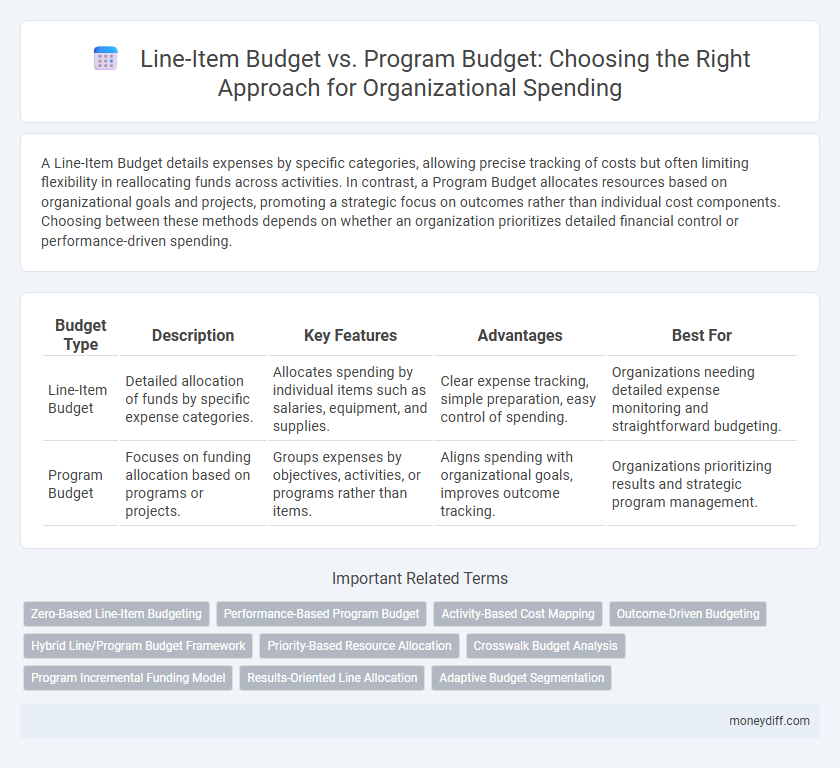
A Line-Item Budget details expenses by specific categories, allowing precise tracking of costs but often limiting flexibility in reallocating funds across activities. In contrast, a Program Budget allocates resources based on organizational goals and projects, promoting a strategic focus on outcomes rather than individual cost components. Choosing between these methods depends on whether an organization prioritizes detailed financial control or performance-driven spending.
Table of Comparison
| Budget Type | Description | Key Features | Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line-Item Budget | Detailed allocation of funds by specific expense categories. | Allocates spending by individual items such as salaries, equipment, and supplies. | Clear expense tracking, simple preparation, easy control of spending. | Organizations needing detailed expense monitoring and straightforward budgeting. |
| Program Budget | Focuses on funding allocation based on programs or projects. | Groups expenses by objectives, activities, or programs rather than items. | Aligns spending with organizational goals, improves outcome tracking. | Organizations prioritizing results and strategic program management. |
Understanding Line-Item and Program Budgets
Line-item budgets detail organizational spending by categorizing expenses into specific accounts such as salaries, supplies, and equipment, enabling precise tracking and control over individual expenditures. Program budgets allocate funds based on specific projects or activities, focusing on the financial resources required to achieve program goals and outcomes, enhancing strategic planning and performance assessment. Understanding the distinctions between these budget types aids organizations in choosing the appropriate approach for effective financial management and aligning spending with organizational priorities.
Key Features of Line-Item Budgeting
Line-item budgeting organizes expenses into specific categories such as salaries, supplies, and equipment, enabling precise tracking and control over individual cost elements. It provides clarity through detailed allocation of funds, facilitating straightforward comparison against actual expenditures. This method enhances accountability by allowing managers to monitor spending at a granular level and quickly identify variances.
Core Principles of Program Budgeting
Program budgeting organizes expenses by specific programs, emphasizing results and accountability, unlike line-item budgeting which categorizes spending by expense type. Core principles of program budgeting include aligning resources with strategic goals, enhancing transparency in how funds contribute to outcomes, and promoting flexibility to reallocate based on performance metrics. This approach improves decision-making by focusing on program effectiveness rather than mere cost tracking.
Comparing Budget Structures: Line-Item vs Program
Line-item budgets allocate funds by specific categories such as salaries, supplies, and equipment, providing detailed financial control and ease of tracking expenditures. Program budgets organize spending around specific projects or objectives, enhancing focus on outcomes and resource allocation efficiency. Organizations often choose line-item budgets for precise expense monitoring, while program budgets better support strategic planning and performance measurement.
Pros and Cons of Line-Item Budgeting
Line-item budgeting offers clear tracking of organizational spending by categorizing expenses into specific items, enhancing financial control and accountability. However, it lacks flexibility, often restricting the ability to reallocate funds quickly in response to changing program needs or strategic priorities. This method may also encourage a focus on controlling costs rather than achieving broader program outcomes, limiting its effectiveness in dynamic environments.
Advantages and Challenges of Program Budgeting
Program budgeting organizes organizational spending by specific projects or programs, enhancing transparency and allowing for easier evaluation of each program's effectiveness and impact. It encourages strategic allocation of resources aligned with organizational goals but can present challenges such as complex tracking, increased administrative workload, and difficulties in comparing expenditures across programs. Despite these challenges, program budgeting supports better decision-making through detailed insight into program costs and outcomes.
Impact on Organizational Financial Transparency
Line-item budgets enhance organizational financial transparency by providing detailed, categorical breakdowns of expenses, allowing stakeholders to track specific cost elements and enforce accountability. Program budgets improve transparency through a results-oriented approach, linking expenditures to organizational goals and outcomes, thereby clarifying resource allocation effectiveness. Both budgeting methods influence how clearly an organization's financial priorities and performance are communicated to internal and external audiences.
How Budget Type Influences Spending Decisions
Line-item budgets allocate funds to specific expense categories, promoting strict control and limiting flexibility in organizational spending decisions. Program budgets focus on funding objectives and outcomes, enabling managers to prioritize resources based on program effectiveness and strategic goals. The choice between line-item and program budgeting significantly impacts how organizations balance accountability with adaptability in resource allocation.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Approach for Your Organization
Line-item budgets provide detailed control over specific expenses, ensuring accountability and simplifying tracking for organizations with strict financial guidelines. Program budgets align spending with strategic goals by grouping costs according to projects, fostering transparency and outcome-based evaluation. Selecting the appropriate budgeting approach depends on organizational priorities, reporting requirements, and the need for flexibility in managing resources.
Best Practices for Effective Budget Management
Line-item budgets provide detailed tracking of expenses by category, enabling precise control over individual spending components, while program budgets allocate funds based on specific organizational goals, enhancing strategic alignment and outcome measurement. Best practices for effective budget management include integrating both approaches to balance accountability with flexibility, regularly reviewing budget performance against objectives, and using data-driven adjustments to improve resource allocation. Employing software tools for real-time monitoring and fostering cross-department collaboration ensures transparency and responsiveness in managing organizational funds.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Line-Item Budgeting
Zero-Based Line-Item Budgeting requires every expense to be justified from scratch, promoting precise control over organizational spending compared to Program Budgeting, which allocates funds based on predetermined programs and objectives. This method enhances transparency and accountability by scrutinizing each line item, fostering efficient resource allocation within departments.
Performance-Based Program Budget
Performance-based program budgets allocate funds according to specific outcomes and objectives, enabling organizations to measure efficiency and effectiveness directly tied to program results rather than just tracking expenses by line items. This approach promotes accountability and strategic resource allocation, enhancing the alignment of spending with organizational goals compared to traditional line-item budgeting.
Activity-Based Cost Mapping
Line-item budgets categorize expenses by specific items, offering detailed tracking but limited insight into activity-driven costs, while program budgets allocate funds based on organizational objectives, promoting strategic spending alignment; Activity-Based Cost Mapping enhances program budgeting by linking expenses directly to activities, improving cost transparency and resource optimization. This method enables organizations to identify high-cost activities and allocate resources more efficiently, driving better financial management and program effectiveness.
Outcome-Driven Budgeting
Line-item budgeting allocates funds by specific expense categories, providing detailed control but often lacking direct links to organizational outcomes; program budgeting organizes expenditures around programs or projects, emphasizing results and facilitating outcome-driven decision-making. Emphasizing outcome-driven budgeting, organizations benefit from program budgets by clearly aligning financial resources with strategic goals, enabling more effective performance measurement and improved accountability.
Hybrid Line/Program Budget Framework
The Hybrid Line/Program Budget Framework integrates detailed expenditure tracking of a Line-Item Budget with the outcome-oriented focus of a Program Budget, enhancing both financial control and strategic resource allocation. This approach allows organizations to manage costs precisely while aligning spending with specific program goals, improving transparency and overall budget efficiency.
Priority-Based Resource Allocation
Line-item budgets allocate funding by specific expense categories, offering detailed expenditure control but limited flexibility for shifting funds between priorities; program budgets group resources by projects or services, enabling priority-based resource allocation that aligns spending with organizational goals and strategic outcomes. Emphasizing program budgets enhances decision-making by linking financial resources directly to performance metrics and priority initiatives, fostering more effective and responsive organizational spending.
Crosswalk Budget Analysis
Line-item budgets provide detailed expense categories, allowing precise tracking of organizational spending, while program budgets align expenditures with specific activities or outcomes for strategic impact measurement. Crosswalk budget analysis bridges these two methods by mapping line-item costs to program objectives, enhancing transparency and facilitating data-driven resource allocation decisions.
Program Incremental Funding Model
The Program Incremental Funding Model allocates resources based on specific program goals and outcomes, enhancing flexibility compared to the rigid structure of a Line-Item Budget that assigns fixed amounts to predefined categories. This approach enables organizations to prioritize funding for initiatives that directly contribute to strategic objectives, optimizing spending efficiency and program effectiveness.
Results-Oriented Line Allocation
Line-item budgets emphasize detailed allocation by specific expense categories, providing clear tracking but limited flexibility and weak direct correlation to organizational outcomes. Program budgets allocate funding based on strategic objectives and results, enhancing accountability and effectiveness by linking expenditures to measurable program performance and impact.
Adaptive Budget Segmentation
Line-item budgets break down expenses by specific categories, offering detailed control over costs, while program budgets allocate resources based on organizational goals and outcomes, enhancing strategic alignment. Adaptive budget segmentation combines these approaches by dynamically adjusting allocations between detailed expenses and program objectives, optimizing flexibility and responsiveness in organizational spending.
Line-Item Budget vs Program Budget for organizational spending. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com