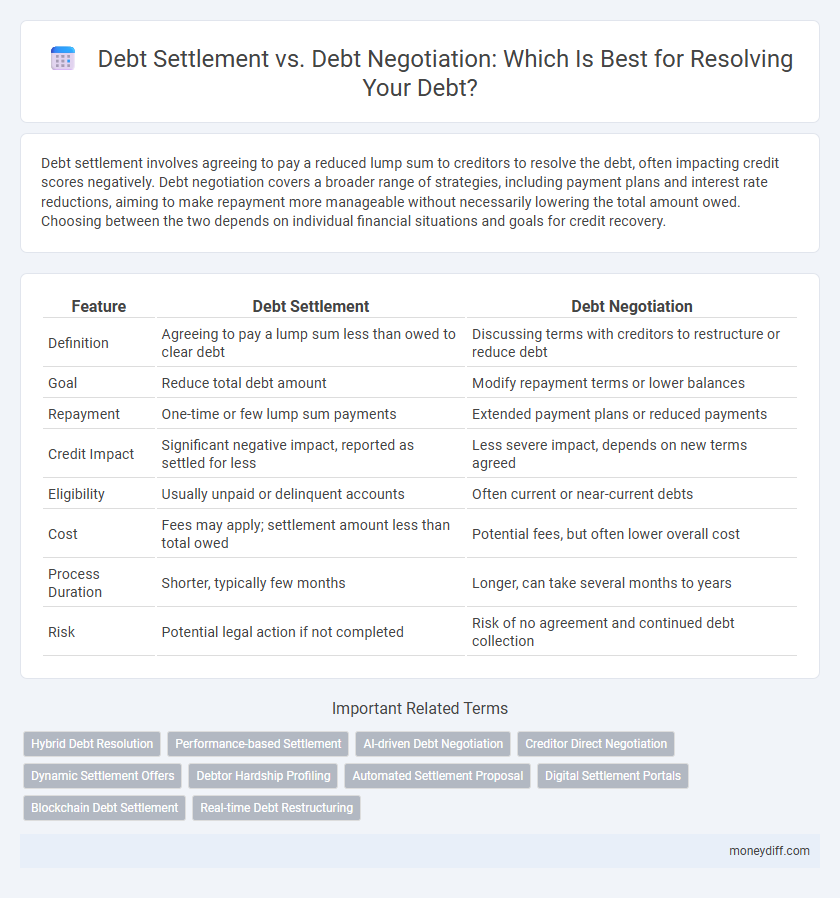
| Feature | Debt Settlement | Debt Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreeing to pay a lump sum less than owed to clear debt | Discussing terms with creditors to restructure or reduce debt |
| Goal | Reduce total debt amount | Modify repayment terms or lower balances |
| Repayment | One-time or few lump sum payments | Extended payment plans or reduced payments |
| Credit Impact | Significant negative impact, reported as settled for less | Less severe impact, depends on new terms agreed |
| Eligibility | Usually unpaid or delinquent accounts | Often current or near-current debts |
| Cost | Fees may apply; settlement amount less than total owed | Potential fees, but often lower overall cost |
| Process Duration | Shorter, typically few months | Longer, can take several months to years |
| Risk | Potential legal action if not completed | Risk of no agreement and continued debt collection |
Understanding Debt Settlement and Debt Negotiation
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to pay a lump sum that is less than the total owed, often reducing the outstanding balance significantly. Debt negotiation encompasses a broader approach where terms such as interest rates, payment schedules, or principal amounts may be modified to achieve a manageable repayment plan. Both strategies aim to alleviate debt burdens but vary in impact on credit scores and potential tax implications.
Key Differences Between Debt Settlement and Debt Negotiation
Debt settlement involves a debtor negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often resulting in a lump-sum payment less than the original debt balance. Debt negotiation focuses on modifying the original debt terms, such as lowering interest rates or extending payment periods, rather than reducing the principal amount. The key differences lie in the financial outcome--debt settlement aims for debt reduction, while debt negotiation seeks manageable repayment conditions without necessarily lowering the overall debt.
Pros and Cons of Debt Settlement
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, offering the advantage of potentially lowering debt significantly and avoiding bankruptcy, but it can severely impact credit scores and may lead to tax liabilities on forgiven amounts. This approach often requires a lump-sum payment or a structured payout plan, which can be challenging for individuals with limited financial resources. While debt settlement can provide relief from overwhelming debt burdens, the risk of accruing additional fees and the possibility of legal action from creditors remain significant drawbacks.
Pros and Cons of Debt Negotiation
Debt negotiation offers borrowers a chance to reduce the total amount owed by negotiating directly with creditors, often resulting in partial debt forgiveness, which can improve financial stability and credit management. However, debt negotiation may negatively impact credit scores, involve potential tax consequences on forgiven amounts, and requires disciplined negotiation skills or professional assistance to secure favorable terms. It provides flexibility and control over repayment plans but can carry risks of prolonged negotiation periods and possible creditor rejection.
How Each Approach Impacts Your Credit Score
Debt settlement typically results in a partial debt forgiveness but may cause significant negative marks on your credit report, lowering your credit score by 50 to 150 points. Debt negotiation focuses on agreeing with creditors to modify payment terms or reduce interest, often preserving credit score better by showing ongoing repayment efforts. Both strategies impact creditworthiness differently, with debt negotiation generally presenting a less damaging effect on future credit opportunities.
Which Debts Qualify for Settlement or Negotiation?
Credit card debt, medical bills, personal loans, and some utility arrears commonly qualify for debt settlement or negotiation, while secured debts like mortgages and auto loans typically do not. Settlement agreements often target unsecured debts with outstanding balances that the creditor considers less likely to be fully repaid. Many lenders and collection agencies accept negotiation proposals for overdue accounts, but government-backed loans such as student loans usually have limited or no settlement options.
Costs and Fees: Comparing Debt Settlement vs. Negotiation
Debt settlement often involves higher fees, typically ranging from 15% to 25% of the settled debt amount, while debt negotiation fees tend to be lower and may be charged as a flat rate or a smaller percentage of the negotiated savings. Debt settlement can also incur additional costs like taxes on forgiven debt, whereas negotiation might minimize these financial impacts. Understanding the specific fee structures and potential hidden costs is crucial when choosing between these debt relief methods.
Legal and Tax Implications of Each Method
Debt settlement often involves a legally binding agreement where the debtor pays a reduced amount to satisfy the full debt, which may trigger taxable forgiven debt income reported to the IRS. Debt negotiation can be less formal and may not always create enforceable contracts, but it also carries the risk of tax consequences if the forgiven amount exceeds $600 and the creditor issues a 1099-C form for canceled debt. Both methods require careful consideration of potential impacts on credit reports, legal obligations, and tax liabilities to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
Choosing the Right Debt Resolution Strategy
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often leading to a lump-sum payment agreement, while debt negotiation may include restructuring payment terms without necessarily lowering the principal balance. Choosing the right debt resolution strategy depends on factors such as the debtor's financial stability, credit score impact, and willingness to make lump-sum payments. Comparing the long-term effects on credit health and potential tax implications is essential for selecting between debt settlement and negotiation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Debt Resolution Methods
Debt settlement involves reaching an agreement with creditors to pay a reduced lump sum, whereas debt negotiation may include various strategies like adjusting payment terms or interest rates without necessarily lowering the principal amount. Common questions focus on the impact on credit scores, potential tax liabilities from forgiven debt, and the likelihood of creditor acceptance. Understanding these distinctions helps individuals choose the most effective method for resolving outstanding debts efficiently.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Debt Resolution
Hybrid debt resolution combines the benefits of debt settlement and debt negotiation by offering tailored repayment plans that reduce overall debt while negotiating favorable terms with creditors, enhancing the likelihood of successful debt resolution. This approach maximizes debt reduction and improves credit recovery by leveraging both negotiated settlements and structured repayment options.
Performance-based Settlement
Performance-based debt settlement offers a results-driven approach where creditors agree to reduce outstanding balances contingent on successful payments, providing borrowers with tangible incentives and measurable outcomes. Debt negotiation, while flexible, often lacks the structured performance metrics that ensure accountability and optimize resolution efficiency.
AI-driven Debt Negotiation
AI-driven debt negotiation leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze debtors' financial data, enabling personalized settlement offers that maximize repayment while minimizing stress and financial impact. Unlike traditional debt settlement, AI enhances negotiation efficiency by predicting creditor responses and optimizing payment plans in real time, leading to better outcomes and faster resolution.
Creditor Direct Negotiation
Debt settlement involves negotiating directly with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often resulting in a lump-sum payment that settles the debt for less than the full balance. Creditor direct negotiation allows borrowers to bypass third-party intermediaries, potentially securing more favorable terms and avoiding additional fees associated with debt settlement companies.
Dynamic Settlement Offers
Dynamic settlement offers leverage real-time financial data and negotiation strategies to provide tailored debt resolution solutions, maximizing creditor acceptance rates while minimizing overall repayment amounts. Unlike traditional debt negotiation, these adaptive offers adjust based on creditor responses and debtor affordability, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of debt settlement processes.
Debtor Hardship Profiling
Debt settlement involves an agreement between debtor and creditor to reduce the total owed balance, often requiring detailed debtor hardship profiling to assess financial capacity and hardship severity. Debt negotiation focuses on restructuring payment terms or interest rates, leveraging debtor hardship profiles to tailor solutions that improve repayment feasibility without necessarily reducing the principal amount.
Automated Settlement Proposal
Automated settlement proposals streamline debt settlement by using algorithm-driven offers to creditors, increasing the efficiency and success rate compared to traditional debt negotiation methods that rely on manual communication. This technology reduces time and costs by generating optimized, personalized payoff options that improve debtor-creditor agreement outcomes.
Digital Settlement Portals
Digital settlement portals streamline the debt settlement process by providing automated tools that facilitate offers and payments directly between debtors and creditors, enhancing transparency and reducing processing time. Debt negotiation, often handled by third-party agencies, involves personalized negotiation strategies that may not be fully integrated with digital platforms, potentially leading to longer resolution periods and less control for the debtor.
Blockchain Debt Settlement
Blockchain debt settlement leverages decentralized ledger technology to securely automate and streamline the debt resolution process, reducing intermediaries and enhancing transparency. Debt negotiation involves direct discussions between debtor and creditor to agree on repayment terms, but blockchain platforms introduce immutable contracts and real-time tracking, making settlements more efficient and trustworthy.
Real-time Debt Restructuring
Debt settlement involves reaching a lump-sum agreement with creditors to pay less than the total owed, while debt negotiation encompasses a broader strategy including payment plans and interest rate adjustments to manage debt more effectively. Real-time debt restructuring leverages instant financial data to dynamically adjust repayment terms, optimizing outcomes and improving creditor-debtor communication during the resolution process.
Debt settlement vs Debt negotiation for resolving debt Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com