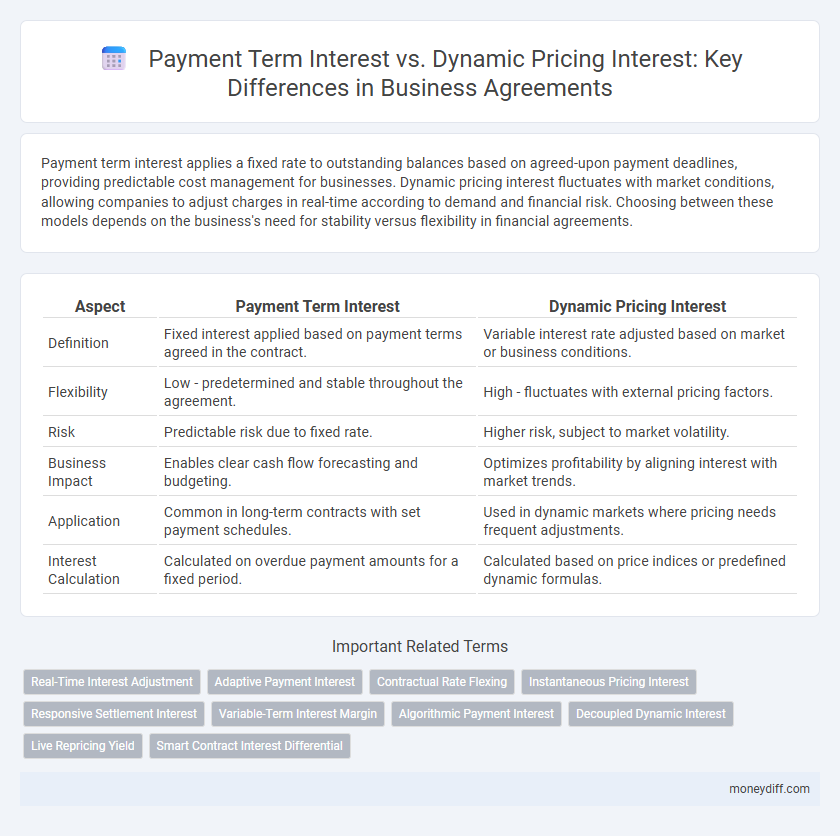
Payment term interest applies a fixed rate to outstanding balances based on agreed-upon payment deadlines, providing predictable cost management for businesses. Dynamic pricing interest fluctuates with market conditions, allowing companies to adjust charges in real-time according to demand and financial risk. Choosing between these models depends on the business's need for stability versus flexibility in financial agreements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Payment Term Interest | Dynamic Pricing Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed interest applied based on payment terms agreed in the contract. | Variable interest rate adjusted based on market or business conditions. |
| Flexibility | Low - predetermined and stable throughout the agreement. | High - fluctuates with external pricing factors. |
| Risk | Predictable risk due to fixed rate. | Higher risk, subject to market volatility. |
| Business Impact | Enables clear cash flow forecasting and budgeting. | Optimizes profitability by aligning interest with market trends. |
| Application | Common in long-term contracts with set payment schedules. | Used in dynamic markets where pricing needs frequent adjustments. |
| Interest Calculation | Calculated on overdue payment amounts for a fixed period. | Calculated based on price indices or predefined dynamic formulas. |
Understanding Payment Term Interest in Business Agreements
Payment Term Interest in business agreements refers to the interest charged on overdue payments based on predefined terms outlined in the contract, ensuring timely cash flow management. This form of interest provides a fixed or variable rate applied after the agreed payment deadline, promoting financial discipline between parties. Understanding Payment Term Interest is essential for businesses to mitigate risks associated with delayed payments and maintain liquidity.
Dynamic Pricing Interest: A Modern Approach to Pricing
Dynamic Pricing Interest leverages real-time market data and consumer behavior analytics to adjust interest rates dynamically, ensuring competitive and flexible payment terms. This approach enhances revenue optimization by aligning interest charges with demand fluctuations and risk factors, unlike fixed Payment Term Interest rates that remain static throughout the agreement. Businesses adopting Dynamic Pricing Interest benefit from increased profitability and adaptability in volatile market conditions.
Key Differences Between Payment Term and Dynamic Pricing Interest
Payment term interest is a fixed rate applied to outstanding balances based on agreed payment schedules, ensuring predictable cost management for businesses. Dynamic pricing interest fluctuates with market conditions or risk factors, enabling more flexible and responsive adjustments to credit costs. The key difference lies in payment term interest offering stability and clarity, while dynamic pricing interest provides adaptability to changes in economic or customer-specific variables.
Impact on Cash Flow: Payment Terms vs Dynamic Pricing
Payment term interest affects cash flow predictability by locking in fixed interest rates tied to specific payment schedules, ensuring businesses can plan expenses with certainty. Dynamic pricing interest fluctuates with market conditions, leading to variable cash outflows that can either improve or strain liquidity depending on interest rate trends. Businesses must weigh the stability of payment term interest against the flexibility and risk associated with dynamic pricing interest when managing working capital.
Risk Management: Fixed Interest vs Fluctuating Interest
Fixed interest payment terms provide businesses with predictable financial obligations, reducing exposure to market volatility and simplifying cash flow management. Dynamic pricing interest, while potentially offering lower rates during favorable conditions, introduces risk due to fluctuating interest rates that can increase borrowing costs unexpectedly. Effective risk management strategies involve evaluating market trends and financial resilience to determine the optimal balance between stability and flexibility in interest terms.
Negotiation Strategies for Interest Terms in Contracts
Negotiation strategies for payment term interest versus dynamic pricing interest in business agreements require a clear understanding of cash flow impact and risk allocation. Payment term interest often involves fixed rates applied to outstanding balances, ensuring predictable costs, while dynamic pricing interest fluctuates based on market variables, introducing variability and potential cost savings. Effective negotiation demands balancing predictability with flexibility by aligning interest terms with the company's financial strategy and risk tolerance.
Legal Considerations: Compliance in Interest Applications
Legal considerations in payment term interest versus dynamic pricing interest focus on strict compliance with consumer protection laws and financial regulations to prevent usury and ensure transparent disclosure of interest rates. Business agreements must explicitly outline the calculation methods, applicable interest rates, and conditions under which interest accrues to avoid disputes and regulatory penalties. Adhering to jurisdiction-specific statutes, such as the Truth in Lending Act (TILA) in the U.S., is critical for lawful application of interest in commercial contracts.
Choosing the Right Interest Model for Your Business
Choosing the right interest model for your business requires analyzing cash flow stability and customer payment behavior. Payment Term Interest offers predictability with fixed interest rates tied to specific payment periods, enhancing budget forecasting accuracy. Dynamic Pricing Interest introduces flexibility by adjusting rates based on market demand or risk factors, optimizing revenue but requiring more sophisticated monitoring.
Case Studies: Business Outcomes of Interest Type Selection
Case studies reveal that businesses choosing Payment Term Interest often experience improved cash flow predictability, reducing financial strain during delayed payments. Conversely, companies implementing Dynamic Pricing Interest benefit from flexibility in adapting to market fluctuations, which can enhance profitability but may introduce complexity in pricing strategies. Selecting the appropriate interest type directly influences financial stability and customer relationship management, underscoring the importance of aligning interest models with specific business goals.
Future Trends: Digitalization and the Evolution of Interest Models
Future trends in business agreements indicate a shift from traditional payment term interest models toward dynamic pricing interest enabled by digital platforms leveraging real-time data analytics and AI algorithms. Digitalization allows for personalized interest rates that reflect fluctuating market conditions and customer risk profiles, enhancing flexibility and competitiveness in financing. The evolution of interest models promises greater transparency, efficiency, and alignment with economic variables, transforming how businesses structure credit and manage financial risks.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Interest Adjustment
Real-time interest adjustment in payment terms allows businesses to dynamically calculate interest based on current rates, enhancing cash flow predictability and reducing overdue payments. Dynamic pricing interest models automatically update rates according to market fluctuations, providing more accurate and flexible financing costs compared to fixed payment term interest.
Adaptive Payment Interest
Adaptive Payment Interest in business agreements adjusts interest rates based on real-time market conditions and payment behavior, offering flexibility compared to fixed Payment Term Interest. This dynamic approach enables businesses to optimize cash flow while mitigating risk through interest rates that respond to economic fluctuations.
Contractual Rate Flexing
Contractual rate flexing in business agreements differentiates Payment Term Interest, which applies fixed interest rates based on agreed payment terms, from Dynamic Pricing Interest that adjusts rates in real-time based on market or risk factors. This flexibility enables businesses to manage cash flow predictability with Payment Term Interest while leveraging market-responsive cost structures through Dynamic Pricing Interest.
Instantaneous Pricing Interest
Instantaneous pricing interest in business agreements enables real-time adjustment of payment terms based on fluctuating market rates, enhancing cash flow management and risk mitigation. This approach offers greater flexibility compared to static payment term interest by aligning financial obligations more closely with current economic conditions and operational performance.
Responsive Settlement Interest
Responsive Settlement Interest adapts to real-time payment behavior, offering businesses a flexible mechanism to incentivize timely settlements and minimize credit risk. Unlike traditional Payment Term Interest, which applies static rates based on fixed intervals, this dynamic pricing interest model enhances cash flow management by aligning interest charges with actual payment responsiveness.
Variable-Term Interest Margin
Variable-term interest margins in payment term interest provide businesses with a predictable cost structure based on agreed-upon rates over a fixed period, enhancing cash flow stability. Dynamic pricing interest adjusts rates in real-time according to market fluctuations, offering flexibility but with potential cost volatility that can impact profit margins and financial planning.
Algorithmic Payment Interest
Algorithmic payment interest leverages dynamic pricing models to adjust interest rates in real-time based on risk factors, market conditions, and payment behaviors, optimizing cash flow and reducing default rates for businesses. Unlike static payment term interest, this approach enhances financial agility by integrating predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms to tailor interest charges throughout the contract lifecycle.
Decoupled Dynamic Interest
Decoupled Dynamic Interest allows businesses to separate interest rates from fixed payment terms, enabling real-time adjustments based on market fluctuations and risk profiles. This approach contrasts with traditional Payment Term Interest, offering enhanced flexibility and optimized cash flow management through adaptable, data-driven interest calculations.
Live Repricing Yield
Payment term interest calculates cost based on fixed credit durations, providing predictable expense estimates, while dynamic pricing interest uses live repricing yield to adjust rates in real-time, optimizing profitability by reflecting current market conditions and demand fluctuations. Businesses leveraging dynamic pricing interest through live repricing yield maximize financial performance by capturing higher margins during peak periods and minimizing losses during low demand.
Smart Contract Interest Differential
Smart Contract Interest Differential leverages blockchain technology to automate and transparently adjust interest rates between fixed Payment Term Interest and variable Dynamic Pricing Interest in business agreements, ensuring real-time alignment with market conditions. This mechanism enhances accuracy in interest calculations, reduces disputes, and optimizes cash flow by dynamically reflecting risk and performance parameters encoded within the smart contract.
Payment Term Interest vs Dynamic Pricing Interest for business agreements. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com