Choosing between a savings account and a high-yield account for asset growth depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance. High-yield accounts offer significantly better interest rates, accelerating asset accumulation while maintaining liquidity and safety. Traditional savings accounts provide more stability with lower returns but may be better suited for emergency funds or short-term savings.
Table of Comparison
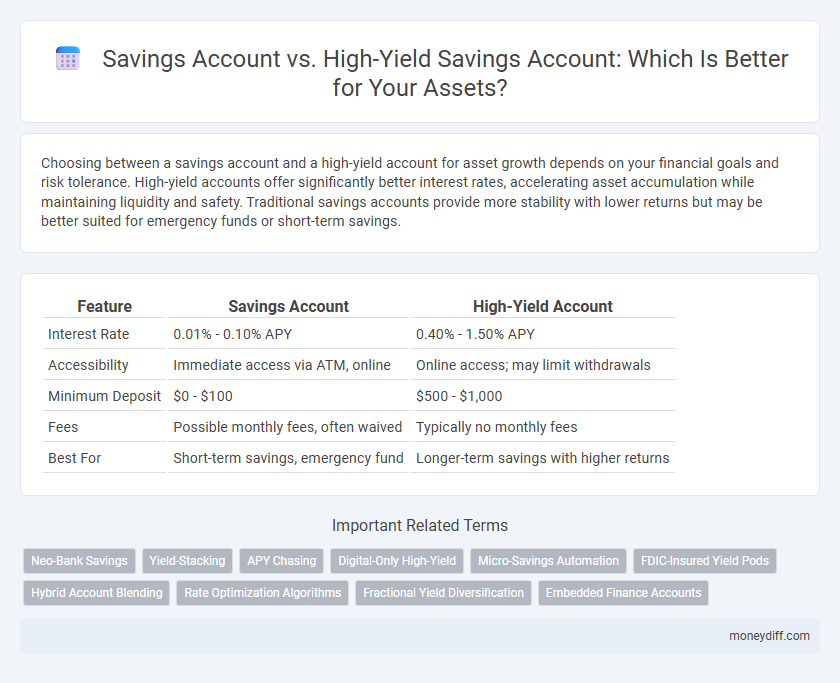
| Feature | Savings Account | High-Yield Account |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | 0.01% - 0.10% APY | 0.40% - 1.50% APY |
| Accessibility | Immediate access via ATM, online | Online access; may limit withdrawals |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 - $100 | $500 - $1,000 |
| Fees | Possible monthly fees, often waived | Typically no monthly fees |
| Best For | Short-term savings, emergency fund | Longer-term savings with higher returns |
Understanding Savings Accounts: Features and Benefits
Savings accounts offer secure, interest-bearing deposits with easy access to funds, making them ideal for emergency assets. These accounts typically have lower interest rates but provide liquidity and FDIC insurance up to $250,000, ensuring your asset's safety. High-yield accounts often offer better returns but might impose withdrawal limits or require higher minimum balances, influencing asset growth strategies.
What is a High-Yield Savings Account?
A high-yield savings account is a type of savings account that offers significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, helping to grow assets more efficiently over time. These accounts typically require higher minimum deposits and may have limited withdrawal options but provide better returns by leveraging higher annual percentage yields (APYs). Investors seeking to maximize asset growth while maintaining liquidity often prefer high-yield savings accounts for their combination of safety and enhanced income potential.
Comparing Interest Rates: Savings vs High-Yield Accounts
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, often ranging from 3% to 5% APY versus the standard 0.01% to 0.10%. This increased yield accelerates asset growth, making high-yield accounts an efficient tool for maximizing returns on liquid savings. Traditional savings accounts provide lower risk and easier accessibility but result in slower asset appreciation due to minimal interest accumulation.
Accessibility and Withdrawal Limits: Which is More Flexible?
Savings accounts typically offer higher accessibility with unlimited withdrawals and easy ATM access, making them ideal for frequent transactions. High-yield accounts often impose withdrawal limits, such as six transactions per month, to maintain higher interest rates and ensure asset growth. For flexibility in accessing assets, savings accounts provide greater ease, while high-yield accounts balance liquidity with higher returns through controlled withdrawal options.
Safety and Security: FDIC Protection Explained
Savings accounts and high-yield accounts both offer FDIC protection, insuring deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per institution, ensuring asset safety. High-yield accounts often provide higher interest rates while maintaining the same level of federal insurance, making them a secure option for growing assets. Choosing between them depends on balancing liquidity needs with maximizing returns without compromising the FDIC-backed security of deposits.
Minimum Balance Requirements for Each Account Type
Savings accounts typically have lower minimum balance requirements, often as low as $25, making them accessible for broad asset building. High-yield accounts usually require higher minimum balances, sometimes $1,000 or more, to access elevated interest rates that boost asset growth. Meeting these minimums is crucial for optimizing returns and maintaining account benefits in asset management.
Fees and Charges: Hidden Costs to Watch For
Savings accounts typically have lower fees and fewer charges, making them suitable for steady asset growth without unexpected costs. High-yield accounts often offer better interest rates but may impose higher minimum balance fees or transaction limits that can reduce overall returns. Examining the fine print for maintenance fees, withdrawal limits, and penalty charges is crucial when selecting the best account to maximize asset value.
How Each Account Supports Your Asset Growth
A Savings Account offers stable, low-risk growth with easy access, making it ideal for short-term asset building and emergency funds. High-Yield Accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, accelerating asset growth over time, though they may require higher minimum balances or limited withdrawals. Choosing between these accounts depends on your asset goals, balancing liquidity needs against maximizing returns.
Choosing the Right Account for Your Financial Goals
Selecting the right savings account depends on your financial goals and liquidity needs; high-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates, often ranging from 3% to 5% APY, compared to traditional savings accounts with rates typically below 0.5% APY. While high-yield accounts can accelerate asset growth, they may require minimum balances or limited transaction capabilities. Evaluating your asset timeline and risk tolerance ensures optimal asset allocation between accessibility and return.
Tips for Maximizing Returns on Your Savings
Maximizing returns on your savings involves choosing between a traditional savings account and a high-yield savings account, the latter offering significantly higher interest rates often above 4% APY compared to standard accounts with rates below 1%. To optimize asset growth, maintain a high-yield account with minimal fees and compound interest frequency, and regularly contribute to leverage the power of compound growth. Monitoring interest rate trends and switching accounts when better rates become available can further enhance savings performance and overall asset accumulation.
Related Important Terms
Neo-Bank Savings
Neo-bank savings accounts offer competitive interest rates that often surpass traditional savings accounts, making them an attractive option to grow assets more efficiently. High-yield accounts within neo-banks typically provide greater liquidity and lower minimum balance requirements, optimizing asset growth with minimal fees and enhanced digital management tools.
Yield-Stacking
Savings accounts provide lower interest rates with high liquidity, making them suitable for emergency funds, while high-yield accounts offer significantly better returns by leveraging yield-stacking strategies that combine multiple interest-earning components. Yield-stacking optimizes asset growth by layering rewards from base interest, promotional rates, and compound interest, maximizing returns without sacrificing access to funds.
APY Chasing
High-yield savings accounts typically offer APYs ranging from 3% to 5%, significantly outperforming traditional savings accounts with APYs around 0.01% to 0.10%, enabling faster asset growth through compound interest. Prioritizing accounts with the highest APY ensures optimized returns on liquid assets while maintaining accessibility and FDIC insurance.
Digital-Only High-Yield
Digital-only high-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, enabling faster asset growth through compounded earnings. These accounts leverage advanced online platforms to provide seamless access, lower fees, and enhanced liquidity, making them an optimal choice for maximizing savings efficiency in a digital-first financial landscape.
Micro-Savings Automation
Micro-savings automation enhances asset growth by directing small, frequent deposits into high-yield accounts, which offer significantly higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts. Leveraging automated transfers maximizes compound interest returns, optimizing long-term asset accumulation through disciplined, effortless saving strategies.
FDIC-Insured Yield Pods
FDIC-insured yield pods like savings accounts offer guaranteed security for assets but typically provide lower interest rates compared to high-yield accounts that maximize earnings with higher but variable yields. When prioritizing asset growth within safe investment vehicles, high-yield accounts present a strategic advantage by increasing returns while maintaining federal insurance protection.
Hybrid Account Blending
A hybrid savings account blends the stability of traditional savings with the enhanced returns of high-yield accounts, optimizing asset growth by offering competitive interest rates alongside liquidity. This combination maximizes asset accumulation potential while maintaining easy access to funds, ideal for balanced financial strategies.
Rate Optimization Algorithms
Savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates compared to high-yield accounts, which leverage advanced rate optimization algorithms to dynamically adjust returns based on market conditions and liquidity demand. Utilizing these algorithms enables high-yield accounts to maximize asset growth by identifying optimal rate benchmarks and minimizing opportunity costs.
Fractional Yield Diversification
Savings accounts offer stable, low-risk returns with easy access to funds, while high-yield accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, enhancing asset growth through elevated yields. Fractional yield diversification involves allocating investments between both account types to balance liquidity and maximize overall returns within a savings portfolio.
Embedded Finance Accounts
Embedded finance accounts integrate savings and high-yield features within digital platforms, offering seamless access to asset growth opportunities without traditional banking constraints. High-yield embedded accounts provide superior interest rates that significantly enhance asset accumulation compared to standard savings accounts, leveraging real-time analytics and automation for optimized financial management.
Savings Account vs High-Yield Account for asset. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com