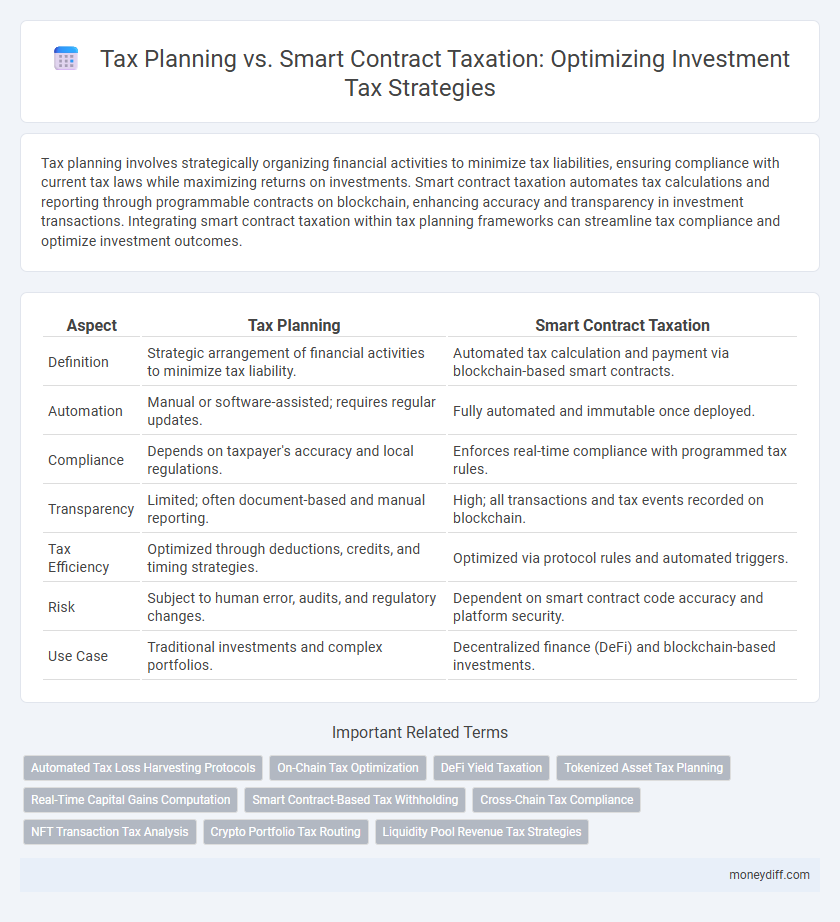
Tax planning involves strategically organizing financial activities to minimize tax liabilities, ensuring compliance with current tax laws while maximizing returns on investments. Smart contract taxation automates tax calculations and reporting through programmable contracts on blockchain, enhancing accuracy and transparency in investment transactions. Integrating smart contract taxation within tax planning frameworks can streamline tax compliance and optimize investment outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tax Planning | Smart Contract Taxation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic arrangement of financial activities to minimize tax liability. | Automated tax calculation and payment via blockchain-based smart contracts. |
| Automation | Manual or software-assisted; requires regular updates. | Fully automated and immutable once deployed. |
| Compliance | Depends on taxpayer's accuracy and local regulations. | Enforces real-time compliance with programmed tax rules. |
| Transparency | Limited; often document-based and manual reporting. | High; all transactions and tax events recorded on blockchain. |
| Tax Efficiency | Optimized through deductions, credits, and timing strategies. | Optimized via protocol rules and automated triggers. |
| Risk | Subject to human error, audits, and regulatory changes. | Dependent on smart contract code accuracy and platform security. |
| Use Case | Traditional investments and complex portfolios. | Decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain-based investments. |
Understanding Tax Planning in Investment
Effective tax planning in investment involves strategizing financial decisions to minimize tax liabilities while maximizing returns through legal mechanisms. It requires a deep understanding of applicable tax codes, deduction opportunities, and timing of income recognition to optimize capital gains and dividend treatments. Mastering these elements empowers investors to enhance portfolio growth by efficiently managing tax obligations.
Introduction to Smart Contract Taxation
Smart contract taxation revolutionizes traditional tax planning by automating tax calculations and compliance through blockchain technology. These contracts execute predefined tax rules instantly on investment transactions, ensuring accuracy and reducing human errors. Integrating smart contract taxation enhances transparency and efficiency, reshaping the investment tax landscape.
Key Differences: Tax Planning vs Smart Contract Taxation
Tax planning involves strategic approaches to minimize tax liability through traditional methods such as deductions, credits, and timing of income recognition, whereas smart contract taxation leverages blockchain technology to automate and enforce tax compliance in real-time via programmable contracts. Tax planning requires manual adjustments and often relies on professional advice to optimize investment outcomes, while smart contract taxation integrates tax rules directly into transactions, reducing errors and increasing transparency. The key difference lies in tax planning's flexibility and customization compared to the automated, code-driven execution and reporting inherent in smart contract taxation.
Benefits of Traditional Tax Planning for Investors
Traditional tax planning provides investors with strategic opportunities to minimize tax liabilities through deductions, credits, and efficient asset allocation. It allows for personalized guidance from tax professionals who can navigate complex regulations and optimize portfolio performance. Utilizing well-established frameworks ensures compliance and maximizes after-tax returns, offering stability compared to emerging smart contract taxation methods.
Advantages of Smart Contract Taxation in Crypto Investments
Smart contract taxation automates tax calculations and reporting, reducing human error and ensuring compliance with real-time transaction tracking on the blockchain. This transparency enhances audit readiness and minimizes the risk of tax evasion, streamlining the overall tax planning process for crypto investors. Compared to traditional tax planning, smart contract taxation offers faster processing, increased accuracy, and improved integrity of financial records.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Tax planning for investments requires meticulous compliance with evolving tax laws to optimize deductions and minimize liabilities, ensuring alignment with IRS regulations. Smart contract taxation introduces regulatory challenges due to its decentralized and automated nature, complicating the traceability of transactions and accurate reporting of taxable events. Navigating these challenges demands integrating blockchain transparency with current tax frameworks to achieve both legal compliance and efficient tax management.
Tax Efficiency Strategies: Traditional vs Blockchain
Tax efficiency strategies for investment differ significantly between traditional tax planning and smart contract taxation. Traditional tax planning involves leveraging deductions, credits, and timing of income recognition to minimize taxable liability, while blockchain-based smart contract taxation automates compliance and optimizes tax events through programmable rules. Blockchain's transparency and immutability enable precise tracking of investment transactions, potentially reducing audit risks and enhancing real-time tax reporting.
Reporting Requirements and Transparency
Tax planning for investments requires comprehensive documentation to comply with reporting requirements imposed by tax authorities, ensuring transparency in income declaration and deductions. Smart contract taxation automates transaction records on blockchain, providing immutable and transparent audit trails that simplify reporting obligations. Leveraging blockchain technology enhances accuracy and real-time transparency, reducing errors and increasing trust in tax compliance processes.
Risks and Limitations of Automated Taxation
Automated tax calculations using smart contracts pose risks such as inaccuracies due to coding errors or outdated tax regulations, potentially leading to costly compliance issues. Limitations include the inability of smart contracts to adapt quickly to complex and evolving tax laws, resulting in misinterpretation of investment gains or deductions. Despite the efficiency of automated systems, manual tax planning remains essential to address nuances and mitigate risks inherent in smart contract taxation.
Future Trends in Investment Taxation
Future trends in investment taxation emphasize the integration of smart contract taxation to automate compliance and reduce errors, transforming traditional tax planning methodologies. Blockchain technology enables real-time tracking of taxable events, optimizing tax liabilities and enhancing transparency for investors and regulators. Advanced algorithms embedded in smart contracts facilitate dynamic tax calculations aligned with evolving tax codes, signaling a paradigm shift in the efficiency of tax planning for investment portfolios.
Related Important Terms
Automated Tax Loss Harvesting Protocols
Automated tax loss harvesting protocols leverage smart contracts to optimize investment tax planning by systematically identifying and executing tax loss harvesting opportunities without manual intervention. These protocols enhance tax efficiency by automatically realizing losses to offset gains, thereby minimizing taxable income and maximizing after-tax returns.
On-Chain Tax Optimization
On-chain tax optimization leverages blockchain transparency and smart contracts to automate accurate tracking of investment transactions, reducing errors and enhancing compliance with tax regulations. Integrating smart contract taxation within tax planning strategies enables real-time calculation of liabilities, minimizing tax burdens through automated deductions and timely reporting.
DeFi Yield Taxation
DeFi yield taxation presents unique challenges in tax planning due to the complex, automated nature of smart contracts that generate income from decentralized finance protocols. Effective tax strategies must incorporate accurate tracking of token transactions and yield events on blockchain networks to comply with evolving regulations and minimize tax liabilities.
Tokenized Asset Tax Planning
Tokenized asset tax planning requires understanding both traditional tax rules and the unique implications of smart contract taxation on investment transactions, which automate event triggers affecting taxable income recognition. Efficient strategies combine compliance with blockchain-specific tax reporting standards to optimize tax liabilities while leveraging the transparency and immutability of tokenized asset records.
Real-Time Capital Gains Computation
Real-time capital gains computation enables precise tax planning by calculating gains instantly during transactions, minimizing liabilities and maximizing investment efficiency. Smart contract taxation automates this process on blockchain, ensuring transparent, accurate, and immediate tax reporting without manual intervention.
Smart Contract-Based Tax Withholding
Smart contract-based tax withholding automates compliance by directly deducting taxes during transactions, reducing errors and ensuring real-time tax collection on investments. This technology enhances transparency and accuracy compared to traditional tax planning methods that rely on manual declarations and estimations.
Cross-Chain Tax Compliance
Tax planning for investment requires comprehensive strategies to optimize liabilities across multiple jurisdictions, while smart contract taxation automates compliance by embedding tax rules directly into blockchain protocols. Cross-chain tax compliance integrates data from diverse blockchain networks, ensuring accurate reporting and adherence to tax regulations in decentralized finance (DeFi) transactions.
NFT Transaction Tax Analysis
Tax planning for NFT transactions involves strategic timing and asset classification to minimize taxable events and optimize capital gains, while smart contract taxation automates tax compliance through programmable rules embedded in blockchain protocols. Analyzing NFT transaction tax requires understanding how smart contracts trigger taxable events such as transfers, sales, or royalties, ensuring accurate reporting and reduced risk of audit discrepancies.
Crypto Portfolio Tax Routing
Effective tax planning for crypto investment optimizes portfolio tax routing by leveraging strategies such as tax-loss harvesting and asset location to minimize liabilities. Smart contract taxation automates transaction tracking and tax rule application, enhancing accuracy and compliance in complex decentralized finance environments.
Liquidity Pool Revenue Tax Strategies
Tax planning for liquidity pool revenue involves optimizing investment structures to minimize taxable events by leveraging deferred recognition and offsetting gains with losses, ensuring compliance with current IRS guidelines. Smart contract taxation automates revenue tracking and reporting on decentralized finance platforms, offering precise allocation of taxable income and facilitating realtime tax strategy adjustments to maximize after-tax returns.
Tax Planning vs Smart Contract Taxation for Investment Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com