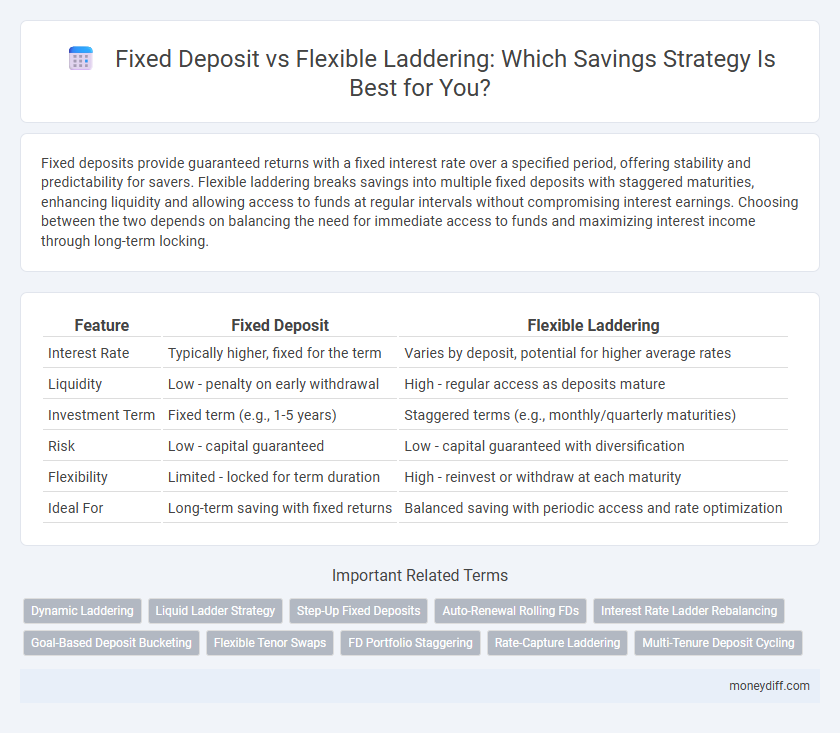
Fixed deposits provide guaranteed returns with a fixed interest rate over a specified period, offering stability and predictability for savers. Flexible laddering breaks savings into multiple fixed deposits with staggered maturities, enhancing liquidity and allowing access to funds at regular intervals without compromising interest earnings. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for immediate access to funds and maximizing interest income through long-term locking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fixed Deposit | Flexible Laddering |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Typically higher, fixed for the term | Varies by deposit, potential for higher average rates |
| Liquidity | Low - penalty on early withdrawal | High - regular access as deposits mature |
| Investment Term | Fixed term (e.g., 1-5 years) | Staggered terms (e.g., monthly/quarterly maturities) |
| Risk | Low - capital guaranteed | Low - capital guaranteed with diversification |
| Flexibility | Limited - locked for term duration | High - reinvest or withdraw at each maturity |
| Ideal For | Long-term saving with fixed returns | Balanced saving with periodic access and rate optimization |
Understanding Fixed Deposits: A Safe Savings Option
Fixed deposits offer a secure savings option by locking funds at a fixed interest rate for a predetermined period, ensuring capital protection and predictable returns. Unlike flexible laddering, which involves dividing investments across multiple deposit terms to balance liquidity and interest rate risk, fixed deposits emphasize stability and risk-free growth. This strategy suits conservative savers prioritizing capital preservation over immediate access to funds.
What is Flexible Laddering in Savings?
Flexible laddering in savings is a strategy that involves dividing your savings into multiple fixed deposits with staggered maturity dates, allowing partial access to funds at regular intervals. This approach balances liquidity and higher interest rates by avoiding locking all funds in a single long-term deposit. It provides flexibility to reinvest or withdraw money based on changing financial needs while optimizing returns compared to traditional fixed deposits.
Fixed Deposits vs Flexible Laddering: Key Differences
Fixed deposits offer a guaranteed interest rate and fixed tenure, providing predictable returns and low risk for savers. Flexible laddering involves splitting funds into multiple fixed deposits maturing at staggered intervals, enhancing liquidity and interest rate benefit by allowing reinvestment at varying rates. While fixed deposits prioritize stability, flexible laddering balances risk and reward by leveraging changing market rates and cash flow needs.
Interest Rates: Which Strategy Offers Better Returns?
Fixed deposits typically offer higher interest rates with guaranteed returns over a fixed term, making them attractive for risk-averse savers seeking predictable income. Flexible laddering spreads investments across multiple fixed deposits with staggered maturities, potentially securing higher average rates by capitalizing on fluctuating market conditions. While fixed deposits provide stability, flexible laddering can optimize returns by reinvesting at varying interest rates, balancing liquidity and yield effectively.
Liquidity and Flexibility: Comparing Access to Funds
Fixed deposits offer high interest rates but restrict liquidity since funds are locked in for a fixed term, leading to penalties on early withdrawal. Flexible laddering provides more frequent access to portions of the investment by staggering maturity dates, enhancing liquidity without sacrificing overall returns. This strategy balances flexibility and steady income, making it ideal for savers needing periodic access to funds.
Risk Management in Fixed Deposits and Flexible Laddering
Fixed deposits offer low-risk, guaranteed returns with fixed interest rates, making them ideal for conservative savers seeking capital protection. Flexible laddering spreads investments across multiple fixed deposits with varying maturities, reducing interest rate risk and providing liquidity at staggered intervals. This strategy balances risk by minimizing exposure to interest rate fluctuations while ensuring consistent access to funds.
Tax Implications: Fixed Deposit vs Flexible Laddering
Fixed deposits typically attract tax on the entire interest earned, often taxed at the investor's marginal rate, which can reduce overall returns. Flexible laddering allows investors to stagger maturities and withdraw or reinvest funds strategically, potentially managing taxable interest income across multiple financial years to minimize tax liability. Choosing flexible laddering can offer better control over tax planning compared to fixed deposits, which have a fixed interest payout and tax event at maturity.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Fixed Deposits?
Fixed deposits suit conservative savers seeking guaranteed returns with minimal risk and a fixed tenure. They are ideal for individuals who prefer predictable interest income and have a specific savings goal or timeframe. Those unwilling to frequently manage investments or tolerate market fluctuations benefit most from fixed deposits over flexible laddering strategies.
Suitability: Who Benefits Most from Flexible Laddering?
Flexible laddering suits savers seeking liquidity and higher returns by staggering fixed deposit maturities, allowing access to funds at regular intervals without penalties. It benefits individuals with fluctuating cash flow needs or those anticipating interest rate changes, as laddering mitigates reinvestment risk. Unlike traditional fixed deposits, flexible laddering provides a balance between capital protection and financial flexibility.
Decision Guide: Choosing the Best Savings Strategy
Fixed deposits offer guaranteed interest rates and principal security, ideal for savers seeking predictability and minimal risk. Flexible laddering diversifies maturity dates, enhancing liquidity and potentially capturing higher rates as market conditions shift. Assess your cash flow needs, risk tolerance, and interest rate outlook to determine whether stability or adaptability aligns best with your financial goals.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Laddering
Dynamic laddering in savings offers a flexible approach by staggering fixed deposit maturities to optimize interest rates and liquidity, unlike traditional fixed deposits that lock funds for a set term. This strategy enables savers to capitalize on fluctuating market rates while maintaining periodic access to their capital, enhancing overall returns and financial agility.
Liquid Ladder Strategy
The liquid ladder strategy offers enhanced liquidity by staggering maturity dates of fixed deposits, allowing savers to access funds at regular intervals without penalties. Compared to traditional fixed deposits, this approach maximizes interest returns while maintaining flexibility to meet unexpected cash flow needs.
Step-Up Fixed Deposits
Step-Up Fixed Deposits offer higher interest rates over time by increasing the deposit rate at predetermined intervals, providing a predictable growth path compared to Flexible Laddering, which allows for staggered maturity dates but with variable interest rates. This structured increment feature in Step-Up FDs enhances returns on long-term savings while maintaining capital security.
Auto-Renewal Rolling FDs
Auto-Renewal Rolling Fixed Deposits (FDs) offer consistent interest rates by automatically renewing principal and interest on maturity, while flexible laddering strategies diversify maturity dates to optimize liquidity and potentially higher cumulative returns. Choosing between Auto-Renewal FDs and flexible laddering depends on prioritizing stable returns with minimal management versus maximizing access to funds and adjusting to interest rate fluctuations.
Interest Rate Ladder Rebalancing
Fixed deposit offers a stable interest rate locked for the term, whereas flexible laddering allows periodic rebalancing by reinvesting matured deposits at current higher rates, maximizing returns amid rate fluctuations. This strategic rebalancing in flexible laddering optimizes interest earnings compared to fixed deposits, which lack the adaptability to capitalize on rising market rates.
Goal-Based Deposit Bucketing
Goal-based deposit bucketing enhances savings strategies by allocating funds into fixed deposits for stable returns and flexible laddering for liquidity and interest rate optimization. This approach maximizes growth potential while aligning with specific financial goals and timelines.
Flexible Tenor Swaps
Flexible tenor swaps within flexible laddering strategies allow savers to adjust deposit maturities according to changing interest rates, optimizing returns compared to fixed deposits locked at a single rate. This dynamic approach enhances liquidity management and capitalizes on rate fluctuations, making it a superior option for maximizing savings growth over rigid fixed deposit terms.
FD Portfolio Staggering
Fixed deposit portfolio staggering involves dividing the investment into multiple fixed deposits with different maturity dates to optimize liquidity and interest rates, reducing the risk of reinvestment at lower rates. Flexible laddering enhances this strategy by allowing partial withdrawals or reinvestments before maturity, providing greater adaptability to changing financial needs while maintaining consistent interest earnings.
Rate-Capture Laddering
Fixed deposit accounts often offer higher interest rates for locking funds over a fixed term, maximizing returns through guaranteed rate capture, while flexible laddering spreads savings across staggered maturities, enabling consistent access to accumulated interest and principal. Rate-capture laddering strategically balances liquidity and yield by securing fixed rates at ladder intervals, reducing exposure to interest rate fluctuations compared to single-term fixed deposits.
Multi-Tenure Deposit Cycling
Fixed deposit offers guaranteed returns with fixed interest rates over set terms, providing stability but limited liquidity. Flexible laddering through multi-tenure deposit cycling enhances liquidity and maximizes interest earnings by staggering maturity dates, allowing savers to reinvest or access funds periodically without sacrificing higher fixed deposit rates.
Fixed deposit vs Flexible laddering for savings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com