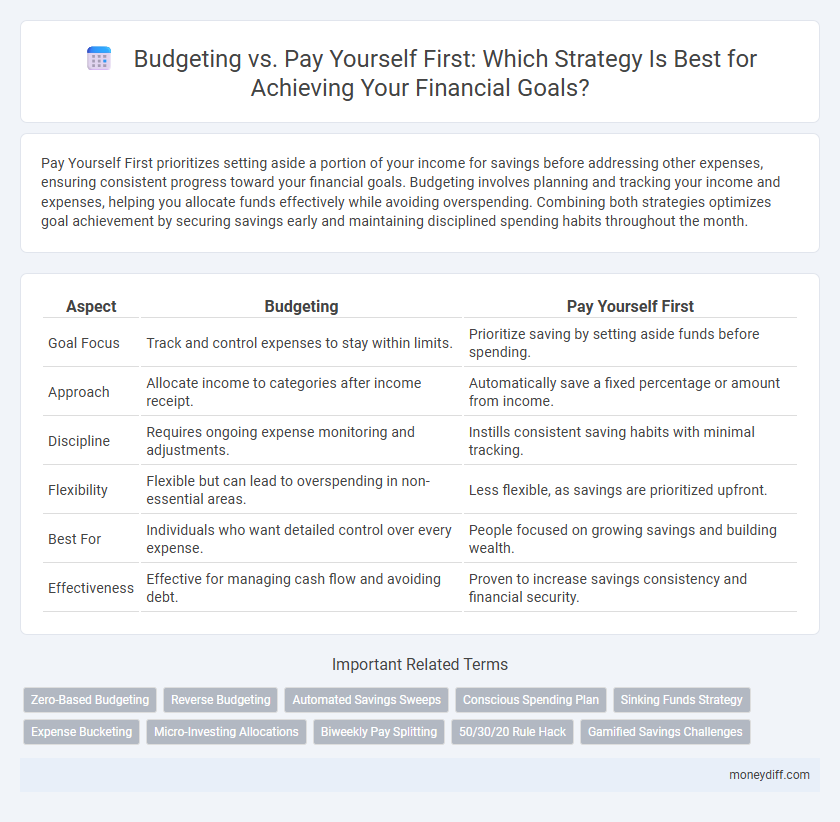
Pay Yourself First prioritizes setting aside a portion of your income for savings before addressing other expenses, ensuring consistent progress toward your financial goals. Budgeting involves planning and tracking your income and expenses, helping you allocate funds effectively while avoiding overspending. Combining both strategies optimizes goal achievement by securing savings early and maintaining disciplined spending habits throughout the month.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Budgeting | Pay Yourself First |
|---|---|---|
| Goal Focus | Track and control expenses to stay within limits. | Prioritize saving by setting aside funds before spending. |
| Approach | Allocate income to categories after income receipt. | Automatically save a fixed percentage or amount from income. |
| Discipline | Requires ongoing expense monitoring and adjustments. | Instills consistent saving habits with minimal tracking. |
| Flexibility | Flexible but can lead to overspending in non-essential areas. | Less flexible, as savings are prioritized upfront. |
| Best For | Individuals who want detailed control over every expense. | People focused on growing savings and building wealth. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for managing cash flow and avoiding debt. | Proven to increase savings consistency and financial security. |
Understanding Money Management Goals
Budgeting establishes a structured plan for allocating income towards expenses, savings, and debt repayment, ensuring clear visibility and control over financial resources. Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving by automatically setting aside a designated portion of income before other expenses, promoting disciplined wealth building. Combining these strategies enhances money management goals by balancing immediate financial obligations with long-term savings objectives.
What Is Budgeting?
Budgeting is a financial planning process that allocates income toward expenses, savings, and debt repayment to achieve specific goals. It involves tracking spending habits, setting spending limits, and adjusting allocations to maintain financial stability. By creating a budget, individuals gain control over their money, ensuring funds are available for both necessary expenses and future objectives.
What Does Pay Yourself First Mean?
Pay Yourself First means prioritizing saving a portion of your income before covering any expenses or discretionary spending. This approach ensures consistent wealth building by automatically setting aside funds for goals such as emergency savings, retirement, or investment growth. Unlike traditional budgeting, which allocates money after expenses, Pay Yourself First creates financial discipline and accelerates achieving long-term financial objectives.
Comparing Budgeting and Pay Yourself First
Budgeting involves allocating funds across various expense categories to control spending and achieve financial goals, while Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving a fixed portion of income before any other expenses. Pay Yourself First fosters consistent saving habits by treating savings as a non-negotiable expense, often resulting in faster wealth accumulation. Budgeting provides a comprehensive overview of income and expenses, enabling detailed financial planning but may require more discipline to avoid overspending.
Advantages of Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting offers clear advantages for goal achievement by providing a detailed financial plan that tracks income, expenses, and savings targets, ensuring disciplined money management. This method helps identify spending patterns, reduce unnecessary costs, and allocate funds effectively toward specific financial goals. Structured budgeting promotes accountability and financial awareness, which support consistent progress and long-term stability.
Benefits of the Pay Yourself First Approach
Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving by automatically allocating a portion of income before any expenses, ensuring consistent progress toward financial goals. This method reduces the temptation to overspend and builds a disciplined savings habit, enhancing long-term wealth accumulation. It also provides a clear framework for financial security and goal achievement without relying solely on post-expense budgeting adjustments.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Goals
Choosing the right strategy for your financial goals depends on your spending habits and long-term priorities. Budgeting provides a detailed plan to control expenses and allocate funds efficiently, while the Pay Yourself First approach ensures consistent savings by prioritizing contributions before other expenditures. Evaluating your discipline and financial objectives helps determine which method aligns better with achieving your specific goals.
Common Mistakes in Money Management
Common mistakes in money management include neglecting to prioritize savings before expenses, which undermines financial goals. Budgeting without allocating a fixed portion of income to savings often leads to overspending and missed opportunities for wealth growth. Implementing a "Pay Yourself First" strategy ensures consistent savings and disciplined money management aligned with long-term financial objectives.
Integrating Both Methods for Success
Integrating budgeting with the pay yourself first strategy maximizes financial discipline and goal achievement, ensuring both expenses are managed and savings grow consistently. Allocating a fixed percentage of income to savings before budgeting for expenses establishes a priority on wealth building while maintaining fiscal responsibility. This dual approach enhances cash flow management and accelerates progress toward long-term financial goals, promoting sustainable success.
Actionable Steps to Achieve Your Savings Goals
Setting clear savings goals requires prioritizing consistent contributions through the "Pay Yourself First" method, which automates saving immediately after income is received. Creating a detailed budget helps identify discretionary expenses and reallocates funds toward these automatic savings, reinforcing financial discipline. Combining these strategies ensures actionable steps by securing savings upfront while maintaining control over spending habits to meet financial objectives efficiently.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting allocates every dollar of income to specific expenses, savings, and debt repayment, ensuring no funds are left unassigned and maximizing goal achievement efficiency. Unlike the pay yourself first approach, which prioritizes savings before expenses, zero-based budgeting provides a detailed plan for all income, enhancing control over financial goals.
Reverse Budgeting
Reverse budgeting prioritizes saving by paying yourself first before allocating funds to expenses, ensuring goal-oriented financial discipline. This method contrasts traditional budgeting by setting savings targets upfront, optimizing goal achievement through focused fund allocation.
Automated Savings Sweeps
Automated savings sweeps enhance goal achievement by transferring funds directly into savings accounts, ensuring consistent contributions without manual effort. This method outperforms traditional budgeting by prioritizing savings first, reducing the risk of overspending and accelerating financial goal progress.
Conscious Spending Plan
A Conscious Spending Plan prioritizes allocating funds purposefully, ensuring essential expenses and savings goals are met before discretionary spending occurs. Unlike traditional budgeting, the Pay Yourself First approach guarantees savings by automatically setting aside money for financial objectives, fostering disciplined progress toward long-term goals.
Sinking Funds Strategy
Sinking funds strategy prioritizes allocating specific amounts toward future expenses before budgeting for discretionary spending, ensuring savings goals are met systematically. This approach aligns with the pay yourself first principle by securing dedicated funds upfront, reducing the risk of overspending and improving financial goal attainment.
Expense Bucketing
Expense bucketing enhances budgeting by categorizing spending, ensuring each cost aligns with financial goals and limits overspending. Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving by allocating funds before expenses, but integrating expense buckets maintains balance between saving and necessary expenditures.
Micro-Investing Allocations
Micro-investing allocations enhance goal achievement by automating small, consistent contributions, emphasizing the pay yourself first strategy over traditional budgeting methods. Prioritizing early investments through micro-allocations leverages compounding growth, making it a more effective approach for reaching financial goals rapidly.
Biweekly Pay Splitting
Biweekly pay splitting enhances goal achievement by allocating funds immediately into savings and essential expenses, optimizing budgeting efficiency. Prioritizing "Pay Yourself First" within this framework ensures steady contributions toward financial goals while maintaining disciplined spending habits.
50/30/20 Rule Hack
Applying the 50/30/20 rule hack streamlines financial goals by allocating 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings or debt repayment, enhancing budget control and prioritizing wealth building. Paying yourself first ensures consistent savings by automatically directing a portion of income toward investments or emergency funds before other expenses.
Gamified Savings Challenges
Gamified savings challenges enhance budgeting effectiveness by turning financial goals into interactive experiences that prioritize paying yourself first, ensuring consistent contributions to savings. These challenges use rewards and progress tracking to motivate disciplined saving habits and accelerate goal achievement.
Budgeting vs Pay Yourself First for goal. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com