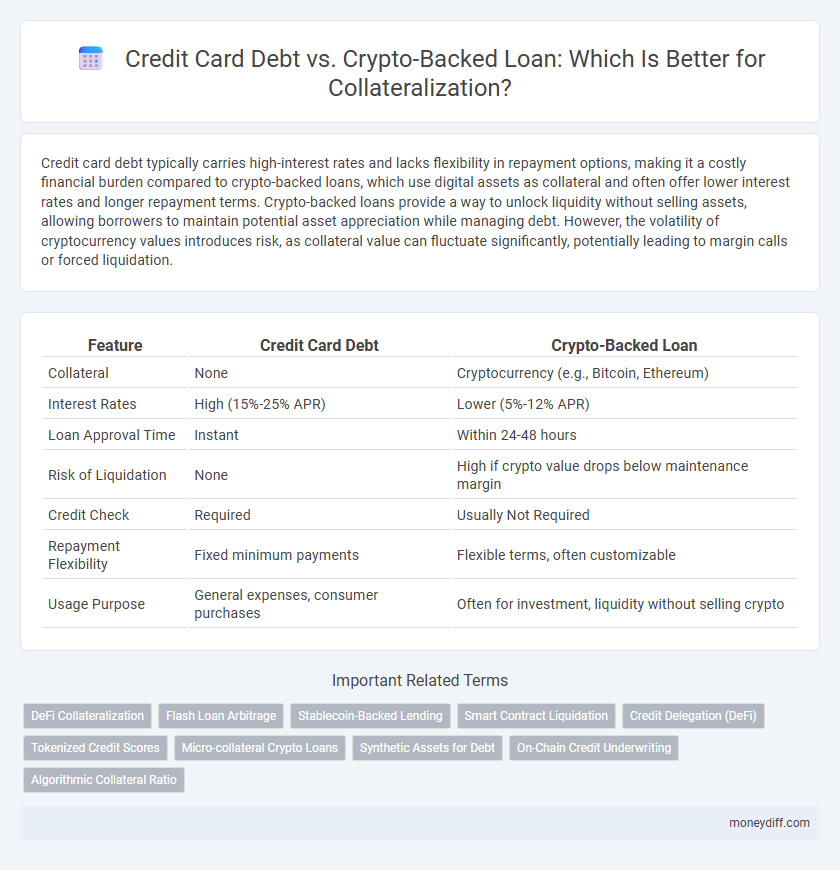
Credit card debt typically carries high-interest rates and lacks flexibility in repayment options, making it a costly financial burden compared to crypto-backed loans, which use digital assets as collateral and often offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms. Crypto-backed loans provide a way to unlock liquidity without selling assets, allowing borrowers to maintain potential asset appreciation while managing debt. However, the volatility of cryptocurrency values introduces risk, as collateral value can fluctuate significantly, potentially leading to margin calls or forced liquidation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Credit Card Debt | Crypto-Backed Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral | None | Cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) |
| Interest Rates | High (15%-25% APR) | Lower (5%-12% APR) |
| Loan Approval Time | Instant | Within 24-48 hours |
| Risk of Liquidation | None | High if crypto value drops below maintenance margin |
| Credit Check | Required | Usually Not Required |
| Repayment Flexibility | Fixed minimum payments | Flexible terms, often customizable |
| Usage Purpose | General expenses, consumer purchases | Often for investment, liquidity without selling crypto |
Understanding Credit Card Debt: Features and Risks
Credit card debt typically involves high interest rates and revolving balances, making it costly and difficult to pay off quickly. The lack of asset backing increases the risk of accumulating unmanageable debt and negatively impacting credit scores. Understanding the terms, interest compounding, and minimum payment requirements is essential to avoid long-term financial strain.
What Are Crypto-Backed Loans?
Crypto-backed loans allow borrowers to use their cryptocurrency holdings as collateral to secure a loan, typically offering lower interest rates compared to traditional credit card debt. Unlike credit card debt, which often carries high-interest rates and can negatively impact credit scores, crypto-backed loans provide a more flexible repayment structure and maintain ownership of the underlying crypto asset. This method leverages digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, enabling users to access liquidity without selling their investments.
Comparing Interest Rates: Credit Cards vs Crypto Loans
Credit card debt typically comes with interest rates ranging from 15% to 25%, significantly higher than crypto-backed loans, which often offer rates between 4% and 12%. Crypto-backed loans use digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, enabling lower risk for lenders and thus more competitive interest rates. Borrowers leveraging crypto collateral can benefit from fixed or variable APRs well below standard credit card rates, making crypto loans a cost-effective alternative for managing debt.
Collateral Requirements and Implications
Credit card debt typically requires no collateral, resulting in higher interest rates and greater risk for lenders, while crypto-backed loans use digital assets as collateral, enabling lower interest rates but exposing borrowers to asset volatility. Collateral requirements for crypto-backed loans often demand a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio between 50% and 70%, impacting borrowing capacity and liquidation risk. Failure to maintain collateral value can trigger automatic liquidation in crypto loans, unlike unsecured credit card debt which relies solely on the borrower's creditworthiness.
Repayment Flexibility: Which Option Suits You?
Credit card debt typically involves fixed monthly payments and high interest rates, limiting repayment flexibility and increasing financial strain. Crypto-backed loans offer adjustable repayment terms and the option to repay in either fiat or cryptocurrency, providing greater adaptability to fluctuating income. Evaluating your financial stability and risk tolerance helps determine whether the rigid structure of credit cards or the dynamic terms of crypto loans better suit your repayment needs.
Impact on Credit Score: Traditional vs Crypto Lending
Credit card debt directly impacts credit scores through credit utilization ratios and payment history reported to credit bureaus, often lowering scores if balances remain high or payments are missed. In contrast, crypto-backed loans generally do not affect credit scores because they are not reported to traditional credit agencies, offering a way to leverage assets without impacting creditworthiness. However, failure to repay crypto-backed loans can result in asset liquidation, posing a risk distinct from credit score implications.
Accessibility and Approval Process
Credit card debt typically involves a straightforward application process with immediate accessibility but often carries higher interest rates and stricter credit score requirements. Crypto-backed loans provide easier collateralization by using digital assets, enabling faster approval with less reliance on traditional credit histories, yet they depend on volatile asset valuations. Accessibility in crypto-backed loans is expanding globally due to decentralized platforms, offering an alternative path for borrowers with limited credit options.
Security Risks: Credit Cards vs Digital Assets
Credit card debt exposes borrowers to risks such as high-interest rates and potential identity theft, while crypto-backed loans carry vulnerabilities including price volatility and smart contract exploits. Unlike credit cards, digital assets used as collateral can rapidly fluctuate in value, resulting in liquidation risks and loss of collateral. Security protocols in crypto lending platforms vary widely, making thorough due diligence essential to minimize fraud and cyberattacks.
Potential for Asset Liquidation and Loss
Credit card debt carries a high risk of escalating interest rates and potential damage to credit scores if payments are missed, often leading to increased financial strain. Crypto-backed loans use digital assets as collateral, which can be rapidly liquidated during market volatility, resulting in a forced sale at unfavorable prices and significant loss of invested assets. The potential for sudden asset liquidation in crypto-backed loans poses a greater risk compared to the more predictable but accumulating interest burden of credit card debt.
Choosing the Right Debt Solution for Your Financial Goals
Credit card debt typically carries high-interest rates and variable repayment terms, which can strain monthly cash flow and increase overall financial burden. Crypto-backed loans offer lower interest rates by using digital assets as collateral, but they present risks of asset volatility and potential liquidation during market downturns. Evaluating factors such as interest rates, repayment flexibility, and risk tolerance is essential in selecting the optimal debt solution aligned with your financial goals.
Related Important Terms
DeFi Collateralization
Credit card debt typically involves high-interest rates and unsecured borrowing, whereas DeFi collateralization through crypto-backed loans offers lower rates and transparent, blockchain-based asset-backed security. Utilizing crypto assets as collateral in decentralized finance platforms enables real-time liquidation and reduces default risk compared to traditional credit models.
Flash Loan Arbitrage
Credit card debt typically carries high-interest rates and limited flexibility, while crypto-backed loans leverage digital assets as collateral, enabling lower costs and faster access to capital. Flash loan arbitrage exploits instant, unsecured loans within blockchain networks, allowing borrowers to perform risk-free, rapid trades without traditional collateral, contrasting with the secured nature of crypto-backed loans.
Stablecoin-Backed Lending
Stablecoin-backed lending offers a more secure and transparent alternative to credit card debt by using pegged digital assets as collateral, reducing the risk of volatile interest rates and enabling faster loan approvals. This innovative approach leverages blockchain technology to provide more predictable repayment terms and improved financial accessibility compared to traditional unsecured credit card borrowing.
Smart Contract Liquidation
Credit card debt typically involves fixed interest rates and centralized control, whereas crypto-backed loans use blockchain-based smart contracts that automatically trigger liquidation upon collateral value dropping below a predefined threshold, ensuring transparent and immediate risk management. Smart contract liquidation minimizes borrower default risk by autonomously enforcing loan terms without manual intervention, contrasting with traditional credit card debt collection processes.
Credit Delegation (DeFi)
Credit card debt carries high interest rates and rigid repayment schedules, whereas crypto-backed loans in DeFi utilize credit delegation to enable trustless collateralization and flexible borrowing without transferring ownership of assets. Credit delegation protocols enhance capital efficiency by allowing delegatees to access delegated credit lines while maintaining decentralized control, reducing reliance on traditional credit assessments.
Tokenized Credit Scores
Tokenized credit scores enhance transparency and risk assessment in both credit card debt and crypto-backed loan collateralization, enabling more accurate borrower profiling and lower default rates. Utilizing blockchain technology, these tokenized scores facilitate seamless credit data sharing while protecting privacy, thereby optimizing loan terms and interest rates for consumers leveraging digital assets or traditional credit.
Micro-collateral Crypto Loans
Micro-collateral crypto loans offer a flexible alternative to traditional credit card debt by allowing borrowers to use small amounts of cryptocurrency as collateral, often resulting in lower interest rates and faster access to funds. Unlike credit card debt, which typically involves high-interest rates and limited borrowing limits, micro-collateral crypto loans leverage blockchain transparency and smart contracts to reduce risk and enhance loan accessibility for users with minimal crypto assets.
Synthetic Assets for Debt
Synthetic assets enable debt collateralization by tokenizing diverse financial instruments, offering an innovative alternative to traditional credit card debt. Using crypto-backed loans with synthetic assets allows borrowers to leverage digital collateral while minimizing exposure to high-interest rates and credit risks associated with unsecured credit card balances.
On-Chain Credit Underwriting
On-chain credit underwriting leverages blockchain data transparency to assess creditworthiness more accurately than traditional credit card debt models, reducing reliance on personal credit scores and enhancing collateralization through crypto-backed loans. Crypto-backed loans offer lower interest rates and flexible repayment options by utilizing digital assets as collateral, enabling borrowers to unlock liquidity without incurring high credit card debt fees and risks.
Algorithmic Collateral Ratio
Credit card debt typically carries high-interest rates without collateral, increasing financial risk, whereas crypto-backed loans utilize an algorithmic collateral ratio that dynamically adjusts based on market volatility to secure the loan and minimize default risk. This algorithmic collateral ratio ensures borrowers maintain a sufficient crypto asset buffer, optimizing loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and enhancing both lender security and borrower flexibility.
Credit card debt vs Crypto-backed loan for collateralization. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com