Assets provide tangible value and direct ownership, offering clearer risk assessment compared to synthetic assets, which replicate asset performance through derivatives and can introduce counterparty risk. Synthetic assets allow for greater flexibility and exposure to multiple risk factors but may increase complexity and potential vulnerabilities in risk management strategies. Managing risk effectively requires balancing the stability of physical assets with the leverage and innovation enabled by synthetic instruments.
Table of Comparison
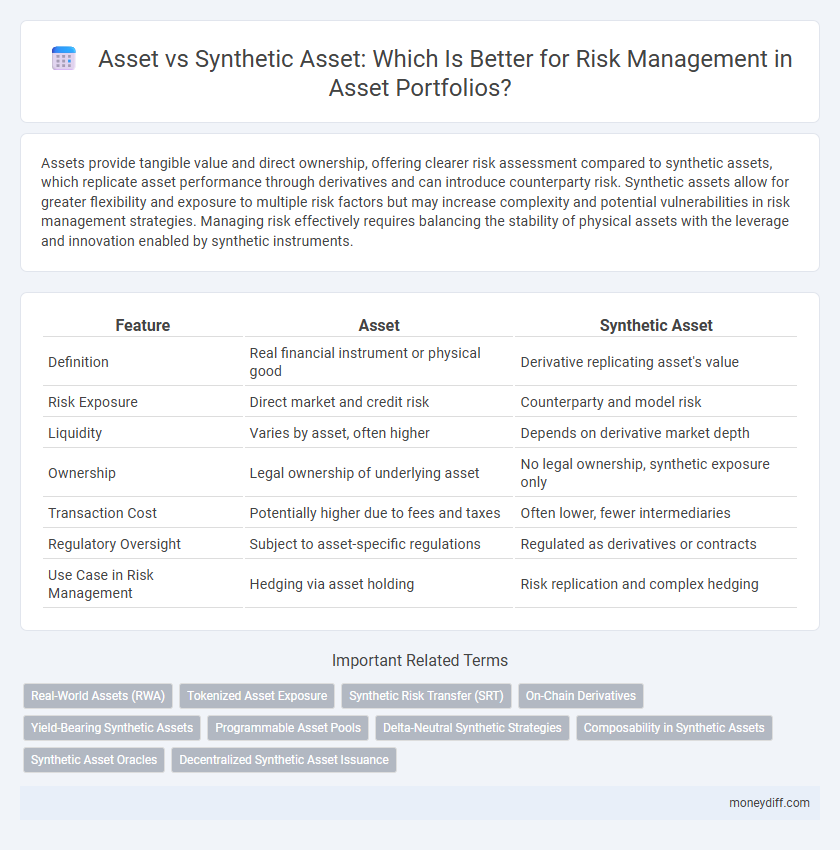
| Feature | Asset | Synthetic Asset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real financial instrument or physical good | Derivative replicating asset's value |
| Risk Exposure | Direct market and credit risk | Counterparty and model risk |
| Liquidity | Varies by asset, often higher | Depends on derivative market depth |
| Ownership | Legal ownership of underlying asset | No legal ownership, synthetic exposure only |
| Transaction Cost | Potentially higher due to fees and taxes | Often lower, fewer intermediaries |
| Regulatory Oversight | Subject to asset-specific regulations | Regulated as derivatives or contracts |
| Use Case in Risk Management | Hedging via asset holding | Risk replication and complex hedging |
Understanding Assets and Synthetic Assets
Assets represent tangible or financial resources owned by an individual or entity, providing intrinsic value and often generating income or capital appreciation. Synthetic assets are engineered financial instruments that replicate the risk and return profiles of traditional assets through derivatives, without requiring direct ownership of the underlying asset. Understanding the differences between these allows for more precise risk management by leveraging synthetic assets to hedge or gain exposure while managing liquidity and counterparty risks.
Key Differences Between Assets and Synthetic Assets
Assets represent ownership of tangible or financial items with inherent value, while synthetic assets are engineered financial instruments that mimic the performance of traditional assets without requiring actual ownership. Key differences include the direct exposure to market risks in assets versus the constructed exposure in synthetic assets, which often involve derivatives like options or swaps to replicate asset returns. Synthetic assets provide flexibility in risk management by allowing tailored exposure and leverage, whereas traditional assets offer straightforward valuation and liquidity.
How Assets Function in Risk Management
Assets serve as tangible financial instruments that provide inherent value and liquidity, essential for mitigating market and credit risks in portfolio management. Unlike synthetic assets, real assets offer direct ownership rights and intrinsic worth, enabling more transparent risk assessment and collateralization. Their stability and predictable cash flows enhance hedging strategies, reducing volatility and potential losses in diverse economic conditions.
The Role of Synthetic Assets in Risk Mitigation
Synthetic assets replicate the economic exposure of traditional assets without requiring ownership, enabling diversified risk management strategies. By using derivatives such as options, futures, and swaps, investors can hedge against market volatility and tailor risk profiles more precisely. This flexibility helps mitigate potential losses while maintaining desired exposure to underlying asset classes.
Advantages of Traditional Assets for Risk Control
Traditional assets provide tangible value and intrinsic worth, offering stability through real-world backing that synthetic assets lack. They generally exhibit lower counterparty risk and greater regulatory oversight, enhancing transparency and investor protection. These characteristics make traditional assets more reliable for effective risk management and portfolio diversification.
Benefits of Synthetic Assets in Portfolio Diversification
Synthetic assets offer enhanced portfolio diversification by enabling exposure to a wide range of underlying assets without direct ownership, reducing concentration risk. They provide tailored risk profiles and access to otherwise inaccessible markets, improving liquidity and flexibility in risk management strategies. These benefits facilitate optimized portfolio construction with improved hedging capabilities and risk-adjusted returns.
Risk Exposure: Assets vs. Synthetic Assets
Traditional assets represent direct ownership and carry inherent market risks tied to the underlying physical or financial entity, exposing investors to price volatility and liquidity constraints. Synthetic assets replicate the performance of these underlying assets through derivatives, enabling tailored risk profiles and hedging strategies that can limit downside exposure and improve capital efficiency. While synthetic assets offer flexibility in risk management, they introduce counterparty risk and complexity, requiring robust assessment to maintain a balanced risk exposure.
Liquidity Considerations in Asset and Synthetic Asset Management
Liquidity considerations in asset management prioritize real assets with established markets to ensure quick conversion to cash and minimize liquidity risk. Synthetic asset management relies on derivatives and financial instruments, which may offer enhanced flexibility but can suffer from lower liquidity during market stress, increasing potential risk. Evaluating liquidity profiles is crucial for balancing risk and return in both asset and synthetic asset portfolios.
Regulatory and Compliance Perspectives
Regulatory frameworks often treat physical assets and synthetic assets differently, with synthetic assets facing stricter compliance requirements due to their derivative nature and potential systemic risks. Regulatory bodies emphasize transparency, valuation accuracy, and counterparty risk mitigation for synthetic assets to prevent market manipulation and ensure financial stability. Physical assets typically have clearer ownership and valuation standards, making regulatory compliance more straightforward in comparison to the complex structures underlying synthetic assets.
Choosing the Right Approach: Asset or Synthetic Asset?
Choosing the right approach between asset and synthetic asset for risk management depends on factors such as liquidity, transparency, and market accessibility. Real assets offer direct ownership and intrinsic value, reducing counterparty risk, while synthetic assets provide customizable exposure and efficient diversification through derivatives. Evaluating risk tolerance and investment objectives enables optimal alignment with financial goals and regulatory compliance.
Related Important Terms
Real-World Assets (RWA)
Real-World Assets (RWA) provide tangible value and inherent stability, making them essential for effective risk management compared to Synthetic Assets, which derive value from derivatives and carry higher counterparty risk. Incorporating RWAs into portfolios enhances liquidity and reduces volatility, offering more predictable risk profiles for asset managers.
Tokenized Asset Exposure
Tokenized asset exposure offers direct ownership of real-world assets, enhancing transparency and reducing counterparty risk compared to synthetic assets, which rely on derivatives and derivatives-based contracts, potentially amplifying systemic risk in volatile markets. Utilizing tokenized assets in risk management allows for precise valuation and real-time tracking, enabling more effective hedging strategies and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Synthetic Risk Transfer (SRT)
Synthetic assets created through derivatives enable tailored risk transfer without direct asset ownership, enhancing capital efficiency in Synthetic Risk Transfer (SRT) programs. SRT structures isolate specific risk exposures such as credit or market risk, providing financial institutions with customizable solutions to manage and hedge their asset portfolios effectively.
On-Chain Derivatives
On-chain derivatives enable risk management by providing synthetic assets that replicate the value of underlying assets without requiring direct ownership, enhancing liquidity and flexibility on decentralized platforms. Synthetic assets offer decentralized exposure to various markets while mitigating counterparty risk typically associated with traditional asset holdings.
Yield-Bearing Synthetic Assets
Yield-bearing synthetic assets provide enhanced risk management by replicating the performance of underlying assets while offering greater flexibility and capital efficiency compared to traditional assets. These instruments allow investors to gain targeted exposure and optimize returns, leveraging derivatives and smart contract protocols to mitigate market volatility and liquidity risks.
Programmable Asset Pools
Programmable Asset Pools enable dynamic allocation and automated risk mitigation in Asset management compared to traditional Synthetic Assets, which often lack real-time adaptability. By leveraging smart contract protocols, these pools facilitate precise exposure adjustments and diversified risk distribution, enhancing overall portfolio resilience.
Delta-Neutral Synthetic Strategies
Delta-neutral synthetic strategies leverage combinations of underlying assets and derivatives to maintain a portfolio with minimal directional risk, enhancing risk management efficiency compared to traditional asset holdings. These strategies enable precise hedging and volatility control by creating synthetic assets that replicate exposure while neutralizing delta, reducing the impact of market movements on portfolio value.
Composability in Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets enhance risk management through superior composability, allowing seamless integration with decentralized finance protocols and customizable exposure to multiple underlying assets. Their programmable nature enables precise risk allocation and dynamic portfolio adjustments, surpassing traditional asset limitations in flexibility and scalability.
Synthetic Asset Oracles
Synthetic asset oracles provide real-time, reliable data feeds enabling accurate valuation and risk assessment of synthetic assets, which replicate traditional asset price movements without actual ownership. These oracles enhance risk management by ensuring transparency, reducing slippage, and minimizing exposure to market manipulation in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Decentralized Synthetic Asset Issuance
Decentralized synthetic asset issuance leverages blockchain technology to replicate traditional asset exposure without direct ownership, enabling efficient risk management through diversified and programmable financial instruments. Unlike physical assets, synthetic assets minimize counterparty risk and enhance liquidity by operating on decentralized protocols that ensure transparency and automated settlement.
Asset vs Synthetic Asset for risk management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com