Mobile banking offers users direct access to their financial accounts through dedicated apps, providing convenience and real-time transaction management. Embedded banking integrates financial services seamlessly within non-bank platforms, allowing users to perform banking tasks while engaging with other digital services. Both approaches enhance user experience but differ in accessibility and scope, with mobile banking focusing on standalone applications and embedded banking prioritizing integration within everyday digital activities.
Table of Comparison
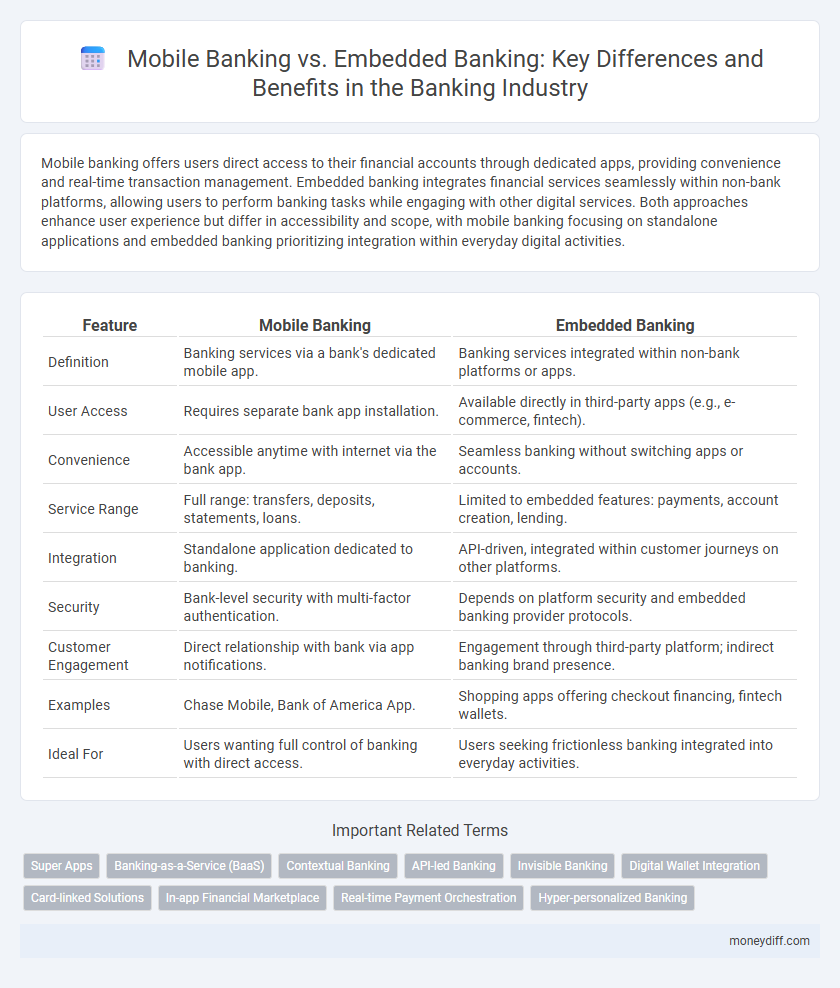
| Feature | Mobile Banking | Embedded Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Banking services via a bank's dedicated mobile app. | Banking services integrated within non-bank platforms or apps. |
| User Access | Requires separate bank app installation. | Available directly in third-party apps (e.g., e-commerce, fintech). |
| Convenience | Accessible anytime with internet via the bank app. | Seamless banking without switching apps or accounts. |
| Service Range | Full range: transfers, deposits, statements, loans. | Limited to embedded features: payments, account creation, lending. |
| Integration | Standalone application dedicated to banking. | API-driven, integrated within customer journeys on other platforms. |
| Security | Bank-level security with multi-factor authentication. | Depends on platform security and embedded banking provider protocols. |
| Customer Engagement | Direct relationship with bank via app notifications. | Engagement through third-party platform; indirect banking brand presence. |
| Examples | Chase Mobile, Bank of America App. | Shopping apps offering checkout financing, fintech wallets. |
| Ideal For | Users wanting full control of banking with direct access. | Users seeking frictionless banking integrated into everyday activities. |
Understanding Mobile Banking: Features and Functions
Mobile banking enables users to perform financial transactions through smartphone applications, offering features such as account monitoring, funds transfer, bill payments, and mobile check deposits. It leverages multi-factor authentication and biometric security to protect user data and ensure secure access. Integration with push notifications and real-time alerts enhances user experience by providing instant updates on account activity.
What is Embedded Banking? Core Concepts Explained
Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms such as e-commerce, payroll, or accounting software, enabling seamless transactions without switching apps. It leverages APIs to embed payments, lending, and account management, enhancing user experience through automation and real-time financial operations. Unlike traditional mobile banking apps, embedded banking eliminates friction by providing contextual financial services within the user's primary workflow.
Mobile Banking vs Embedded Banking: Key Differences
Mobile Banking offers users a dedicated app or website to manage their bank accounts, perform transactions, and access financial services directly from their smartphones, emphasizing user control and security. In contrast, Embedded Banking integrates banking features seamlessly within non-bank platforms such as e-commerce sites or accounting software, providing convenience by enabling financial transactions without switching apps. The key differences lie in Mobile Banking's standalone interface versus Embedded Banking's contextual, integrated approach that prioritizes user experience within existing digital ecosystems.
User Experience: Comparing Convenience and Accessibility
Mobile banking offers users direct access to financial services through dedicated banking apps, providing convenience with real-time transaction alerts, biometric security, and personalized dashboards that enhance user experience. Embedded banking integrates financial services within non-banking platforms like e-commerce or ride-sharing apps, enabling seamless transactions without switching apps, thus increasing accessibility and reducing friction. Both approaches prioritize user convenience, but embedded banking excels in context-aware services, while mobile banking delivers comprehensive control over financial management.
Security and Privacy in Mobile vs Embedded Banking
Mobile banking integrates advanced encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to safeguard user data during transactions, ensuring robust security across diverse networks. Embedded banking leverages contextual data and seamless API integrations within third-party platforms, enhancing security by minimizing data exposure and reducing reliance on standalone apps. Both approaches emphasize user privacy, with embedded banking offering enhanced control through in-app permissions and data localization, while mobile banking relies on device-level protections and regular security updates.
Integration Capabilities: Advantages for Businesses
Mobile banking offers businesses seamless integration with existing financial systems through dedicated apps, enabling real-time account management and transaction tracking. Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-banking platforms, providing businesses with instant payment processing, lending, and wallet services without requiring customers to switch apps. This advanced integration capability enhances operational efficiency, customer experience, and drives increased revenue opportunities for businesses.
Cost Efficiency: Analyzing Fees and Implementation
Mobile banking typically incurs lower upfront implementation costs due to existing app infrastructure, whereas embedded banking often requires significant investment in API integration and partnership development. Fee structures in mobile banking are generally more transparent with standard transaction charges, while embedded banking frequently involves complex revenue-sharing models that can impact overall cost efficiency. Financial institutions must weigh the trade-offs between immediate operational expenses in mobile banking and long-term scalability costs associated with embedded banking platforms.
Impact on Financial Inclusion and Customer Reach
Mobile banking significantly enhances financial inclusion by providing users with easy access to banking services through smartphones, especially in underbanked regions where traditional banks have limited presence. Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms, expanding customer reach by meeting consumers within everyday digital environments like e-commerce and ride-sharing apps. Both approaches reduce barriers to financial access, but embedded banking leverages existing user bases to offer seamless, context-specific financial solutions, further driving inclusion and engagement.
Future Trends: Innovations in Mobile and Embedded Banking
Mobile banking continues to evolve with AI-driven personalized financial management tools and biometric security features enhancing user experience and safety. Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms, enabling seamless transactions within apps and IoT devices, expanding accessibility and convenience. Future trends indicate a convergence where mobile banking functionalities blend with embedded banking ecosystems, powered by open banking APIs and real-time data analytics to deliver hyper-personalized and context-aware financial services.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors for Banks to Consider
Choosing the right banking solution requires evaluating customer engagement, technological integration, and cost efficiency. Mobile banking offers direct client access with customized apps, while embedded banking integrates financial services seamlessly into third-party platforms, enhancing user experience. Banks should assess target audience preferences, development resources, and regulatory compliance to optimize digital banking strategies.
Related Important Terms
Super Apps
Super Apps integrate embedded banking services directly into multifunctional platforms, offering seamless payment, lending, and investment options without requiring users to switch applications. Mobile banking apps provide dedicated financial services with robust security and personalized features but often lack the convenience and ecosystem integration that super apps deliver through embedded banking.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Mobile banking offers customers direct access to their financial accounts through dedicated apps, emphasizing user convenience and real-time transaction capabilities. Embedded banking, powered by Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms, integrates financial services seamlessly into non-bank ecosystems, enabling businesses to offer customized banking features without traditional infrastructure.
Contextual Banking
Mobile banking offers users direct access to financial services through dedicated apps, enabling convenient account management and transactions anytime. Embedded banking integrates financial capabilities within non-bank platforms, providing seamless contextual banking experiences by embedding payments, lending, or account services directly into apps like e-commerce or ride-sharing, enhancing user engagement through contextual relevance.
API-led Banking
API-led banking enables seamless integration of mobile banking apps with core financial systems, offering users real-time access to account management, payments, and personalized services. Embedded banking leverages APIs to embed financial services directly into non-bank platforms, enhancing customer experience by providing banking functions within ecosystems like e-commerce or fintech applications.
Invisible Banking
Invisible banking integrates financial services seamlessly within non-banking apps, providing users with frictionless transactions without switching platforms, whereas mobile banking requires a dedicated banking app interface for access. This seamless integration enhances user experience by embedding banking features directly into everyday activities, reducing barriers and increasing engagement through context-aware, real-time services.
Digital Wallet Integration
Mobile banking allows users to securely access their bank accounts and perform transactions through dedicated apps, offering seamless digital wallet integration for contactless payments and instant fund transfers. Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into third-party platforms, enabling digital wallets to facilitate real-time payments and personalized financial management without switching apps.
Card-linked Solutions
Card-linked solutions in mobile banking enable users to make payments and earn rewards directly through their smartphones, enhancing convenience and real-time transaction tracking. Embedded banking integrates card-linked features seamlessly into non-banking platforms, allowing businesses to offer banking services like payments, loyalty programs, and personalized financial insights without requiring a separate banking app.
In-app Financial Marketplace
In-app financial marketplaces integrate embedded banking services directly within non-banking apps, offering seamless access to loans, payments, and investments without switching platforms, unlike traditional mobile banking apps that require users to open separate banking applications. This embedded approach enhances user engagement by delivering personalized financial products in real-time, leveraging data-driven insights for targeted offerings and improved customer experience.
Real-time Payment Orchestration
Real-time payment orchestration in mobile banking relies on dedicated apps allowing users to execute instant transactions with personalized interfaces and security protocols. Embedded banking integrates payment orchestration directly into non-banking platforms, enabling seamless, context-driven real-time payments within ecosystems like e-commerce or ride-sharing apps.
Hyper-personalized Banking
Hyper-personalized banking in mobile banking leverages real-time data analytics and AI-driven insights to tailor financial products and services directly through user-friendly mobile apps. Embedded banking integrates seamless financial experiences within third-party platforms, enabling businesses to offer highly customized banking solutions that anticipate customer needs and enhance engagement without redirecting users to traditional banking interfaces.
Mobile Banking vs Embedded Banking for banking. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com