Debt consolidation simplifies managing multiple liabilities by combining them into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate, reducing monthly payments and easing financial stress. Debt snowflake involves making small, frequent extra payments toward debts, accelerating repayment without altering loan terms. Choosing debt consolidation offers structured relief and predictable budgeting, while the debt snowflake method emphasizes incremental progress and flexibility in reducing overall debt faster.
Table of Comparison
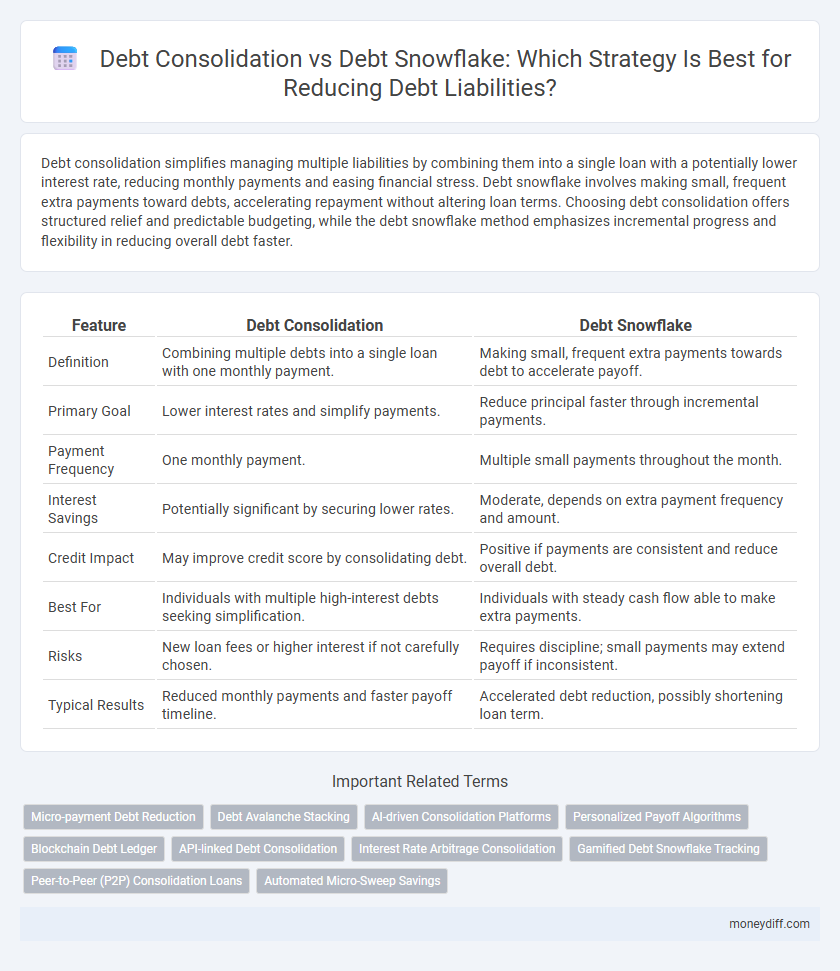
| Feature | Debt Consolidation | Debt Snowflake |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple debts into a single loan with one monthly payment. | Making small, frequent extra payments towards debt to accelerate payoff. |
| Primary Goal | Lower interest rates and simplify payments. | Reduce principal faster through incremental payments. |
| Payment Frequency | One monthly payment. | Multiple small payments throughout the month. |
| Interest Savings | Potentially significant by securing lower rates. | Moderate, depends on extra payment frequency and amount. |
| Credit Impact | May improve credit score by consolidating debt. | Positive if payments are consistent and reduce overall debt. |
| Best For | Individuals with multiple high-interest debts seeking simplification. | Individuals with steady cash flow able to make extra payments. |
| Risks | New loan fees or higher interest if not carefully chosen. | Requires discipline; small payments may extend payoff if inconsistent. |
| Typical Results | Reduced monthly payments and faster payoff timeline. | Accelerated debt reduction, possibly shortening loan term. |
Understanding Debt Consolidation: Key Concepts
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple high-interest debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, simplifying repayment and potentially reducing overall interest costs. This method improves cash flow management by consolidating credit card balances, personal loans, and other liabilities into one monthly payment, often with fixed terms and predictable schedules. Key concepts include assessing the total debt amount, interest rates, loan terms, and fees to determine if consolidation reduces financial burden effectively compared to alternative strategies like the debt snowflake method.
What is the Debt Snowflake Method?
The Debt Snowflake Method involves making small, frequent extra payments toward debts using spare change or unexpected funds, accelerating overall debt reduction by leveraging minor cash flows. Unlike Debt Consolidation, which combines multiple debts into a single loan with usually lower interest rates, the snowflake approach focuses on incremental progress without restructuring existing debts. This method maximizes cash flow efficiency by allocating small amounts toward principal reductions, potentially shortening the payoff timeline and reducing total interest paid.
Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation simplifies multiple high-interest debts into a single monthly payment, often with a lower interest rate, which can improve cash flow and make budgeting easier. However, it may extend the repayment period, potentially increasing total interest paid, and risks accumulating more debt if spending habits are not controlled. This method is best suited for individuals seeking structured repayment and easier management of existing liabilities.
Benefits and Drawbacks of the Debt Snowflake Approach
The Debt Snowflake approach allows for frequent small payments towards multiple debts, accelerating overall liability reduction and improving cash flow management by targeting high-interest balances incrementally. Its flexibility in using spare change or incidental income reduces financial stress but can prolong repayment time compared to lump-sum options. However, inconsistent payment amounts may complicate budgeting and tracking progress, potentially diminishing motivation without disciplined commitment.
Comparing Interest Savings: Consolidation vs Snowflakes
Debt consolidation typically offers lower interest rates by merging multiple high-interest debts into a single loan, resulting in significant interest savings over time. Debt snowflaking, which involves making extra payments on specific debts using small, irregular amounts, reduces principal faster but may yield smaller interest savings compared to consolidation. Comparing these methods, consolidation often maximizes interest reduction through lower rates, while snowflaking emphasizes accelerated payoff without necessarily obtaining lower interest rates.
Impact on Credit Score: Which Method is Safer?
Debt consolidation typically improves credit scores by reducing credit utilization and making payments more manageable, while debt snowflake methods involve smaller, frequent payments that can maintain consistent activity but may cause variable impact. Consolidation loans often lead to a more stable credit profile by lowering outstanding balances and simplifying accounts, reducing the risk of missed payments. Snowflake payments help avoid delinquency but require disciplined budgeting to positively affect credit score stability over time.
Monthly Payment Strategies for Each Approach
Debt consolidation typically involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with one monthly payment, often at a lower interest rate, simplifying budgeting and potentially reducing total monthly expenses. In contrast, the debt snowflake method focuses on making frequent, smaller extra payments towards individual debts using leftover funds from daily expenses, accelerating debt reduction without changing the structure of monthly payments. Choosing between these strategies depends on whether a borrower prioritizes streamlined payments and possible interest savings or the flexibility of making incremental reductions across multiple debts.
Suitability: Which Debt Reduction Method Fits Your Situation?
Debt consolidation suits individuals with multiple high-interest debts seeking a single, manageable monthly payment, often through lower interest rates and structured plans. Debt snowflake is ideal for those with irregular extra cash inflows, enabling small, frequent payments to multiple debts without formal restructuring. Assessing income stability, debt types, and personal financial discipline determines the most effective approach for reducing liabilities efficiently.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a Debt Reduction Strategy
Choosing between debt consolidation and debt snowflake methods often leads to common mistakes such as underestimating interest rates in consolidation loans or overestimating small payments' impact in the snowflake approach. Many individuals fail to consider the total repayment timeline or hidden fees associated with consolidation, which can extend debt duration. Ignoring budget discipline and neglecting to track incremental snowflake payments can reduce the effectiveness of debt snowflake strategies and result in prolonged liabilities.
Creating an Action Plan: Consolidation or Snowflake for Success
Creating an effective action plan for reducing liabilities involves choosing between debt consolidation and the debt snowflake method based on individual financial behavior and goals. Debt consolidation simplifies payments by combining multiple debts into a single loan with lower interest rates, while the debt snowflake method accelerates repayment through small, frequent extra payments from everyday savings. Careful assessment of interest rates, cash flow, and discipline ensures the chosen strategy maximizes debt reduction and improves credit health efficiently.
Related Important Terms
Micro-payment Debt Reduction
Debt consolidation streamlines multiple balances into a single loan with a fixed interest rate, simplifying payments and often lowering monthly costs, while the debt snowflake method targets micro-payments--small, frequent amounts redirected from daily expenses--to accelerate principal reduction and minimize interest accrual. Utilizing micro-payment strategies within a debt snowflake approach can enhance cash flow efficiency and reduce liabilities faster compared to traditional consolidation plans.
Debt Avalanche Stacking
Debt Avalanche Stacking prioritizes paying off high-interest debts first, accelerating liability reduction more efficiently than Debt Consolidation or Debt Snowflake methods by minimizing total interest paid over time. This strategy targets loans with the highest APR, leveraging strategic repayment sequencing to optimize debt elimination while maintaining manageable payments.
AI-driven Consolidation Platforms
AI-driven debt consolidation platforms leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze multiple liabilities and create optimized payment strategies, significantly reducing interest rates and overall debt faster than traditional methods. Unlike the debt snowflake approach, which relies on sporadic small payments, these AI systems provide a structured, data-driven roadmap for efficient liability reduction tailored to individual financial profiles.
Personalized Payoff Algorithms
Personalized payoff algorithms optimize debt reduction by analyzing individual liabilities and payment behaviors, enabling tailored strategies in both debt consolidation and debt snowflake methods. Debt consolidation simplifies monthly obligations into a single payment, while debt snowflake uses frequent small payments, both enhanced by algorithm-driven prioritization for maximum interest savings and faster liability reduction.
Blockchain Debt Ledger
Debt consolidation centralizes multiple liabilities into a single blockchain debt ledger, enhancing transparency and immutability while simplifying repayment tracking. Debt snowflake strategies leverage micro-payments distributed across various blockchain addresses, optimizing incremental liability reduction with real-time ledger updates for precise debt management.
API-linked Debt Consolidation
API-linked debt consolidation offers seamless integration of multiple liabilities into a single payment platform, enhancing efficiency and reducing default risks through automated tracking and payment scheduling. In contrast, the debt snowflake method leverages small, frequent payments to gradually lower debt but lacks the centralized control and real-time data analytics provided by API-driven consolidation services.
Interest Rate Arbitrage Consolidation
Debt consolidation leverages interest rate arbitrage by unifying multiple high-interest debts into a single loan with a lower average interest rate, thereby reducing overall interest costs and simplifying repayment. In contrast, the debt snowflake method involves making small, frequent payments towards multiple debts, offering less opportunity for interest rate arbitrage and often resulting in higher cumulative interest expenses over time.
Gamified Debt Snowflake Tracking
Gamified Debt Snowflake Tracking leverages micro-payments and interactive challenges to accelerate debt reduction by turning everyday spending into strategic liability payments, contrasting with traditional Debt Consolidation which combines multiple debts into a single loan with a fixed interest rate. This innovative approach increases user engagement and consistency, making it particularly effective for those seeking gradual but steady progress in managing and reducing individual debts.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Consolidation Loans
Peer-to-peer (P2P) consolidation loans offer a streamlined approach to managing multiple debts by combining liabilities into a single, lower-interest payment, reducing overall financial burden more effectively than debt snowflake methods. Unlike debt snowflaking, which relies on small, sporadic payments to various debts, P2P consolidation loans provide structured repayment plans and often access to competitive interest rates from individual lenders, enhancing debt reduction efficiency.
Automated Micro-Sweep Savings
Debt consolidation streamlines multiple high-interest debts into a single, lower-interest loan, simplifying repayments and reducing total liabilities, while the debt snowflake method leverages automated micro-sweep savings by capturing small, frequent savings from daily transactions to aggressively pay down multiple debts simultaneously. Automated micro-sweep savings optimize cash flow by reallocating minor disposable funds towards debt reduction, accelerating liability repayment without restructuring existing loans.
Debt Consolidation vs Debt Snowflake for reducing liabilities. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com