Traditional credit reports rely on historical data from credit bureaus, such as payment history and outstanding debts, to assess creditworthiness, often limiting insight for those with thin credit files. Open banking data enhances financial evaluation by providing real-time access to transactional information, income patterns, and spending behavior, offering a more holistic and accurate picture of an individual's financial health. Lenders leveraging open banking can make more informed decisions, potentially improving access to credit for underserved customers.
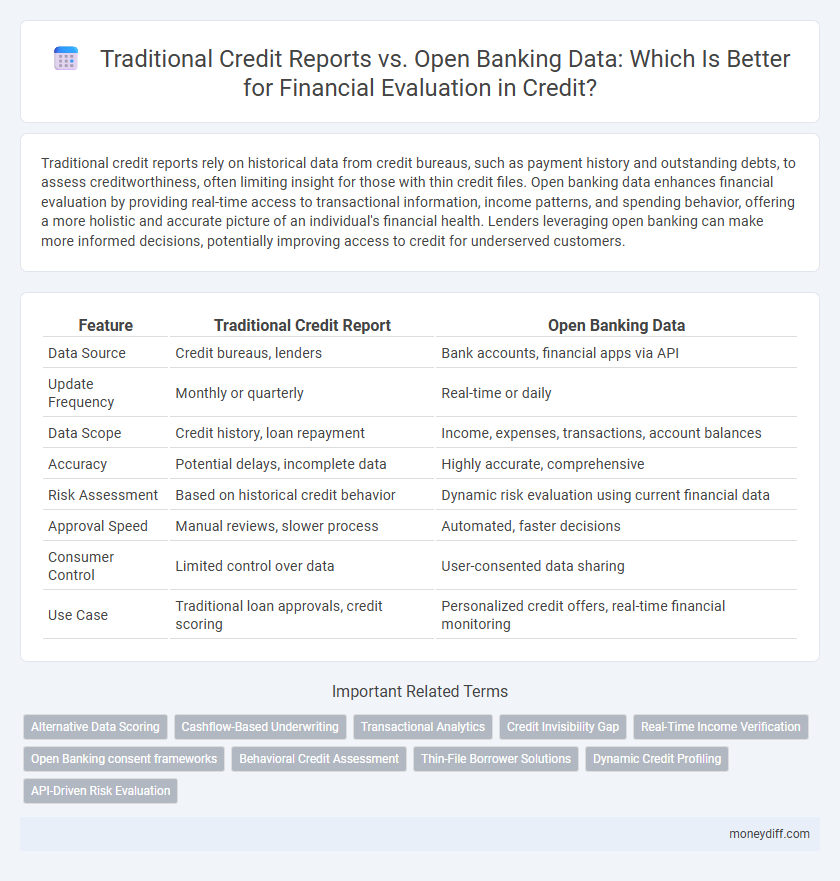
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Credit Report | Open Banking Data |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Credit bureaus, lenders | Bank accounts, financial apps via API |
| Update Frequency | Monthly or quarterly | Real-time or daily |
| Data Scope | Credit history, loan repayment | Income, expenses, transactions, account balances |
| Accuracy | Potential delays, incomplete data | Highly accurate, comprehensive |
| Risk Assessment | Based on historical credit behavior | Dynamic risk evaluation using current financial data |
| Approval Speed | Manual reviews, slower process | Automated, faster decisions |
| Consumer Control | Limited control over data | User-consented data sharing |
| Use Case | Traditional loan approvals, credit scoring | Personalized credit offers, real-time financial monitoring |
Introduction: Evolving Methods of Financial Evaluation
Traditional credit reports rely heavily on historical credit data and payment behavior tracked by major credit bureaus, often overlooking real-time financial activities and alternative income sources. Open banking data enhances financial evaluation by providing comprehensive, up-to-date insights into a consumer's cash flow, spending patterns, and income streams directly from bank accounts. This evolving method allows lenders to assess creditworthiness more accurately, reduce risk, and increase financial inclusion for individuals with limited credit history.
What Is a Traditional Credit Report?
A traditional credit report is a detailed record maintained by credit bureaus, containing historical data such as payment history, credit accounts, outstanding debts, and public records like bankruptcies. This report is primarily used by lenders to assess an individual's creditworthiness based on past borrowing and repayment behavior. Unlike real-time financial information, traditional credit reports often rely on periodic updates and may not reflect current income or cash flow status.
Understanding Open Banking Data
Open Banking data enhances financial evaluation by providing real-time access to detailed transaction histories, income patterns, and spending behaviors directly from bank accounts, offering a more dynamic and accurate credit profile compared to traditional credit reports. Traditional credit reports primarily rely on historical credit activity, such as loan repayments and credit card usage, which can miss current financial health indicators. Leveraging Open Banking data allows lenders to assess creditworthiness with greater precision by incorporating holistic financial behavior insights.
Key Differences Between Credit Reports and Open Banking
Traditional credit reports compile historical credit data from established credit bureaus, emphasizing past loan repayments, credit card usage, and public financial records. Open banking data provides real-time access to customers' financial transactions, offering a dynamic view of income, spending patterns, and cash flow directly from bank accounts. This shift enhances credit assessment accuracy by integrating continuous transactional insights rather than relying solely on static credit history.
Accuracy and Scope of Financial Data
Traditional credit reports rely heavily on historical credit behavior, offering a limited snapshot primarily based on loans and credit cards, which can omit significant financial aspects. Open banking data provides a more comprehensive and real-time view of an individual's financial status by incorporating transaction history, income patterns, and spending behavior from various accounts. This broader scope enhances the accuracy of financial evaluations, enabling lenders to make better-informed decisions with a finer understanding of creditworthiness.
Speed and Accessibility of Credit Evaluation
Traditional credit reports rely on historical financial data from credit bureaus, often causing delays due to manual processing and limited update frequency. Open banking data enables real-time access to a consumer's transactional information directly from bank accounts, significantly accelerating credit evaluations. This immediate data retrieval enhances accessibility for lenders, facilitating faster and more accurate credit decisions.
Impact on Financial Inclusion
Traditional credit reports rely on historical credit usage and payment behavior, often excluding individuals with limited credit history from financial opportunities. Open Banking data incorporates a broader range of financial information, including transaction patterns and income stability, enabling lenders to assess creditworthiness more accurately. This expanded data access significantly enhances financial inclusion by providing underserved populations with improved access to credit products.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Traditional credit reports consolidate borrowing history from multiple lenders, raising privacy concerns due to centralized data storage that can be vulnerable to breaches. Open banking data leverages real-time financial information directly from user-authorized bank accounts, enhancing control over data sharing while necessitating robust encryption and consent protocols to ensure security. Both methods must address stringent regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA to protect consumer privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
Which Method Do Lenders Prefer?
Lenders increasingly prefer open banking data over traditional credit reports for financial evaluation due to its real-time accuracy and comprehensive insight into a borrower's spending habits and cash flow. Traditional credit reports, while reliable for historical credit behavior, often lack the immediacy and depth provided by open banking, making it harder to assess current financial health. Open banking data enables more personalized risk assessment, leading to better-informed lending decisions and potentially quicker loan approvals.
Future Trends: Integrating Credit Reports and Open Banking
Future financial evaluations increasingly merge traditional credit reports with open banking data to provide a more comprehensive borrower profile. This integration enhances risk assessment accuracy by incorporating real-time transactional insights alongside historical credit information. Financial institutions leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze combined datasets, driving more personalized credit decisions and promoting financial inclusion.
Related Important Terms
Alternative Data Scoring
Traditional credit reports rely heavily on historical credit transactions and repayment patterns, often excluding valuable financial behaviors like utility payments and rental history. Alternative data scoring using open banking data enhances financial evaluation by incorporating real-time transaction analysis, income verification, and spending habits, offering a more comprehensive risk assessment for lenders.
Cashflow-Based Underwriting
Traditional credit reports rely heavily on historical credit data and payment histories, which may not accurately reflect real-time financial behavior, while open banking data enables cashflow-based underwriting by providing detailed, up-to-date transaction records and income streams. This dynamic approach enhances risk assessment and decision-making by capturing an individual's current financial health and cashflow patterns rather than just past credit activity.
Transactional Analytics
Transactional analytics in traditional credit reports rely heavily on historical credit behavior and static data, often missing real-time financial activities and spending patterns. Open banking data enhances financial evaluation by providing dynamic, granular transactional insights that offer a more comprehensive and current view of an individual's financial health.
Credit Invisibility Gap
Traditional credit reports rely on historical loan and repayment data, often excluding individuals without formal credit history, thereby exacerbating the credit invisibility gap affecting over 45 million American adults. Open banking data enables lenders to assess alternative financial behaviors such as transaction patterns and income flows, reducing the credit invisibility gap by providing a more inclusive and real-time view of consumers' financial health.
Real-Time Income Verification
Traditional credit reports rely on historical data from credit bureaus, often causing delays and inaccuracies in assessing a borrower's current financial status; open banking data enables real-time income verification by providing instant access to recent transaction data directly from bank accounts. This real-time insight improves the accuracy of financial evaluations, reduces fraud risk, and streamlines the lending decision process for both lenders and consumers.
Open Banking consent frameworks
Open Banking consent frameworks enable consumers to securely share real-time financial data from multiple accounts, offering a more comprehensive and accurate assessment compared to traditional credit reports that rely on static historical data. This enhanced transparency improves credit evaluations by incorporating up-to-date transactional information, reducing biases, and enabling personalized lending decisions.
Behavioral Credit Assessment
Traditional credit reports rely primarily on historical credit data such as payment history, credit utilization, and outstanding debts, providing a static snapshot of an individual's financial behavior. Open banking data enhances behavioral credit assessment by incorporating real-time transaction insights, income patterns, and cash flow dynamics, enabling more accurate and comprehensive risk evaluation.
Thin-File Borrower Solutions
Traditional credit reports often lack comprehensive data for thin-file borrowers, limiting accurate financial evaluation and credit risk assessment. Open banking data provides enhanced insights by incorporating real-time transaction information, enabling lenders to better assess creditworthiness and extend credit to underserved populations.
Dynamic Credit Profiling
Traditional credit reports rely on static historical data such as past loans and payment history, often missing real-time financial behavior, while Open Banking data enables dynamic credit profiling by continuously analyzing current account transactions and cash flow patterns. This real-time insight improves risk assessment accuracy and allows lenders to make faster, more personalized credit decisions.
API-Driven Risk Evaluation
API-driven risk evaluation leverages open banking data to provide real-time access to comprehensive financial transactions, enabling more accurate credit assessments compared to traditional credit reports that rely on static historical data. Integrating open banking APIs enhances predictive accuracy by incorporating dynamic cash flow insights, reducing default risk and expanding credit access for underserved consumers.
Traditional Credit Report vs Open Banking Data for financial evaluation. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com