Tax evasion involves illegally avoiding taxes through deceptive practices, which carries severe legal consequences and penalties. In contrast, tax optimization uses legitimate strategies such as deductions, credits, and efficient income structuring to minimize tax liability within the bounds of the law. Effective income management relies on tax optimization to enhance savings and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Table of Comparison
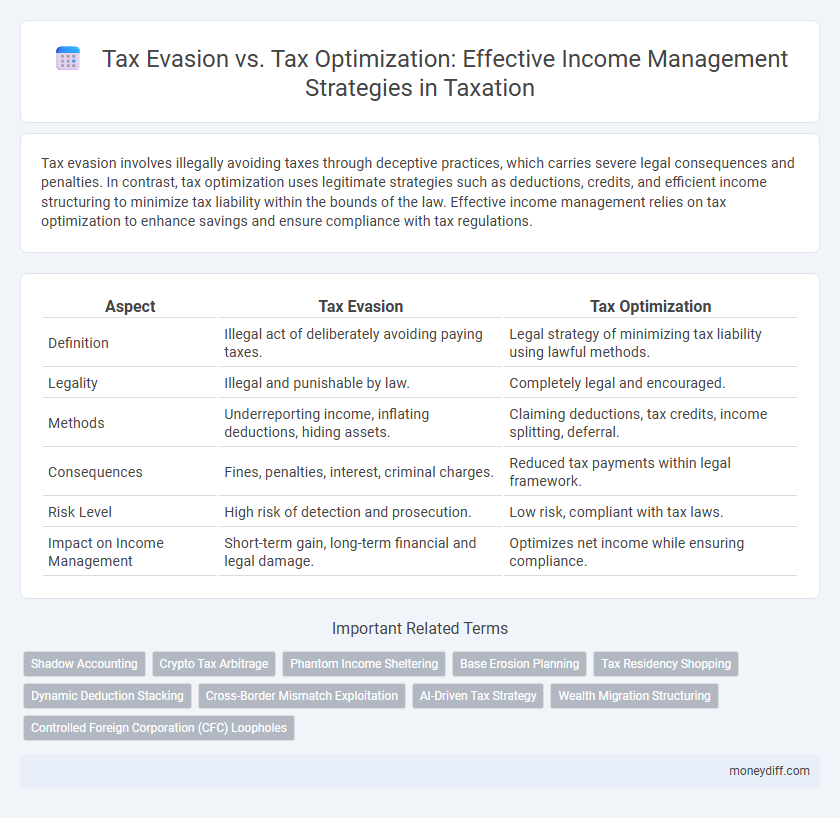
| Aspect | Tax Evasion | Tax Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal act of deliberately avoiding paying taxes. | Legal strategy of minimizing tax liability using lawful methods. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Completely legal and encouraged. |
| Methods | Underreporting income, inflating deductions, hiding assets. | Claiming deductions, tax credits, income splitting, deferral. |
| Consequences | Fines, penalties, interest, criminal charges. | Reduced tax payments within legal framework. |
| Risk Level | High risk of detection and prosecution. | Low risk, compliant with tax laws. |
| Impact on Income Management | Short-term gain, long-term financial and legal damage. | Optimizes net income while ensuring compliance. |
Understanding Tax Evasion and Tax Optimization
Tax evasion involves illegally avoiding taxes through deceptive practices such as underreporting income or inflating deductions, which is punishable by law. Tax optimization, also known as tax planning, uses legal strategies like leveraging deductions, credits, and exemptions to minimize tax liability effectively. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing income responsibly while remaining compliant with tax regulations.
Key Differences Between Tax Evasion and Tax Optimization
Tax evasion involves illegal practices such as underreporting income or inflating deductions to reduce tax liability, leading to penalties and legal consequences. In contrast, tax optimization uses lawful strategies like tax credits, deductions, and income timing to minimize taxes while complying with regulations. The key difference lies in legality, where tax optimization aligns with tax laws, and tax evasion violates them, posing significant financial risks.
Legal Implications of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion involves illegally underreporting income or inflating deductions to reduce tax liability, leading to severe legal consequences including fines, penalties, and potential imprisonment. In contrast, tax optimization uses lawful strategies such as deductions, credits, and income shifting to minimize tax burden within legal boundaries. Understanding the strict enforcement of tax laws by agencies like the IRS or HMRC is crucial to differentiate permissible tax planning from illegal evasion practices.
Methods and Strategies of Tax Optimization
Tax optimization involves strategic planning through legal methods such as income splitting, tax deductions, credits, and deferrals to minimize taxable income and reduce overall tax liability. Utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, leveraging retirement contributions, and investing in tax-efficient assets are key strategies for effective income management. Employing professional tax advisors to navigate complex regulations ensures compliance while maximizing financial benefits.
Common Examples of Tax Evasion Tactics
Common examples of tax evasion tactics include underreporting income, inflating deductions or expenses, and hiding assets in offshore accounts. Individuals and businesses may also resort to falsifying records or using fake invoices to reduce taxable income illegally. These actions violate tax laws and can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
Ethical Considerations in Income Tax Management
Tax evasion involves illegal practices to avoid paying taxes, harming public resources and violating ethical standards. Tax optimization uses legal methods to minimize tax liability through deductions, credits, and strategic planning, aligning with responsible financial management. Ethical income tax management requires transparency, compliance with laws, and a commitment to contributing fairly to societal needs.
Benefits of Legitimate Tax Optimization
Legitimate tax optimization enhances income management by maximizing deductions, credits, and lawful tax incentives, resulting in reduced tax liabilities and increased savings. Utilizing strategies such as tax-advantaged investments and retirement accounts ensures compliance with tax laws while improving cash flow and long-term financial health. This approach supports sustainable financial planning, minimizes audit risks, and promotes transparency with tax authorities.
Risks and Consequences of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion involves illegal practices to avoid paying taxes, leading to severe penalties including fines, interest charges, and potential criminal prosecution. Authorities actively monitor and investigate suspicious financial activities, increasing the likelihood of audits and asset seizures for tax evaders. Unlike lawful tax optimization, tax evasion risks damaging personal and business reputations while causing long-term financial instability due to imposed sanctions.
How to Optimize Taxes Without Breaking the Law
Tax optimization involves strategically managing income, deductions, and credits to minimize tax liability within legal boundaries, using methods such as tax-deferred accounts, lawful deductions, and income splitting. Employing tax-advantaged investments, maximizing contributions to retirement plans, and utilizing available tax credits ensure compliance while effectively reducing taxable income. Maintaining thorough documentation and consulting tax professionals helps safeguard against penalties and aligns financial planning with current tax regulations.
Role of Financial Advisors in Tax Management
Financial advisors play a crucial role in tax management by guiding clients through legal tax optimization strategies that maximize income retention and reduce liabilities without crossing into tax evasion. They leverage in-depth knowledge of tax laws and current regulations to design personalized plans involving deductions, credits, and investment choices that comply with tax codes. Their expertise helps individuals and businesses maintain financial transparency while effectively minimizing tax burdens, ensuring long-term financial health and regulatory compliance.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Accounting
Shadow accounting plays a critical role in distinguishing tax optimization from tax evasion by ensuring transparent and compliant income management through accurate, off-the-books tracking of financial transactions. This technique helps businesses minimize tax liabilities legally while avoiding the illegal concealment of income that constitutes tax evasion.
Crypto Tax Arbitrage
Tax evasion involves illegal practices like underreporting crypto income or hiding assets to avoid paying taxes, while tax optimization uses legal strategies such as leveraging crypto tax arbitrage opportunities to minimize taxable income. Crypto tax arbitrage exploits differences in tax treatments across jurisdictions or timing of transactions to reduce overall tax liability within regulatory compliance.
Phantom Income Sheltering
Phantom income sheltering strategically minimizes taxable income by deferring recognition of unrealized gains without violating tax laws, contrasting with illegal tax evasion that conceals true income to evade tax liabilities. Effective income management leverages phantom income techniques within regulatory frameworks to optimize tax burdens while ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties.
Base Erosion Planning
Base erosion planning involves strategies to minimize taxable income by exploiting gaps and mismatches in tax rules, distinguishing it from illegal tax evasion which conceals income or falsifies information. Effective tax optimization leverages legal mechanisms such as deductions, credits, and transfer pricing adjustments to reduce tax liability without breaching regulatory compliance.
Tax Residency Shopping
Tax residency shopping involves strategically choosing a country with favorable tax laws to minimize liability legally, contrasting with tax evasion, which is illegal and involves deliberately misreporting income or assets. Utilizing legitimate tax optimization strategies through residency planning can significantly reduce tax burdens while complying with international tax regulations and avoiding penalties.
Dynamic Deduction Stacking
Dynamic Deduction Stacking leverages tax codes strategically to maximize allowable deductions and credits, enhancing tax optimization without crossing the legal boundaries of tax evasion. By systematically aligning income management with evolving tax regulations, taxpayers can reduce taxable income and improve compliance while avoiding penalties associated with illicit tax evasion schemes.
Cross-Border Mismatch Exploitation
Cross-border mismatch exploitation occurs when taxpayers leverage differences in tax regulations between countries to reduce their global tax liabilities without violating legal boundaries, distinguishing it from illegal tax evasion. Effective tax optimization strategies involve aligning income management with international tax treaties and compliance standards to minimize risks and enhance fiscal efficiency.
AI-Driven Tax Strategy
AI-driven tax strategies enhance income management by leveraging machine learning algorithms to identify legal deductions and credits, maximizing tax optimization while minimizing risks of tax evasion. Automated data analysis and real-time compliance monitoring enable taxpayers to implement efficient tax planning, ensuring adherence to tax laws and reducing audit exposure.
Wealth Migration Structuring
Tax optimization through strategic wealth migration structuring legally minimizes tax liabilities by leveraging jurisdictional advantages and compliant income management techniques. In contrast, tax evasion involves illegal practices to hide income or falsify financial records, risking severe penalties and reputational damage.
Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) Loopholes
Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) loopholes enable taxpayers to shift income to low-tax jurisdictions, facilitating tax evasion by hiding profits and avoiding tax liabilities. In contrast, legitimate tax optimization uses CFC rules to structure income efficiently within legal boundaries, minimizing taxes without violating anti-avoidance regulations.
Tax Evasion vs Tax Optimization for income management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com