ETFs offer diversified exposure to broad market indices, providing stability and lower risk, while thematic ETFs target specific sectors or trends, allowing investors to capitalize on growth opportunities in niche areas. Thematic ETFs may yield higher returns but carry increased volatility due to concentrated holdings. Choosing between them depends on an investor's risk tolerance and investment goals.
Table of Comparison
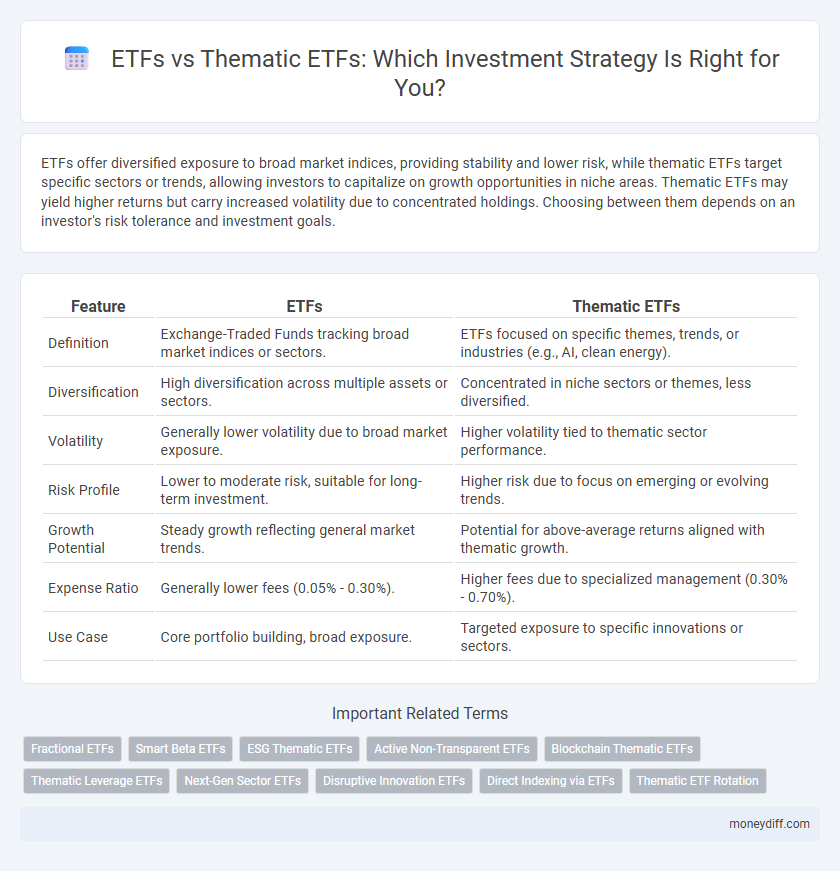
| Feature | ETFs | Thematic ETFs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange-Traded Funds tracking broad market indices or sectors. | ETFs focused on specific themes, trends, or industries (e.g., AI, clean energy). |
| Diversification | High diversification across multiple assets or sectors. | Concentrated in niche sectors or themes, less diversified. |
| Volatility | Generally lower volatility due to broad market exposure. | Higher volatility tied to thematic sector performance. |
| Risk Profile | Lower to moderate risk, suitable for long-term investment. | Higher risk due to focus on emerging or evolving trends. |
| Growth Potential | Steady growth reflecting general market trends. | Potential for above-average returns aligned with thematic growth. |
| Expense Ratio | Generally lower fees (0.05% - 0.30%). | Higher fees due to specialized management (0.30% - 0.70%). |
| Use Case | Core portfolio building, broad exposure. | Targeted exposure to specific innovations or sectors. |
Understanding ETFs: A Quick Overview
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) offer diversified exposure by tracking broad market indexes or specific sectors, providing cost-effective investment options with high liquidity. Thematic ETFs focus on targeted trends or industries such as clean energy, AI, or biotechnology, allowing investors to capitalize on specific growth themes. Understanding ETF structures and expense ratios is crucial for optimizing portfolio performance and aligning with investment goals.
What Are Thematic ETFs?
Thematic ETFs are investment funds that focus on specific trends, industries, or themes such as technology innovation, clean energy, or healthcare advancements, offering targeted exposure compared to broad market ETFs. These funds invest in companies aligned with a particular theme, allowing investors to capitalize on niche growth opportunities and sector-specific dynamics. Thematic ETFs provide a strategic way to diversify portfolios by concentrating on emerging market themes with high growth potential.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Thematic ETFs
Traditional ETFs typically track broad market indices or specific sectors, offering diversified exposure with lower risk and steady performance. Thematic ETFs, however, concentrate on specific trends or themes like clean energy, technology innovation, or demographic shifts, providing targeted growth potential but higher volatility. Investors should evaluate risk tolerance and investment goals when choosing between broad-based diversification of traditional ETFs and the focused opportunity of thematic ETFs.
Risk Factors: ETFs vs Thematic ETFs
ETFs generally offer broader market exposure with lower risk due to diversified holdings across multiple sectors. Thematic ETFs concentrate investments on specific trends or sectors, increasing exposure to sector-specific risks and volatility. Investors in thematic ETFs face higher fluctuations driven by the performance of targeted industries compared to traditional ETFs' more balanced risk profile.
Portfolio Diversification with ETFs
ETFs offer broad market exposure, allowing investors to diversify across multiple sectors and asset classes with a single purchase. Thematic ETFs concentrate on specific trends or industries, such as technology or clean energy, providing targeted growth potential but higher sector risk. Incorporating both traditional broad-market ETFs and thematic ETFs can enhance portfolio diversification by balancing stable core holdings with focused growth opportunities.
Thematic ETFs: Riding Investment Trends
Thematic ETFs offer targeted exposure to specific investment trends like clean energy, artificial intelligence, or cybersecurity, providing investors with focused portfolio diversification. These funds capitalize on evolving market themes driven by technological advancements and socio-economic shifts, often delivering higher growth potential compared to broad-market ETFs. By aligning investments with emerging sectors, thematic ETFs enable strategic participation in long-term structural changes shaping global economies.
Performance Comparison: ETFs vs Thematic ETFs
Traditional ETFs typically offer broad market exposure and lower expense ratios, resulting in stable, long-term returns aligned with overall market performance. Thematic ETFs, which focus on specific sectors or trends like technology or clean energy, often exhibit higher volatility but can deliver superior short-term gains during periods of sector outperformance. Performance comparison reveals that while traditional ETFs provide consistency, thematic ETFs may enhance portfolio returns through targeted growth opportunities linked to emerging market themes.
Costs and Fees: What Investors Need to Know
ETFs generally offer lower expense ratios compared to thematic ETFs, which often carry higher fees due to specialized sector exposure and active management strategies. Investors should carefully examine the total cost of ownership, including trading commissions and bid-ask spreads, which can impact overall returns. Understanding these cost differences is crucial for optimizing investment portfolios and maximizing long-term gains.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Traditional ETFs offer broad market exposure suitable for conservative investors seeking diversification and lower risk, while thematic ETFs target specific sectors or trends, appealing to growth-oriented investors comfortable with higher volatility. Conservative investors prioritize stability and income generation, making broad-market ETFs ideal, whereas aggressive investors aiming for capital appreciation often prefer thematic ETFs aligned with emerging technologies or societal shifts. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market knowledge is crucial when choosing between conventional ETFs and thematic ETFs for portfolio alignment.
Choosing Between ETFs and Thematic ETFs for Your Investment Strategy
ETFs offer broad market exposure with diversified holdings tracking indexes, suitable for long-term, stable growth. Thematic ETFs concentrate on specific sectors or trends like technology or clean energy, providing targeted investment aligned with emerging opportunities. Investors should assess risk tolerance and investment objectives to determine whether broad diversification or focused thematic exposure better complements their portfolio strategy.
Related Important Terms
Fractional ETFs
Fractional ETFs enable investors to purchase partial shares, enhancing accessibility and diversification with lower capital requirements compared to traditional ETFs; thematic ETFs, however, focus on specific sectors or trends, offering targeted exposure but often at higher costs and volatility. Utilizing fractional ETFs within thematic investing strategies can optimize portfolio allocation by balancing precision in thematic exposure and cost-efficiency in share acquisition.
Smart Beta ETFs
Smart Beta ETFs offer a disciplined, rules-based approach to investment by weighting assets according to factors like volatility, size, and value, enhancing returns compared to traditional market-cap-weighted ETFs. Thematic ETFs focus on specific trends or sectors but may carry higher risk and volatility, whereas Smart Beta ETFs balance strategic factor exposure with broad market diversification, appealing to investors seeking targeted yet stable growth.
ESG Thematic ETFs
ESG Thematic ETFs offer targeted exposure to companies excelling in environmental, social, and governance criteria, enabling investors to align portfolios with sustainable values while capturing sector-specific growth trends. Compared to broad traditional ETFs, ESG Thematic ETFs provide enhanced opportunities for impact investing by focusing on themes such as clean energy, social equality, and corporate responsibility within a diversified framework.
Active Non-Transparent ETFs
Active non-transparent ETFs offer enhanced portfolio management and reduced tracking error compared to traditional ETFs by allowing managers to implement dynamic strategies while maintaining confidentiality of holdings. Thematic ETFs focus on specific sectors or trends but often lack the flexibility and confidentiality benefits inherent in active non-transparent ETFs, making the latter more suitable for investors seeking strategic agility and reduced front-running risk.
Blockchain Thematic ETFs
Blockchain thematic ETFs offer targeted exposure to companies developing or utilizing blockchain technology, potentially capturing higher growth opportunities compared to traditional ETFs that track broad market indices. Investors seeking to capitalize on blockchain innovation may prefer thematic ETFs for their focused approach and sector-specific insights.
Thematic Leverage ETFs
Thematic Leverage ETFs offer amplified exposure to specific market trends or sectors, enabling investors to capitalize on targeted growth opportunities with increased risk and reward potential compared to traditional broad-market ETFs. These leveraged vehicles use derivatives and debt to magnify returns, making them suitable for sophisticated investors seeking aggressive strategies within thematic investment frameworks.
Next-Gen Sector ETFs
Next-Gen Sector ETFs offer targeted exposure to emerging industries like clean energy, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology, providing investors with focused growth opportunities beyond traditional broad-market ETFs. While conventional ETFs track diversified indexes, thematic ETFs concentrate on disruptive technologies and trends, aligning portfolios with future-oriented innovation sectors.
Disruptive Innovation ETFs
Disruptive Innovation ETFs focus on companies driving groundbreaking technologies and market shifts, offering targeted exposure to high-growth sectors such as artificial intelligence, biotech, and clean energy within thematic ETFs. Traditional broad-market ETFs provide diversified investment across established industries, while thematic ETFs emphasize concentration in innovation-driven companies poised to reshape global markets.
Direct Indexing via ETFs
Direct indexing via ETFs offers investors customized exposure by replicating specific indexes with tax efficiency and cost-effectiveness, unlike traditional ETFs that track broad market indexes. Thematic ETFs focus on targeted sectors or trends but direct indexing provides greater flexibility for personalized portfolio construction and precise factor targeting within an ETF structure.
Thematic ETF Rotation
Thematic ETFs concentrate on specific trends or sectors, allowing investors to capitalize on emerging market opportunities, while ETF rotation strategies optimize portfolio performance by reallocating investments among thematic ETFs based on market cycles and momentum indicators. This dynamic approach enhances risk management and aims to maximize returns by aligning asset allocations with evolving economic and industry trends.
ETFs vs Thematic ETFs for investment Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com