Wire transfers rely on traditional banking networks that often involve intermediaries, resulting in longer processing times and higher fees. Blockchain transfers use decentralized ledgers to enable faster, more transparent, and cost-effective transactions, reducing the risk of fraud. Choosing between the two depends on factors like transaction speed, cost, security, and the need for regulatory compliance in banking operations.
Table of Comparison
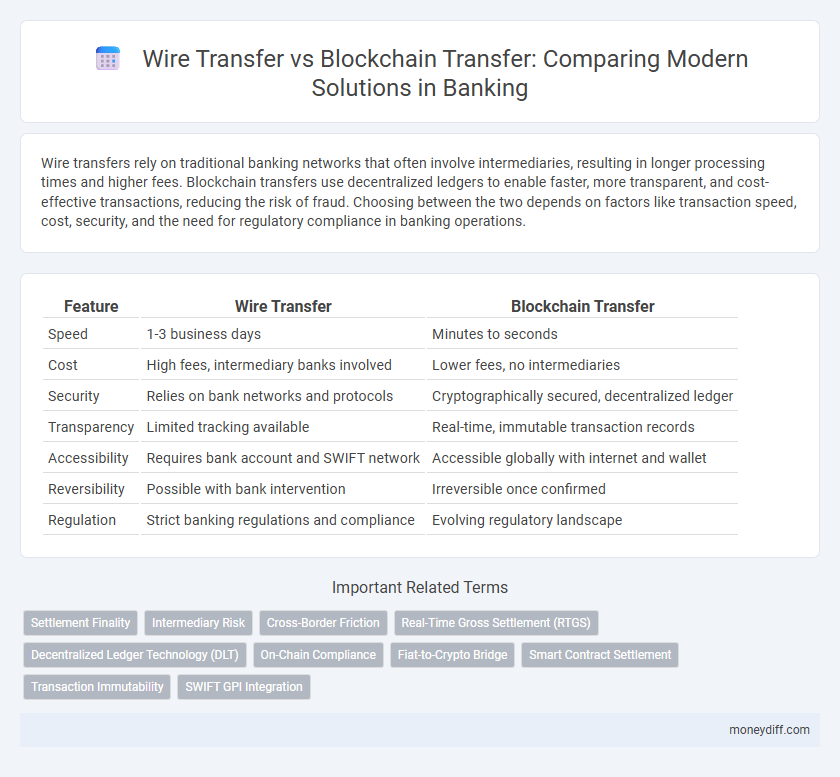
| Feature | Wire Transfer | Blockchain Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 1-3 business days | Minutes to seconds |
| Cost | High fees, intermediary banks involved | Lower fees, no intermediaries |
| Security | Relies on bank networks and protocols | Cryptographically secured, decentralized ledger |
| Transparency | Limited tracking available | Real-time, immutable transaction records |
| Accessibility | Requires bank account and SWIFT network | Accessible globally with internet and wallet |
| Reversibility | Possible with bank intervention | Irreversible once confirmed |
| Regulation | Strict banking regulations and compliance | Evolving regulatory landscape |
Introduction: Understanding Transfer Methods in Modern Banking
Wire transfers in banking rely on traditional correspondent banking networks to move funds securely but often involve higher fees and longer processing times. Blockchain transfers utilize decentralized ledger technology to enable faster, more transparent, and cost-effective cross-border payments with enhanced security. Comparing these methods highlights a shift toward modern banking solutions prioritizing efficiency and reduced operational costs.
What is a Wire Transfer?
A wire transfer is a traditional method of electronically sending funds between banks or financial institutions, typically through established networks such as SWIFT or Fedwire. It enables secure, real-time transfer of money domestically or internationally with guaranteed delivery and traceability. Wire transfers usually involve fees and processing times that vary depending on the banks and countries involved.
What is a Blockchain Transfer?
A blockchain transfer is a method of moving funds or assets using a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and security. Unlike traditional wire transfers that rely on intermediary banks and can take several days, blockchain transfers occur in near real-time with reduced fees and enhanced traceability. This technology leverages cryptographic algorithms to authenticate transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and enabling cross-border payments without the need for central clearinghouses.
Speed of Transactions: Wire vs Blockchain
Wire transfers typically process within 1 to 3 business days due to intermediary banks and clearing systems, whereas blockchain transfers can be completed in minutes or seconds by utilizing decentralized ledgers and real-time consensus mechanisms. Blockchain technology reduces settlement time significantly, enabling near-instantaneous cross-border payments without relying on traditional banking hours. The speed advantage of blockchain transfers enhances liquidity and improves transaction efficiency in global banking operations.
Security Comparison: Wire Transfer vs Blockchain Transfer
Wire transfers rely on centralized banking networks and are subject to regulatory oversight, reducing fraud but posing risks like interception or human error. Blockchain transfers use decentralized ledgers secured by cryptographic algorithms, offering enhanced transparency and immutability that prevent unauthorized alterations. While wire transfers depend on trusted intermediaries, blockchain transfers eliminate single points of failure, providing superior protection against fraud and cyberattacks.
Transaction Costs and Fees Analysis
Wire transfers typically incur higher transaction fees, ranging from $25 to $50 per domestic transfer and up to $75 for international transfers, due to intermediary banks and currency conversion costs. Blockchain transfers offer lower fees, often less than $5, by eliminating intermediaries and utilizing decentralized networks, which significantly reduces overhead costs. The faster settlement times and transparency of blockchain further contribute to cost efficiency compared to traditional wire transfer systems.
Global Accessibility and Availability
Wire transfers rely on traditional banking networks and centralized intermediaries, often limiting global accessibility to regions with established banking infrastructure and fixed operating hours. Blockchain transfers operate on decentralized ledgers available 24/7 worldwide, enabling instant cross-border payments without intermediary restrictions. This continuous global availability enhances financial inclusion by reaching unbanked populations and supporting real-time international transactions.
Transparency and Traceability in Transfers
Wire transfers rely on centralized banking systems, offering limited transparency and traceability visible primarily to participating financial institutions. Blockchain transfers utilize decentralized ledgers, enabling real-time tracking and immutable records accessible to all authorized parties, greatly enhancing transparency. This increased visibility in blockchain transfers reduces fraud risk and simplifies auditing processes compared to traditional wire transfers.
Regulatory Compliance and Oversight
Wire transfers are subject to strict regulatory compliance and oversight by banking authorities, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) protocols, ensuring transaction transparency and security. Blockchain transfers, while offering decentralized and faster settlements, face evolving regulatory frameworks that vary by jurisdiction, with ongoing efforts to integrate AML and KYC measures for enhanced compliance. Financial institutions increasingly evaluate both methods based on their adherence to regulatory standards and the robustness of compliance mechanisms to mitigate risks and ensure legal conformity.
Which is Better for Banking: Wire or Blockchain Transfer?
Wire transfers offer established infrastructure with high reliability and widespread acceptance among banks globally, ensuring secure and regulated fund movements. Blockchain transfers provide faster settlement times, lower transaction costs, and enhanced transparency through decentralized ledgers, especially beneficial for cross-border payments. For banking, the choice depends on prioritizing either traditional network security and regulatory compliance or innovative speed and cost efficiency driven by blockchain technology.
Related Important Terms
Settlement Finality
Wire transfers offer settlement finality through centralized clearinghouses that ensure transactions are completed within a defined timeframe, typically one to three business days. Blockchain transfers provide near-instant settlement finality by leveraging decentralized consensus mechanisms, reducing counterparty risk and enabling transparent, immutable transaction records.
Intermediary Risk
Wire transfers rely on multiple intermediaries such as correspondent banks, increasing the risk of delays, errors, and fraud due to complex verification processes. Blockchain transfers minimize intermediary risk by enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions on a decentralized ledger, enhancing transparency and reducing the potential for unauthorized interference.
Cross-Border Friction
Wire transfers often involve multiple intermediary banks, leading to higher fees and slower settlement times across borders, while blockchain transfers utilize decentralized ledgers to enable near-instantaneous, low-cost cross-border payments without intermediaries. The transparency and immutability of blockchain technology reduce fraud risk and compliance friction compared to traditional wire transfers.
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
Wire transfers through Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems enable secure, high-value transactions settled in real-time across central banks, ensuring immediate liquidity and finality. Blockchain transfers offer decentralized, transparent ledgers that can reduce intermediaries and enhance cross-border payment efficiencies, but RTGS remains the preferred method for instantaneous, large-scale banking settlements.
Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT)
Wire transfers typically rely on centralized banking networks that can involve multiple intermediaries and longer processing times, whereas blockchain transfers utilize Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT) to enable secure, transparent, and near-instantaneous transactions without the need for central authorities. DLT enhances trust and reduces the risk of fraud by maintaining an immutable record of all transactions across a distributed network, revolutionizing how cross-border payments are executed in banking.
On-Chain Compliance
Wire transfers rely on traditional banking networks with stringent regulatory oversight but often lack real-time transparency and traceability, complicating compliance monitoring. Blockchain transfers enable on-chain compliance through immutable ledger records and programmable smart contracts, allowing instant verification of transaction legitimacy and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Fiat-to-Crypto Bridge
Wire transfer offers a traditional banking method for fiat-to-crypto transactions but often involves higher fees and longer processing times due to intermediary banks and regulatory compliance. Blockchain transfer serves as a faster, more cost-effective alternative by directly bridging fiat currencies to cryptocurrencies with enhanced transparency and reduced reliance on centralized institutions.
Smart Contract Settlement
Wire transfers rely on trusted intermediaries and traditional clearing systems, resulting in longer settlement times and higher fees. Blockchain transfers with smart contract settlement automate transaction validation and fund release, enhancing transparency, reducing costs, and enabling near-instantaneous cross-border payments.
Transaction Immutability
Wire transfers rely on centralized banking systems, which can be subject to errors or reversals, limiting transaction immutability. Blockchain transfers utilize distributed ledger technology to ensure transactions are permanently recorded and tamper-proof, providing enhanced security and transparency in banking operations.
SWIFT GPI Integration
SWIFT GPI integration enhances wire transfers by providing real-time tracking, transparency, and faster settlement times, streamlining cross-border payments within traditional banking networks. Blockchain transfer offers decentralized ledger technology with immutable records and reduced intermediary costs but lacks the widespread adoption and standardized integration like SWIFT GPI in global banking systems.
Wire Transfer vs Blockchain Transfer for banking. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com