Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, often below the inflation rate, which can diminish the purchasing power of your cash over time. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, helping your savings grow faster while maintaining liquidity and security. Effective cash management benefits greatly from leveraging high-yield accounts to maximize interest earnings without sacrificing access to funds.
Table of Comparison
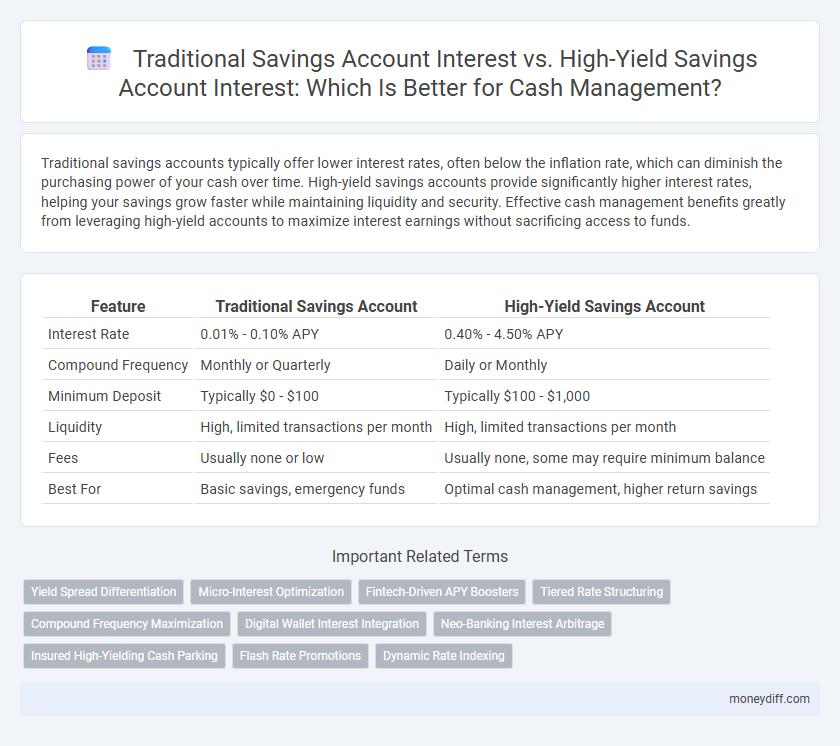
| Feature | Traditional Savings Account | High-Yield Savings Account |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | 0.01% - 0.10% APY | 0.40% - 4.50% APY |
| Compound Frequency | Monthly or Quarterly | Daily or Monthly |
| Minimum Deposit | Typically $0 - $100 | Typically $100 - $1,000 |
| Liquidity | High, limited transactions per month | High, limited transactions per month |
| Fees | Usually none or low | Usually none, some may require minimum balance |
| Best For | Basic savings, emergency funds | Optimal cash management, higher return savings |
Understanding Traditional Savings Account Interest Rates
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, often ranging from 0.01% to 0.10% APY, making them less effective for significant cash growth. These accounts provide easy access and FDIC insurance up to $250,000, prioritizing liquidity over high yields. Understanding this rate structure helps individuals balance safety with minimal interest returns in cash management strategies.
What Sets High-Yield Savings Account Interest Rates Apart
High-yield savings account interest rates significantly outperform traditional savings account rates, often offering APYs up to 20 times higher, which accelerates cash growth more effectively. These accounts leverage online banking platforms with lower overhead costs, enabling banks to pass higher earnings to customers through elevated interest rates. Enhanced compounding frequency and reduced fees further optimize cash management, making high-yield savings accounts ideal for maximizing passive income.
How Interest is Calculated: Traditional vs High-Yield Accounts
Interest on traditional savings accounts is typically calculated using a simple interest formula based on a lower annual percentage yield (APY), resulting in slower growth over time. High-yield savings accounts use compound interest, often compounded daily, with significantly higher APYs that maximize earnings by reinvesting interest. The combination of higher rates and frequent compounding in high-yield accounts offers a more effective cash management strategy for accelerating savings growth.
Accessibility and Convenience: Comparing Account Types
Traditional savings accounts offer easy access and convenience with widespread availability at most banks and immediate withdrawal options, making them ideal for everyday cash management. High-yield savings accounts provide higher interest rates but may have limitations like online-only access and withdrawal restrictions, affecting liquidity and ease of use. Evaluating the balance between accessibility and higher returns is crucial for optimizing cash management strategies.
Impact of Inflation on Different Savings Accounts
Traditional savings account interest rates often fail to keep pace with inflation, causing the real value of savings to erode over time. High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates significantly above the national average, helping to offset inflation's impact and preserving purchasing power more effectively. Investors managing cash for short-term needs should prioritize accounts with compounded interest rates that exceed the current inflation rate to maintain wealth growth.
Minimum Balance Requirements: Traditional vs High-Yield Accounts
Traditional savings accounts typically require lower minimum balances, often around $100, making them accessible for everyday cash management. High-yield savings accounts usually have higher minimum balance requirements, sometimes $1,000 or more, to access their superior interest rates. Understanding these balance thresholds is crucial for optimizing interest earnings while maintaining liquidity.
Fees and Hidden Costs to Watch For
Traditional savings accounts typically have lower interest rates but may include monthly maintenance fees and minimum balance requirements that can erode overall returns. High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates, although some may charge fees for excessive transactions or require a higher minimum balance to avoid penalties. Evaluating fee structures and understanding hidden costs like withdrawal limits or transfer fees is crucial to maximizing interest earnings and efficient cash management.
Risk Factors in Traditional and High-Yield Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates with minimal risk, insured by the FDIC up to $250,000, delivering stable but modest returns ideal for conservative cash management. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates but may come with stricter withdrawal limits, variable rates influenced by market fluctuations, and potential online-only access, which can affect liquidity and immediate cash availability. Both account types carry minimal default risk due to federal insurance, but evaluating interest rate variability and account accessibility is crucial for effective cash management strategies.
Maximizing Cash Management with Strategic Account Selection
Traditional savings accounts typically offer interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, providing minimal growth on idle cash, whereas high-yield savings accounts deliver significantly higher interest rates, often ranging from 3% to 5%, enabling more effective cash management by maximizing returns. Selecting a high-yield savings account leverages compounding interest to increase earnings while maintaining liquidity, crucial for optimal cash flow management. Comparing annual percentage yields (APYs) and account fees ensures strategic account selection aligns with individual cash management goals for maximum financial efficiency.
Choosing the Best Savings Account for Your Financial Goals
High-yield savings accounts offer interest rates several times higher than traditional savings accounts, typically ranging from 3% to 5% APY compared to 0.01% to 0.10% APY. For effective cash management, selecting a high-yield savings account can significantly boost your earnings on idle funds while maintaining liquidity and security through FDIC insurance. Evaluate your financial goals, such as emergency fund growth or short-term savings, to choose an account that optimizes interest income without compromising accessibility.
Related Important Terms
Yield Spread Differentiation
High-yield savings accounts offer interest rates typically 10 to 20 times higher than traditional savings accounts, creating a significant yield spread that maximizes cash management returns. This yield spread differentiation enables savers to grow their funds more efficiently without sacrificing liquidity or security.
Micro-Interest Optimization
Traditional savings accounts offer lower interest rates typically around 0.01% to 0.10%, resulting in minimal micro-interest accumulation on idle cash balances. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher returns, often 3.50% or more, enabling more effective micro-interest optimization by maximizing incremental daily interest earnings for cash management.
Fintech-Driven APY Boosters
High-yield savings accounts offered by Fintech platforms leverage advanced algorithms and automation to provide APYs significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, often exceeding 4.5%, whereas traditional savings accounts typically offer APYs below 1%. These Fintech-driven interest boosters optimize cash management by dynamically allocating funds to maximize returns while maintaining liquidity and FDIC insurance coverage.
Tiered Rate Structuring
Traditional savings accounts typically offer a fixed, lower interest rate regardless of the balance, while high-yield savings accounts utilize tiered rate structuring to provide higher interest rates as account balances increase, optimizing returns on larger cash holdings. Tiered rates encourage better cash management by rewarding higher balances with progressively increased interest earnings, making high-yield accounts more advantageous for maximizing growth on liquid assets.
Compound Frequency Maximization
High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates that are multiple times higher than traditional savings accounts, significantly enhancing compound frequency maximization by allowing more frequent interest compounding, which accelerates cash growth over time. Choosing accounts with daily or monthly compounding periods maximizes the effective annual yield, optimizing cash management through exponential interest accrual rather than linear gains.
Digital Wallet Interest Integration
High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates 3 to 5 times higher than traditional savings accounts, enhancing cash management by growing idle funds more effectively. Integrating these accounts with digital wallets allows seamless interest accrual and instant access, optimizing liquidity and maximizing returns without sacrificing convenience.
Neo-Banking Interest Arbitrage
Traditional savings accounts typically offer interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, whereas high-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher rates, often between 3.00% and 5.00%, enhancing cash management through superior returns. Neo-banking platforms capitalize on this interest rate arbitrage by leveraging partnerships with multiple high-yield account providers, optimizing user deposits for maximum interest accumulation without sacrificing liquidity.
Insured High-Yielding Cash Parking
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, often ranging from 0.50% to 4.50% APY, while maintaining FDIC insurance up to $250,000 per depositor. This makes insured high-yield savings accounts an optimal choice for cash parking and effective cash management, combining safety with enhanced earning potential.
Flash Rate Promotions
Traditional savings account interest rates typically range from 0.01% to 0.10%, offering minimal returns on idle cash, while high-yield savings accounts with flash rate promotions can provide temporary boosts up to 4.00% or higher, significantly enhancing short-term cash management strategies. Flash rate promotions often last 2-6 months, enabling savers to maximize interest earnings before rates revert, making them ideal for optimizing liquidity and growing emergency funds efficiently.
Dynamic Rate Indexing
High-yield savings accounts leverage dynamic rate indexing tied to market benchmarks, enabling interest rates to adjust more responsively compared to traditional savings accounts with fixed or minimally variable rates. This indexed approach maximizes returns on cash management by closely tracking economic conditions and providing higher, more competitive interest earnings.
Traditional Savings Account Interest vs High-Yield Savings Account Interest for cash management Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com