Personal loans from banks offer predictable interest rates and fixed repayment schedules, providing stability and security for borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors, often resulting in faster approval and potentially lower rates but with higher risk and less regulatory protection. Understanding these differences helps individuals choose the best financing option based on their credit profile, urgency, and tolerance for financial risk.
Table of Comparison
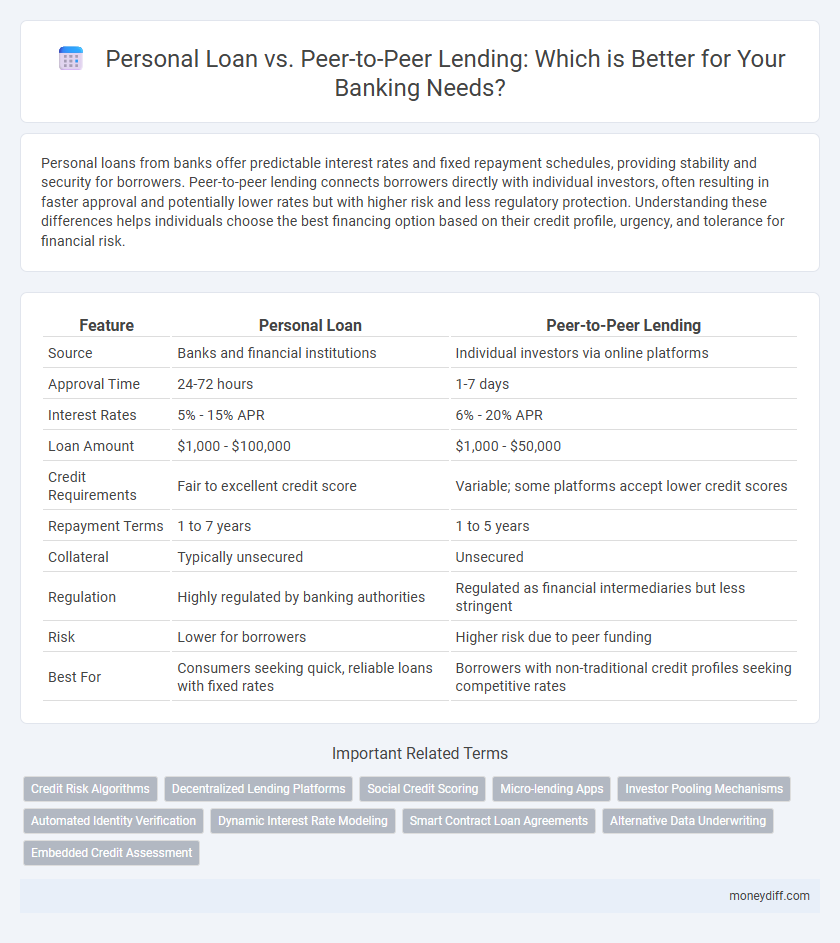
| Feature | Personal Loan | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Banks and financial institutions | Individual investors via online platforms |
| Approval Time | 24-72 hours | 1-7 days |
| Interest Rates | 5% - 15% APR | 6% - 20% APR |
| Loan Amount | $1,000 - $100,000 | $1,000 - $50,000 |
| Credit Requirements | Fair to excellent credit score | Variable; some platforms accept lower credit scores |
| Repayment Terms | 1 to 7 years | 1 to 5 years |
| Collateral | Typically unsecured | Unsecured |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by banking authorities | Regulated as financial intermediaries but less stringent |
| Risk | Lower for borrowers | Higher risk due to peer funding |
| Best For | Consumers seeking quick, reliable loans with fixed rates | Borrowers with non-traditional credit profiles seeking competitive rates |
Understanding Personal Loans: Traditional Banking Approach
Personal loans from traditional banks offer fixed interest rates, set repayment terms, and are typically backed by a strong regulatory framework ensuring borrower protection. These loans require a thorough credit evaluation, which can impact approval speed but provides a secure lending environment. Compared to peer-to-peer lending, bank personal loans benefit from established financial stability, predictable monthly payments, and often lower default risk.
What Is Peer-to-Peer Lending?
Peer-to-peer lending is a financial platform that connects individual borrowers directly with investors, bypassing traditional banking institutions. This decentralized approach offers competitive interest rates and faster approval processes compared to personal loans from banks. By leveraging online marketplaces, peer-to-peer lending enhances accessibility to credit while diversifying investment opportunities for lenders.
Key Differences Between Personal Loans and P2P Lending
Personal loans are typically offered by traditional financial institutions such as banks and credit unions, featuring fixed interest rates and structured repayment schedules. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending connects borrowers directly with individual investors on online platforms, often resulting in more flexible terms and potentially lower interest rates. The key differences include the source of funds, approval processes, and risk profiles, with personal loans backed by regulated institutions and P2P loans relying on investor funding and platform mediation.
Eligibility Requirements: Banks vs. Peer-to-Peer Platforms
Banks typically require a strong credit score, stable income, and detailed documentation to qualify for personal loans, ensuring lower risk and predictable repayment. Peer-to-peer lending platforms often have more flexible eligibility criteria, using alternative data like social media activity or cash flow assessments, which can accommodate borrowers with limited credit history. Differences in eligibility requirements influence borrower accessibility and interest rates across both banking and peer-to-peer lending options.
Interest Rates Comparison: Personal Loans vs. P2P Lending
Interest rates for personal loans typically range from 6% to 36%, depending on creditworthiness, loan amount, and term, while peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms often offer rates starting as low as 5% but can rise to 30% based on risk assessment and investor demand. Personal loans from traditional banks usually have fixed interest rates, providing borrowers with predictable payments, whereas P2P lending rates can be variable due to the decentralized nature of funding sources and market fluctuations. Borrowers with strong credit profiles might secure lower personal loan rates, whereas P2P lending can present opportunities for lower rates for those with moderate credit, though with potential for higher costs depending on platform fees and loan performance.
Application and Approval Process: Which Is Simpler?
Personal loans typically require a thorough credit check and documentation verification, leading to a more rigid and longer approval process through traditional banks. Peer-to-peer lending platforms leverage automated algorithms and social data, making the application process quicker and often more accessible for borrowers with varied credit profiles. This streamlined digital approach generally results in faster decisions and less stringent requirements compared to conventional personal loan approvals.
Risks and Security in Personal Loans and P2P Lending
Personal loans offered by banks typically provide stronger security due to regulated underwriting processes, collateral requirements, and FDIC protections, minimizing default risks. Peer-to-peer lending carries higher risk exposure for both lenders and borrowers as platforms often lack extensive regulatory oversight, making fraud and loan default more probable. Evaluating creditworthiness and platform reputation is crucial in P2P lending, whereas personal loans benefit from established financial institution safeguards and legal recourse.
Flexibility and Loan Terms: Bank Loans vs. P2P Options
Personal loans from banks typically offer fixed interest rates and structured repayment schedules, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments and established legal protections. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms often feature more flexible loan terms, including variable rates and customizable repayment plans tailored to individual borrower profiles. However, P2P loans may carry higher risk due to less regulatory oversight and varied lender criteria compared to the standardized processes of traditional bank loans.
Impact on Credit Score: Both Lending Methods Compared
Personal loans typically require a hard credit inquiry, which can cause a temporary dip in the borrower's credit score, while timely repayments may improve credit health. Peer-to-peer lending platforms also perform credit checks but often use alternative data to assess risk, potentially benefiting those with limited credit history. Both methods report to credit bureaus, so consistent repayments positively impact credit scores, although defaults can cause significant damage regardless of loan type.
Choosing the Best Option: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a personal loan and peer-to-peer lending, consider interest rates, loan terms, and credit score requirements. Personal loans from banks often offer fixed rates and predictable repayments, while peer-to-peer platforms may provide competitive rates but variable terms. Evaluate fees, approval speed, and borrower protections to determine the best fit for your financial needs.
Related Important Terms
Credit Risk Algorithms
Personal loan credit risk algorithms rely on traditional credit scoring models, analyzing borrowers' credit history, income stability, and debt-to-income ratios to assess loan eligibility and default probabilities. Peer-to-peer lending platforms use advanced machine learning algorithms incorporating social data, transactional behavior, and alternative credit indicators to more dynamically predict credit risk and optimize investor outcomes.
Decentralized Lending Platforms
Decentralized lending platforms in peer-to-peer lending eliminate traditional bank intermediaries, allowing borrowers to access funds directly from individual lenders, often at competitive interest rates and with faster approval processes. Personal loans from banks typically involve centralized credit assessments and regulatory oversight, resulting in more standardized terms but less flexibility compared to the customizable options offered by blockchain-based decentralized lending systems.
Social Credit Scoring
Personal loans typically rely on traditional credit scoring models that assess individual credit history and financial behavior, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms increasingly incorporate social credit scoring by analyzing alternative data such as social networks and online behavior to evaluate borrower credibility. Social credit scoring in P2P lending often provides a more nuanced risk assessment, potentially expanding credit access to individuals with limited conventional credit histories.
Micro-lending Apps
Micro-lending apps leverage peer-to-peer lending platforms to offer faster approval and lower interest rates compared to traditional personal loans provided by banks. These apps connect individual borrowers directly with private lenders, reducing overhead costs and increasing accessibility for users with limited credit history.
Investor Pooling Mechanisms
Personal loans rely on traditional banking institutions pooling funds from a broad base of depositors to finance individual borrowers, while peer-to-peer lending platforms aggregate funds directly from individual investors to lend to borrowers, bypassing conventional intermediaries. The investor pooling mechanisms in peer-to-peer lending enable diversified risk allocation and potentially higher returns compared to the fixed interest margins maintained by banks in personal loan portfolios.
Automated Identity Verification
Automated identity verification accelerates approval processes in personal loans by securely validating borrower credentials through AI-driven biometric and document analysis, reducing fraud risk. Peer-to-peer lending platforms integrate similar verification technologies to ensure trusted borrower-lender interactions while maintaining decentralized, transparent credit assessment.
Dynamic Interest Rate Modeling
Personal loans typically feature fixed or variable interest rates determined by traditional credit risk models, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms employ dynamic interest rate modeling using real-time borrower data and market conditions to optimize lender returns and risk. This adaptive approach in peer-to-peer lending enhances pricing accuracy and borrower accessibility compared to conventional banking interest structures.
Smart Contract Loan Agreements
Smart Contract Loan Agreements in personal loans automate repayment schedules and enforce terms securely through blockchain technology, reducing default risk and administrative costs. Peer-to-peer lending leverages these smart contracts to directly connect borrowers and investors, enhancing transparency and eliminating traditional banking intermediaries.
Alternative Data Underwriting
Personal loans typically rely on traditional credit scores and income verification for underwriting, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms increasingly utilize alternative data such as social media activity, utility payments, and online behavior to assess borrower creditworthiness. Leveraging alternative data underwriting enables P2P lenders to offer credit access to underserved borrowers and potentially reduce default rates through more comprehensive risk profiling.
Embedded Credit Assessment
Personal loans typically rely on embedded credit assessment algorithms integrated within traditional banking systems, providing quick risk evaluation and approval based on credit scores and financial history. Peer-to-peer lending platforms use innovative embedded credit assessment models leveraging alternative data and machine learning, enabling more inclusive lending decisions and personalized interest rates.
Personal loan vs Peer-to-peer lending for banking. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com