Traditional budgeting relies on historical data and fixed allocations, often leading to rigid expense plans that may not align with current business priorities. Value-based budgeting prioritizes funding projects and expenses based on their potential return on investment and strategic impact, ensuring resources are directed toward initiatives that drive growth and efficiency. This approach enhances financial agility by continuously adjusting budgets to reflect organizational goals and market dynamics.
Table of Comparison
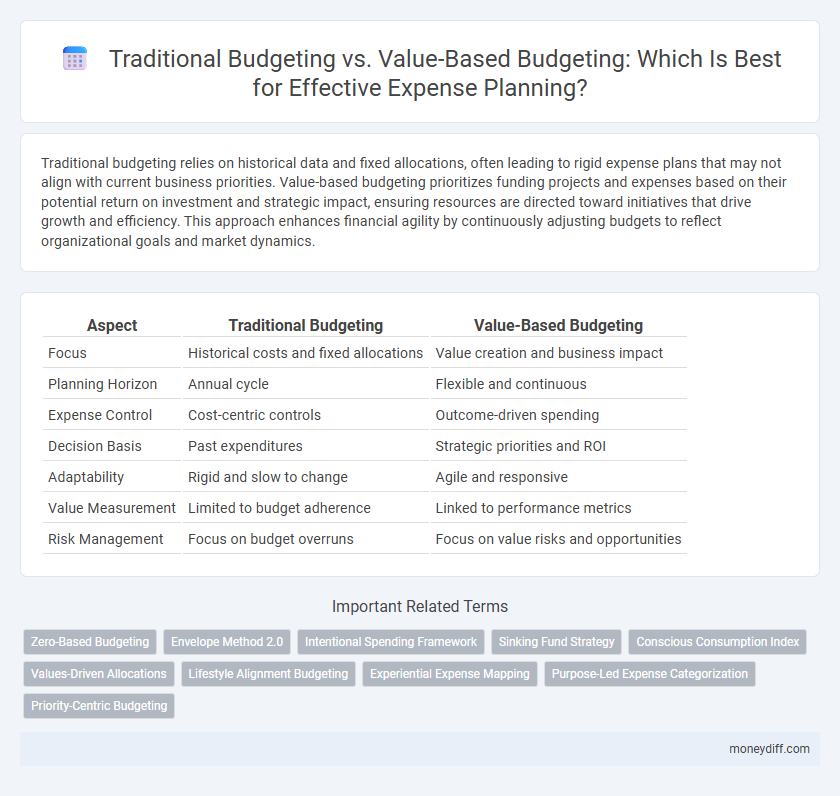
| Aspect | Traditional Budgeting | Value-Based Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Historical costs and fixed allocations | Value creation and business impact |
| Planning Horizon | Annual cycle | Flexible and continuous |
| Expense Control | Cost-centric controls | Outcome-driven spending |
| Decision Basis | Past expenditures | Strategic priorities and ROI |
| Adaptability | Rigid and slow to change | Agile and responsive |
| Value Measurement | Limited to budget adherence | Linked to performance metrics |
| Risk Management | Focus on budget overruns | Focus on value risks and opportunities |
Introduction to Budgeting Methods
Traditional budgeting allocates expenses based on past financial data and fixed line items, emphasizing cost control and incremental adjustments. Value-based budgeting prioritizes funding projects and departments that deliver the highest return on investment or strategic impact, aligning resources with organizational goals. Choosing between these methods impacts financial flexibility, resource optimization, and aligns expense planning with overall business strategy.
Overview of Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting relies on historical financial data and incremental adjustments to allocate resources, emphasizing cost control and fixed expense targets. This approach typically involves detailed line-item reviews and standardized processes aimed at maintaining financial discipline within departments. While it offers predictability, traditional budgeting often lacks flexibility and may not directly align expenditures with strategic value creation or changing business priorities.
Understanding Value-Based Budgeting
Value-Based Budgeting prioritizes expenses that directly contribute to organizational goals and measurable outcomes, unlike Traditional Budgeting which often relies on historical spending patterns. This approach enhances resource allocation efficiency by linking expenditures to value creation and strategic impact. Implementing Value-Based Budgeting requires detailed performance metrics and stakeholder alignment to optimize financial planning and drive business growth.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Value-Based Budgeting
Traditional budgeting focuses on allocating fixed amounts based on historical expenses and departmental needs, emphasizing cost control and adherence to set limits. Value-based budgeting prioritizes funding initiatives that deliver the highest return on investment and strategic impact, aligning resources with organizational goals and value creation. This approach shifts the expense planning process from rigid allocation to dynamic resource optimization driven by measurable outcomes.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting offers a structured and predictable framework for expense planning, facilitating consistent financial control and accountability across departments. However, it often relies on historical data and fixed allocations, which can limit flexibility and responsiveness to changing market conditions or strategic priorities. This approach may also encourage cost-cutting measures that hinder innovation and long-term value creation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Value-Based Budgeting
Value-Based Budgeting prioritizes expenditures that directly contribute to organizational goals, enhancing resource allocation efficiency by aligning spending with strategic value creation. This approach offers advantages such as improved financial discipline, better accountability, and flexibility to adapt to changing business priorities, while its disadvantages include complexity in measuring value accurately and potential undervaluation of indirect yet essential expenses. Compared to Traditional Budgeting, which often emphasizes historical costs and fixed allocations, Value-Based Budgeting fosters a dynamic planning process but requires robust data analytics and stakeholder collaboration for effective implementation.
How to Implement Traditional Budgeting
Implementing traditional budgeting involves setting fixed expense limits based on historical financial data and predefined targets, emphasizing cost control and predictability. Departments submit detailed budget proposals aligned with organizational goals, which are then reviewed and adjusted by finance teams to ensure overall fiscal discipline. Regular variance analysis is conducted to monitor performance against the budget, enabling corrective actions to maintain financial stability.
Steps to Adopt Value-Based Budgeting
Identify key value drivers by evaluating which activities directly contribute to organizational goals and customer satisfaction. Align expense allocation with these drivers, prioritizing investments that maximize value creation rather than simply adhering to historical spending patterns. Implement continuous performance measurement and feedback loops to adjust budgets dynamically, ensuring resources consistently support strategic priorities.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method
Traditional budgeting relies on historical data and fixed allocations, often leading to rigid expense planning that may not reflect current business priorities; value-based budgeting prioritizes expenditures based on the expected value and impact on organizational goals, enhancing resource allocation efficiency. Choosing the right budgeting method depends on company size, industry dynamics, and strategic focus, with value-based budgeting offering greater flexibility and alignment in fast-changing environments. Analyzing cost drivers and expected outcomes helps decision-makers select a budgeting approach that maximizes return on investment and supports sustainable financial management.
Conclusion: Making Informed Budgeting Decisions
Traditional budgeting relies on historical expenses and fixed allocations, often limiting flexibility and responsiveness to market changes. Value-based budgeting prioritizes expenditures that directly contribute to organizational goals and measurable outcomes, enhancing resource efficiency. Combining historical data with value-driven insights enables more informed budgeting decisions that optimize financial performance and strategic impact.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) differs from traditional budgeting by requiring every expense to be justified from scratch, eliminating previous budget baselines and focusing on value creation rather than historical allocations. This approach aligns resources directly with organizational goals, driving more efficient expense planning and maximizing return on investments.
Envelope Method 2.0
The Envelope Method 2.0 enhances traditional budgeting by allocating funds into specific, goal-oriented categories that align with value-based budgeting principles, promoting efficient expense planning and optimized resource distribution. This approach integrates real-time tracking and adaptive adjustments, ensuring budgets reflect actual spending priorities and maximize financial outcomes.
Intentional Spending Framework
Traditional budgeting often relies on rigid, historical expense allocations that limit flexibility and fail to prioritize value outcomes, whereas Value-Based Budgeting emphasizes allocating resources aligned with strategic goals and measurable returns on investment. Integrating an Intentional Spending Framework within Value-Based Budgeting ensures each expense drives purposeful value creation, enhancing decision-making and financial efficiency.
Sinking Fund Strategy
Traditional budgeting relies on fixed allocations and periodic reviews, often overlooking long-term asset replacement needs, whereas value-based budgeting incorporates a sinking fund strategy to allocate expenses systematically for future liabilities. This approach ensures financial stability by setting aside funds incrementally, aligning expenditure planning with asset depreciation and replacement cycles.
Conscious Consumption Index
Traditional budgeting relies on historical spending patterns and fixed allocations, often leading to inefficiencies and misaligned priorities; in contrast, value-based budgeting integrates the Conscious Consumption Index to optimize expense planning by prioritizing sustainability and social impact. Incorporating the Conscious Consumption Index enables organizations to align budgets with ethical consumption trends, enhancing resource allocation that supports long-term value creation and responsible expenditure.
Values-Driven Allocations
Traditional budgeting allocates expenses based on historical costs and fixed categories, often limiting flexibility and responsiveness to changing priorities. Value-based budgeting prioritizes spending by aligning allocations with organizational goals and measurable outcomes, ensuring funds drive maximum impact and support strategic initiatives.
Lifestyle Alignment Budgeting
Lifestyle Alignment Budgeting prioritizes personal values and long-term goals in expense planning, contrasting traditional budgeting's emphasis on rigid spending categories and historical data. This approach enhances financial well-being by aligning expenditures with an individual's lifestyle preferences and future aspirations, promoting more meaningful and sustainable financial decisions.
Experiential Expense Mapping
Traditional budgeting relies on historical expense data to allocate funds, often overlooking the direct impact on customer experience, whereas value-based budgeting prioritizes funding based on the experiential value generated, making experiential expense mapping critical for identifying high-impact cost areas. This approach enhances resource allocation efficiency by linking expenses to customer satisfaction and long-term business growth, enabling more strategic financial planning.
Purpose-Led Expense Categorization
Traditional budgeting organizes expenses by fixed categories rooted in historical spending patterns, often limiting flexibility and alignment with strategic goals; value-based budgeting prioritizes expenses based on their contribution to organizational objectives, enabling purpose-led expense categorization that drives optimized resource allocation and measurable impact. Purpose-led expense categorization enhances decision-making by linking every budget item to specific value outcomes, fostering transparency and accountability in financial planning.
Priority-Centric Budgeting
Priority-centric budgeting emphasizes allocating funds based on strategic value and organizational priorities rather than historical expenditures, enhancing resource efficiency and impact. Traditional budgeting often rigidly follows past spending patterns, while value-based approaches dynamically prioritize expenses driving the highest value and return.
Traditional Budgeting vs Value-Based Budgeting for expense planning. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com