Fixed interest rates provide borrowers with predictable repayment amounts, reducing uncertainty and facilitating budgeting over the loan term. Risk-based pricing adjusts interest rates according to the borrower's creditworthiness and risk profile, leading to more personalized loan costs that reflect potential default probabilities. Lenders use these approaches to balance risk management with competitive pricing strategies in the credit market.
Table of Comparison
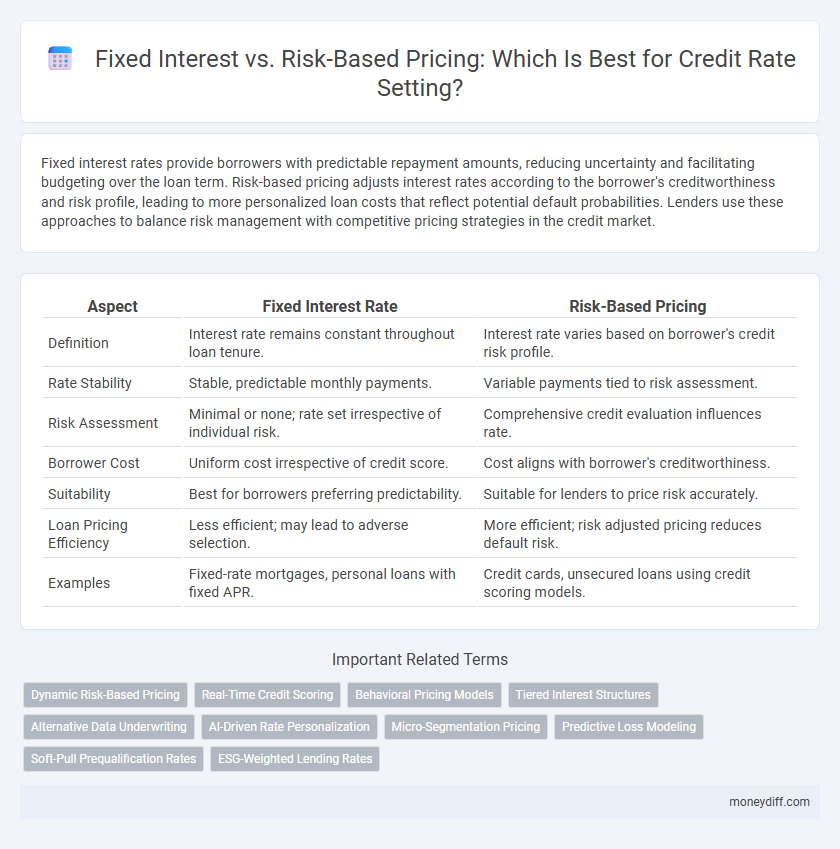
| Aspect | Fixed Interest Rate | Risk-Based Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interest rate remains constant throughout loan tenure. | Interest rate varies based on borrower's credit risk profile. |
| Rate Stability | Stable, predictable monthly payments. | Variable payments tied to risk assessment. |
| Risk Assessment | Minimal or none; rate set irrespective of individual risk. | Comprehensive credit evaluation influences rate. |
| Borrower Cost | Uniform cost irrespective of credit score. | Cost aligns with borrower's creditworthiness. |
| Suitability | Best for borrowers preferring predictability. | Suitable for lenders to price risk accurately. |
| Loan Pricing Efficiency | Less efficient; may lead to adverse selection. | More efficient; risk adjusted pricing reduces default risk. |
| Examples | Fixed-rate mortgages, personal loans with fixed APR. | Credit cards, unsecured loans using credit scoring models. |
Understanding Fixed Interest and Risk-Based Pricing
Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the loan term, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments and shielding them from market fluctuations. Risk-based pricing adjusts interest rates based on the borrower's creditworthiness, income stability, and repayment history, allowing lenders to price loans according to individual risk profiles. Understanding the trade-offs between fixed interest and risk-based pricing helps borrowers make informed decisions about cost predictability versus potential savings linked to credit risk factors.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Risk-Based Rates
Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and shielding borrowers from market fluctuations. Risk-based pricing adjusts rates according to the borrower's creditworthiness and financial behavior, often resulting in higher rates for riskier profiles but potentially lower costs for low-risk individuals. The key difference lies in predictability and customization: fixed rates offer stability, while risk-based rates align pricing with the borrower's risk level.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Interest Pricing
Fixed interest pricing provides predictable monthly payments and simplifies budgeting, making it a favored choice for borrowers seeking stability. It eliminates the uncertainty of rate fluctuations tied to market conditions or credit risk, but can result in higher initial rates compared to risk-based pricing that adjusts rates based on individual credit profiles. Fixed interest may limit lenders' ability to price risk accurately, potentially leading to less competitive offers for higher-risk borrowers or less profitability for lenders.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Risk-Based Pricing
Risk-based pricing offers lenders the advantage of tailoring interest rates to individual borrower credit risk, enhancing profitability by charging higher rates to riskier applicants while rewarding low-risk borrowers with lower rates. This customization improves credit access for diverse profiles but can also lead to higher rates for borrowers with poorer credit, potentially limiting affordability and increasing default risk. Critics argue it may exacerbate financial inequality, as economically vulnerable groups often face disproportionately higher costs.
Impact on Borrower Affordability
Fixed interest rates provide borrowers with predictable monthly payments, enhancing budgeting stability and long-term affordability. Risk-based pricing adjusts rates according to individual credit profiles, potentially increasing costs for higher-risk borrowers and affecting their repayment capacity. This dynamic pricing model can limit access to credit for borrowers with lower credit scores due to higher interest expenses.
Credit Assessment Methods in Rate Setting
Fixed interest rates provide borrowers with predictable monthly payments, relying primarily on standard credit scores and historical credit behavior in the credit assessment process. Risk-based pricing adjusts interest rates according to the borrower's individual risk profile, incorporating more granular data such as debt-to-income ratio, employment stability, and repayment history. Credit assessment methods in rate setting leverage advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to evaluate creditworthiness dynamically, enabling personalized rate proposals that reflect the true risk level of each borrower.
Lender Risk Management Strategies
Lender risk management strategies often weigh fixed interest rates against risk-based pricing to optimize loan profitability and borrower accessibility. Fixed interest rates provide stability in repayment terms, reducing uncertainty for both lenders and borrowers, while risk-based pricing adjusts rates according to individual credit risk profiles, enabling more precise risk mitigation. Implementing a hybrid approach allows lenders to balance portfolio risk and competitive positioning in diverse credit markets.
Regulatory Considerations for Interest Rate Pricing
Regulatory considerations for interest rate pricing emphasize transparency and fairness in both fixed interest and risk-based pricing models. Fixed interest rates offer predictability but may face scrutiny for potentially disadvantaging higher-risk borrowers, while risk-based pricing requires stringent compliance with anti-discrimination laws to ensure rates reflect genuine credit risk without bias. Regulators often mandate clear disclosure of rate-setting criteria and ongoing monitoring to prevent predatory lending and ensure equitable treatment of all credit applicants.
Market Trends Influencing Rate Setting Models
Market trends reveal a shift from traditional fixed interest rates to risk-based pricing models driven by advancements in big data analytics and machine learning algorithms. Lenders increasingly leverage real-time credit risk assessments and borrower behavior patterns to tailor interest rates, optimizing profitability while managing default risk. Regulatory focus on transparency and fairness simultaneously shapes the evolution of these dynamic rate-setting mechanisms in the credit industry.
Choosing the Best Pricing Model for Your Institution
Fixed interest rates provide predictable loan payments, enabling institutions to manage cash flow and reduce uncertainty in revenue forecasts. Risk-based pricing aligns rates with borrower credit profiles, improving risk management by pricing loans according to default probabilities and enhancing profitability on higher-risk loans. Selecting the best pricing model depends on the institution's risk tolerance, portfolio composition, and strategic goals for balancing growth and credit risk exposure.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Risk-Based Pricing
Dynamic risk-based pricing adjusts interest rates in real time using advanced algorithms that analyze borrower credit profiles, market conditions, and behavioral data to optimize risk assessment and profitability. This approach surpasses fixed interest rates by providing tailored pricing that reflects individual risk levels and adapts to changing financial environments, improving credit access and lender risk management.
Real-Time Credit Scoring
Real-time credit scoring enhances risk assessment accuracy by analyzing dynamic borrower data instantaneously, enabling lenders to implement risk-based pricing that reflects individual credit profiles more precisely than traditional fixed interest rates. This adaptive approach reduces default risk and improves loan portfolio performance by aligning interest rates with actual credit risk in real time.
Behavioral Pricing Models
Behavioral pricing models leverage detailed credit behavior data and payment histories to tailor interest rates beyond traditional fixed interest and risk-based approaches, enhancing precision in credit pricing. By analyzing real-time borrower actions and patterns, these models dynamically adjust rates to reflect true credit risk and incentivize positive financial behavior, optimizing profitability and customer retention.
Tiered Interest Structures
Tiered interest structures in credit pricing offer predefined rates based on creditworthiness tiers, ensuring transparency and predictability for borrowers. Unlike fixed interest rates that remain constant regardless of risk, tiered models adjust rates according to risk segments, balancing lender protection with borrower affordability.
Alternative Data Underwriting
Fixed interest rates provide borrowers with predictable payment schedules, while risk-based pricing adjusts rates according to individual credit risk profiles derived from alternative data such as utility payments, rental history, and social behavior. Alternative data underwriting enhances credit access by enabling lenders to more accurately assess borrower risk beyond traditional credit scores, promoting fairer and more inclusive rate setting.
AI-Driven Rate Personalization
AI-driven rate personalization leverages machine learning to analyze vast datasets, enabling more precise differentiation between fixed interest and risk-based pricing models by predicting individual credit risk and repayment behavior. This technology enhances rate setting accuracy, optimizing borrower affordability while minimizing lender risk through dynamic, data-driven adjustments.
Micro-Segmentation Pricing
Micro-segmentation pricing enables lenders to set fixed interest rates tailored to narrowly defined borrower profiles, enhancing predictability and simplifying credit risk management. Risk-based pricing, leveraging detailed borrower risk metrics, optimizes rate assignments within micro-segments, balancing profitability and default probability more precisely.
Predictive Loss Modeling
Predictive loss modeling enhances risk-based pricing by analyzing borrower credit data and behavior patterns to estimate potential default losses more accurately than fixed interest rate models. This data-driven approach enables lenders to set personalized interest rates that reflect individual risk profiles, optimizing credit profitability and reducing overall portfolio risk.
Soft-Pull Prequalification Rates
Soft-pull prequalification rates in credit allow borrowers to compare fixed interest rates, which offer consistent payments, against risk-based pricing that adjusts rates based on individual credit profiles, enhancing personalized lending options. This approach reduces the impact on credit scores while providing borrowers transparency in potential rates before committing to a hard inquiry.
ESG-Weighted Lending Rates
ESG-weighted lending rates integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria into risk assessment, offering a nuanced alternative to traditional fixed interest and risk-based pricing models. By prioritizing sustainable borrower profiles, lenders can optimize loan portfolios for long-term value while mitigating credit risk through dynamic rate adjustments aligned with ESG performance.
Fixed Interest vs Risk-Based Pricing for rate setting. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com