Stocks provide full ownership of a single company's shares, allowing investors to benefit from dividends and voting rights, but may require significant capital for diversification. Fractional shares enable investors to buy portions of expensive stocks, lowering the cost barrier and facilitating wider diversification across various companies. Utilizing fractional shares promotes balanced asset allocation, reducing risk while maximizing exposure across multiple sectors.
Table of Comparison
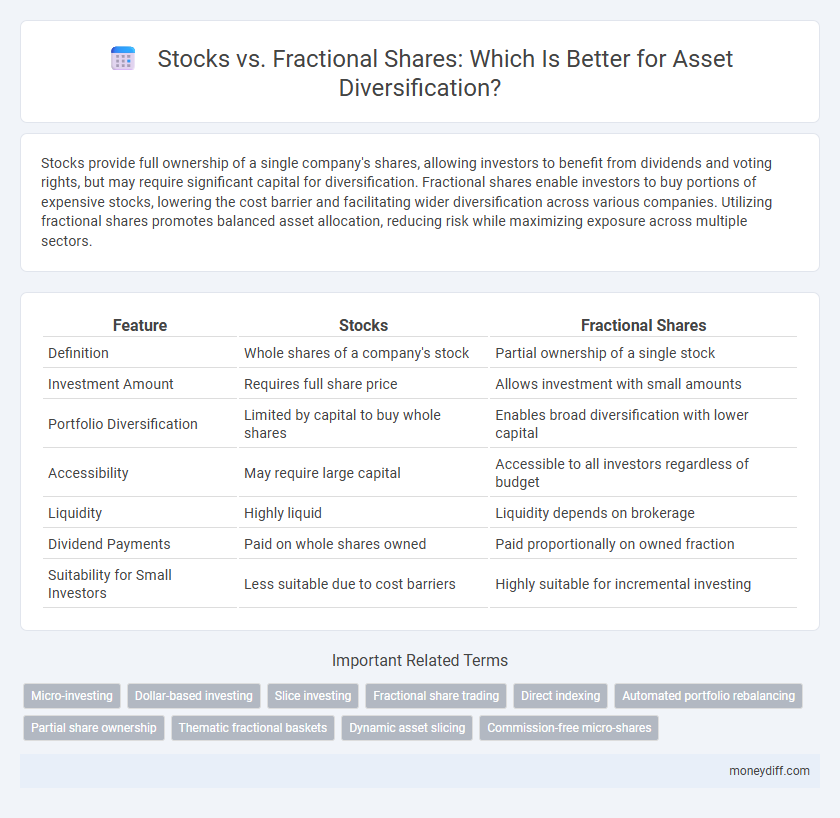
| Feature | Stocks | Fractional Shares |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Whole shares of a company's stock | Partial ownership of a single stock |
| Investment Amount | Requires full share price | Allows investment with small amounts |
| Portfolio Diversification | Limited by capital to buy whole shares | Enables broad diversification with lower capital |
| Accessibility | May require large capital | Accessible to all investors regardless of budget |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid | Liquidity depends on brokerage |
| Dividend Payments | Paid on whole shares owned | Paid proportionally on owned fraction |
| Suitability for Small Investors | Less suitable due to cost barriers | Highly suitable for incremental investing |
Understanding Stocks and Fractional Shares
Stocks represent whole ownership units in a company, allowing investors to benefit from dividends and capital gains tied to the company's performance. Fractional shares enable investors to buy a portion of a stock, making it easier to diversify portfolios with limited capital. Both forms offer unique advantages for asset diversification by providing access to various market sectors and reducing investment risk.
The Basics of Asset Diversification
Asset diversification involves spreading investments across different types of stocks and fractional shares to reduce risk and enhance portfolio stability. Stocks offer full ownership in a company, often requiring higher initial capital, while fractional shares allow investors to purchase a portion of a stock, enabling access to high-value assets with lower investment amounts. Utilizing both stocks and fractional shares enables effective diversification by mixing complete and partial ownership in various industries and market sectors.
Comparing Full Shares vs Fractional Shares
Full shares provide ownership of entire stocks, allowing investors to benefit from dividends and voting rights, whereas fractional shares represent partial ownership, enabling investment in high-priced stocks with smaller capital. Fractional shares offer greater flexibility for asset diversification by allowing allocation across multiple companies regardless of share price. Investors seeking broad market exposure and balanced portfolios often prefer fractional shares to optimize risk distribution and capital efficiency.
Accessibility: Lowering Entry Barriers with Fractional Shares
Fractional shares enhance asset diversification by lowering entry barriers, allowing investors to purchase portions of high-priced stocks without needing full share capital. This accessibility broadens investment opportunities, enabling portfolio diversification across various sectors and market capitalizations with minimal initial investment. Embracing fractional shares democratizes stock ownership and fosters more inclusive, balanced asset allocation strategies.
Risk Management in Asset Allocation
Stocks offer direct ownership in companies, providing full voting rights and dividends, which can enhance portfolio control but require larger capital investment. Fractional shares allow investors to diversify with smaller amounts, reducing exposure to individual stock risk and improving overall risk management in asset allocation. Incorporating fractional shares increases portfolio flexibility and enables precise adjustment of asset allocation to meet risk tolerance and investment goals.
Portfolio Customization: Stocks vs Fractional Shares
Portfolio customization allows investors to optimize diversification by choosing between whole stocks and fractional shares, enabling precise allocation aligned with financial goals. Whole stocks offer clear ownership and voting rights but may limit diversification due to higher individual prices, whereas fractional shares provide access to high-value stocks with smaller investments, enhancing portfolio balance. Utilizing fractional shares increases flexibility in asset distribution, facilitating tailored exposure across industry sectors and market capitalizations.
Cost Efficiency and Investment Flexibility
Stocks offer direct ownership with full share purchases, often requiring higher capital but providing clear voting rights and dividends, while fractional shares enable investors to diversify portfolios cost-efficiently by buying portions of expensive stocks with smaller investments. Fractional shares enhance investment flexibility, allowing allocation across multiple assets and minimizing the risk linked to single-stock exposure without the need for large upfront costs. Cost efficiency is improved through fractional investing by reducing barriers and enabling precise portfolio customization aligned with financial goals.
Liquidity Differences Between Stocks and Fractional Shares
Stocks typically offer higher liquidity with the ability to be bought or sold instantly during market hours, allowing investors quick access to funds. Fractional shares, while providing accessibility to expensive stocks at lower costs, may experience limited liquidity due to platform restrictions or market availability. The liquidity difference impacts how quickly assets can be converted to cash, influencing portfolio flexibility and asset diversification strategies.
Tax Considerations for Diverse Holdings
Stocks and fractional shares both offer opportunities for asset diversification, but tax considerations vary significantly between them. Whole stocks often benefit from established tax advantages like long-term capital gains rates, while fractional shares may complicate tax reporting due to partial ownership and varied purchase dates. Investors managing diverse holdings should consult tax regulations and consider potential implications like dividend taxation and capital gains events to optimize after-tax returns.
Choosing the Best Approach for Diversified Growth
Stocks offer direct ownership and voting rights in a company, making them ideal for investors seeking full asset control and potential dividend income. Fractional shares provide an accessible way to diversify portfolios by allowing investment in high-value stocks with smaller capital, enabling broad market exposure. For diversified growth, combining whole stocks with fractional shares optimizes asset allocation, balancing risk while maximizing investment opportunities across sectors.
Related Important Terms
Micro-investing
Stocks offer full ownership units allowing straightforward portfolio diversification, while fractional shares enable micro-investing by letting investors buy partial shares tailored to smaller budgets, enhancing asset diversification with minimal capital. Micro-investing platforms leverage fractional shares to democratize access, allowing accumulation of diversified stock positions without the need for large upfront investments.
Dollar-based investing
Dollar-based investing through fractional shares enables precise asset diversification by allowing investors to allocate specific amounts of money across multiple stocks, regardless of individual share prices. This approach enhances portfolio balance and accessibility, especially when compared to traditional whole-share purchases that may limit diversification due to higher entry costs.
Slice investing
Slice investing enables asset diversification by allowing investors to purchase fractional shares of high-value stocks, which lowers the entry barrier for portfolio variety. Unlike traditional stocks requiring full-share purchases, fractional shares maximize capital efficiency and risk management across diverse sectors.
Fractional share trading
Fractional share trading enables investors to diversify their portfolios by purchasing partial shares of high-value stocks, lowering entry barriers and reducing capital requirements. This approach enhances asset diversification by allowing strategic allocation across multiple companies, optimizing risk management and potential returns.
Direct indexing
Direct indexing enables investors to diversify their stock assets by purchasing fractional shares of individual securities, allowing precise replication of an index while optimizing tax efficiency and reducing management fees. This strategy offers greater customization and control compared to traditional stock investments, enhancing asset allocation tailored to specific financial goals.
Automated portfolio rebalancing
Automated portfolio rebalancing optimizes asset allocation by adjusting stocks and fractional shares to maintain target diversification efficiently. Utilizing fractional shares enables precise rebalancing with smaller investments, reducing portfolio drift and enhancing risk management.
Partial share ownership
Partial share ownership through fractional shares enables investors to diversify their portfolios by allocating capital across multiple high-value stocks without requiring full share purchases. This approach maximizes asset diversification while minimizing initial investment barriers and enhances access to broader market opportunities.
Thematic fractional baskets
Thematic fractional baskets enable investors to diversify asset portfolios by acquiring fractional shares of stocks aligned with specific economic sectors or trends, enhancing exposure without requiring full share purchases. This approach optimizes diversification by combining multiple fractional shares within a themed strategy, reducing individual stock risk while capturing targeted market opportunities.
Dynamic asset slicing
Dynamic asset slicing enables investors to customize portfolio allocations by purchasing fractional shares, allowing precise exposure to diverse stocks without requiring full-share purchases. This flexibility enhances asset diversification by optimizing investment mixes in stocks of varying market values, reducing entry barriers and promoting efficient capital deployment.
Commission-free micro-shares
Commission-free fractional shares offer investors the ability to diversify their stock portfolios by purchasing smaller portions of high-value assets, reducing the capital required for broad exposure. These micro-shares eliminate traditional trading fees, enabling efficient allocation across multiple stocks to optimize asset diversification and risk management.
Stocks vs Fractional Shares for asset diversification Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com