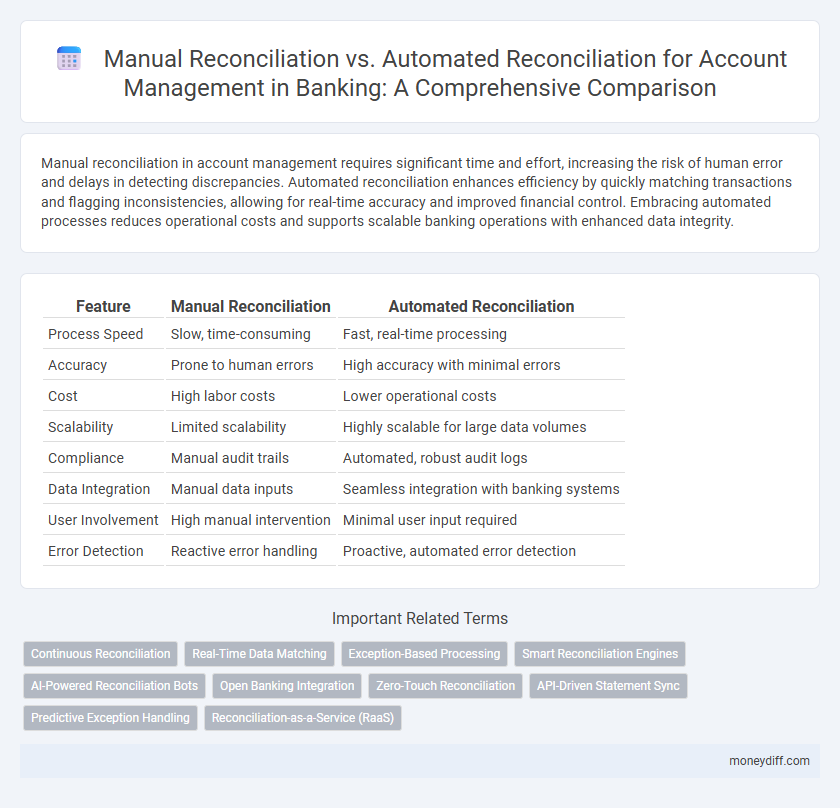
Manual reconciliation in account management requires significant time and effort, increasing the risk of human error and delays in detecting discrepancies. Automated reconciliation enhances efficiency by quickly matching transactions and flagging inconsistencies, allowing for real-time accuracy and improved financial control. Embracing automated processes reduces operational costs and supports scalable banking operations with enhanced data integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Reconciliation | Automated Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Process Speed | Slow, time-consuming | Fast, real-time processing |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors | High accuracy with minimal errors |
| Cost | High labor costs | Lower operational costs |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable for large data volumes |
| Compliance | Manual audit trails | Automated, robust audit logs |
| Data Integration | Manual data inputs | Seamless integration with banking systems |
| User Involvement | High manual intervention | Minimal user input required |
| Error Detection | Reactive error handling | Proactive, automated error detection |
Introduction to Account Reconciliation in Banking
Account reconciliation in banking ensures accuracy between internal records and external statements, minimizing discrepancies and financial risks. Manual reconciliation involves human review of transactions, which can be time-consuming and error-prone, while automated reconciliation leverages software algorithms to match and verify accounts rapidly and consistently. Implementing automated reconciliation enhances efficiency, reduces operational costs, and strengthens compliance with regulatory standards in account management.
What Is Manual Reconciliation?
Manual reconciliation involves the process of verifying and matching transactions in bank statements with internal financial records by hand, ensuring accuracy and identifying discrepancies. This method requires significant time and effort from accounting personnel, increasing the risk of human error and delays in detecting issues. Despite being labor-intensive, manual reconciliation is often used in smaller organizations or when dealing with complex transactions that automated systems cannot easily interpret.
What Is Automated Reconciliation?
Automated reconciliation utilizes sophisticated software algorithms and artificial intelligence to match transactions and update account records with high accuracy and speed. It reduces human errors and operational costs by instantly processing large volumes of financial data compared to manual reconciliation methods. This technology integrates seamlessly with core banking systems, enhancing real-time visibility into account discrepancies and improving overall financial control.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Reconciliation
Manual reconciliation in banking requires human intervention to compare and verify transactions, often leading to higher error rates and longer processing times. Automated reconciliation utilizes advanced software algorithms to match transactions swiftly and accurately, significantly reducing operational costs and minimizing discrepancies. Key differences include speed, accuracy, scalability, and the ability of automated systems to integrate seamlessly with core banking platforms.
Benefits of Manual Reconciliation for Account Management
Manual reconciliation offers enhanced accuracy by allowing detailed scrutiny of complex transactions and discrepancies that automated systems might overlook. It provides greater control and flexibility, enabling account managers to customize checks based on unique client accounts and specific financial scenarios. This hands-on approach supports thorough verification, reducing the risk of false positives or missed errors in account management.
Advantages of Automated Reconciliation in Banking
Automated reconciliation in banking significantly reduces human error by leveraging advanced algorithms to match transactions accurately and swiftly. It enhances operational efficiency, enabling real-time account management and faster identification of discrepancies compared to manual processes. Integration with core banking systems supports seamless data flow, increasing accuracy and minimizing the time and cost associated with manual reconciliation tasks.
Common Challenges in Manual Reconciliation
Manual reconciliation in banking often faces challenges such as increased human error due to data entry mistakes, time-consuming processes that delay financial reporting, and difficulties in matching large volumes of transactions efficiently. The manual approach struggles with scalability when handling complex accounts or high transaction frequencies, leading to potential discrepancies and audit risks. Inefficient error detection and resolution further complicate account management, making the process less reliable compared to automated solutions.
How Automation Enhances Accuracy and Efficiency
Automated reconciliation significantly improves accuracy by reducing human errors commonly found in manual data entry and matching processes within account management. It accelerates transaction verification through advanced algorithms and real-time data integration, enabling faster identification of discrepancies in financial statements. Banks benefit from enhanced operational efficiency and risk mitigation by leveraging automation tools that streamline reconciliation workflows and generate audit-ready reports.
Choosing Between Manual and Automated Reconciliation
Choosing between manual and automated reconciliation depends on transaction volume, error tolerance, and resource availability in account management. Manual reconciliation suits low-volume, complex accounts requiring detailed review but is time-consuming and prone to human error. Automated reconciliation leverages software algorithms to process high-volume transactions rapidly, reducing discrepancies and operational costs while enhancing accuracy and compliance in banking operations.
Future Trends in Account Reconciliation Technology
Future account reconciliation technology is increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance accuracy and reduce processing time. Automated reconciliation systems are evolving to integrate real-time data matching, predictive analytics, and blockchain for secure transaction verification. These advancements promise to minimize human error, improve compliance, and deliver faster financial closing processes for banking institutions.
Related Important Terms
Continuous Reconciliation
Continuous reconciliation in account management leverages automated reconciliation systems to provide real-time matching of transactions, reducing errors and improving efficiency compared to manual reconciliation processes that involve slower, labor-intensive data verification. Automated reconciliation integrates advanced algorithms and machine learning to identify discrepancies instantly, enabling faster resolution and enhanced accuracy in financial reporting.
Real-Time Data Matching
Manual reconciliation in banking relies on human effort to compare transaction records, often causing delays and errors in account management. Automated reconciliation leverages real-time data matching technologies, enabling instant verification of transactions and improving accuracy and operational efficiency.
Exception-Based Processing
Exception-based processing in automated reconciliation significantly reduces errors and accelerates account management by automatically identifying and flagging discrepancies, whereas manual reconciliation relies heavily on human intervention, increasing the risk of oversight and delayed resolution. Automated systems enhance efficiency through real-time exception detection and prioritization, allowing banking professionals to focus on resolving critical issues rather than routine data matching.
Smart Reconciliation Engines
Smart Reconciliation Engines leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning to automate the matching of transactions, significantly reducing errors and processing time compared to manual reconciliation methods. This automation enhances accuracy and efficiency in account management by continuously learning from data patterns and integrating seamlessly with banking systems.
AI-Powered Reconciliation Bots
AI-powered reconciliation bots enhance account management by automatically matching transactions with high accuracy, significantly reducing errors and manual labor associated with traditional manual reconciliation. Leveraging machine learning algorithms, these bots identify discrepancies in real-time, improve compliance, and accelerate financial closing processes, leading to greater operational efficiency in banking institutions.
Open Banking Integration
Automated reconciliation with Open Banking integration streamlines account management by instantly matching transactions using real-time data from multiple financial institutions, dramatically reducing errors and processing time compared to manual reconciliation. Leveraging APIs, this approach enhances transparency and accuracy while enabling faster detection of discrepancies and improved cash flow visibility.
Zero-Touch Reconciliation
Zero-touch reconciliation leverages advanced AI and machine learning to streamline account management, significantly reducing errors and processing time compared to manual reconciliation. Automated reconciliation ensures real-time data validation and seamless integration with banking systems, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency while minimizing human intervention.
API-Driven Statement Sync
Manual reconciliation relies heavily on human input to match transactions, increasing the risk of errors and delays in account management. API-driven automated reconciliation enables real-time statement synchronization, enhancing accuracy and efficiency by instantly updating transaction data across banking platforms.
Predictive Exception Handling
Manual reconciliation relies heavily on human intervention to identify discrepancies in accounts, often leading to slower detection of anomalies and increased risk of errors. Automated reconciliation leverages predictive exception handling powered by AI algorithms to proactively flag irregularities, enhancing accuracy and reducing the turnaround time for resolving account mismatches.
Reconciliation-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Manual reconciliation in account management involves time-consuming processes prone to human error, whereas Automated Reconciliation, especially through Reconciliation-as-a-Service (RaaS), leverages AI and machine learning to deliver accurate, real-time transaction matching and anomaly detection. RaaS platforms enhance efficiency by integrating seamlessly with banking systems, reducing operational costs, and improving compliance through automated audit trails.
Manual Reconciliation vs Automated Reconciliation for account management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com