Personal budgeting prioritizes individual financial goals, tracking income, expenses, and savings to achieve personal stability and growth. Social budgeting expands this concept to communities or organizations, allocating resources to meet collective needs and promote shared well-being. Effective money management balances personal discipline with collaborative planning to optimize overall financial health.
Table of Comparison
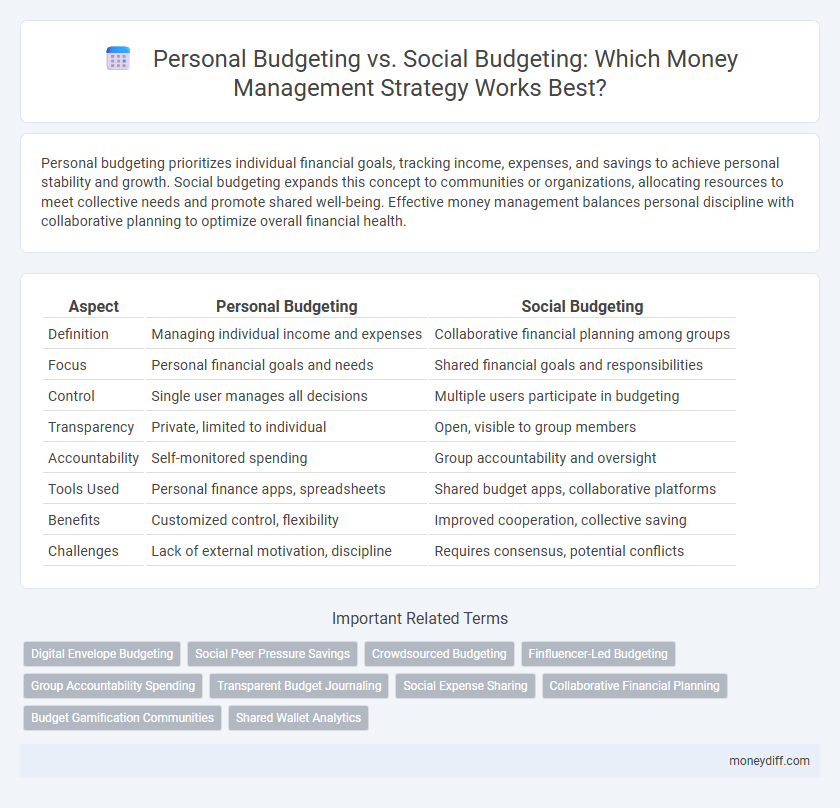
| Aspect | Personal Budgeting | Social Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing individual income and expenses | Collaborative financial planning among groups |
| Focus | Personal financial goals and needs | Shared financial goals and responsibilities |
| Control | Single user manages all decisions | Multiple users participate in budgeting |
| Transparency | Private, limited to individual | Open, visible to group members |
| Accountability | Self-monitored spending | Group accountability and oversight |
| Tools Used | Personal finance apps, spreadsheets | Shared budget apps, collaborative platforms |
| Benefits | Customized control, flexibility | Improved cooperation, collective saving |
| Challenges | Lack of external motivation, discipline | Requires consensus, potential conflicts |
Understanding Personal Budgeting
Personal budgeting involves tracking individual income and expenses to allocate funds effectively for necessities, savings, and discretionary spending. It emphasizes setting financial goals, monitoring spending habits, and adjusting expenses to maintain fiscal responsibility. Mastering personal budgeting enhances money management skills and promotes long-term financial stability.
Exploring Social Budgeting Concepts
Social budgeting involves collaboratively managing finances within a community or group, promoting transparency and shared financial goals. Unlike personal budgeting, which focuses on individual income and expenses, social budgeting leverages collective pooling of resources to prioritize mutual benefits such as community projects or social welfare. Data shows that social budgeting enhances financial accountability and supports sustainable development by aligning budgets with communal needs and values.
Key Differences Between Personal and Social Budgeting
Personal budgeting centers on managing individual or household income and expenses to achieve financial goals, emphasizing personal savings, debt repayment, and discretionary spending control. Social budgeting involves allocating resources within communities or organizations, focusing on collective needs, public welfare, and equitable distribution of funds. Key differences include the scope of financial responsibility, with personal budgeting targeting individual priorities and social budgeting addressing broader societal objectives and shared resource management.
Benefits of Personal Budgeting
Personal budgeting enhances financial control by allowing individuals to track income and expenses, which prevents overspending and promotes savings growth. It enables tailored goal setting, helping users prioritize debt repayment, emergency funds, or investment opportunities with clear visibility on funds allocation. This method improves financial awareness and discipline, fostering long-term fiscal stability and reducing stress related to money management.
Advantages of Social Budgeting for Money Management
Social budgeting enhances money management by promoting transparency and collective responsibility, leading to more equitable resource allocation. It facilitates collaborative decision-making, which can improve accountability and reduce individual financial stress. This approach leverages shared insights and diverse perspectives, optimizing budget outcomes and fostering community support.
Risks and Challenges of Each Budgeting Approach
Personal budgeting faces risks such as unpredictable individual income fluctuations, overspending due to emotional decisions, and lack of financial literacy leading to poor money management. Social budgeting encounters challenges including conflicting priorities among group members, difficulty in reaching consensus on expenditure allocation, and potential misuse of shared funds. Both approaches require disciplined monitoring to mitigate risks associated with mismanagement and financial instability.
Impact on Financial Goals and Priorities
Personal budgeting allows individuals to tailor spending and saving habits directly to their unique financial goals, ensuring immediate priorities like debt repayment or emergency funds receive focused attention. Social budgeting, often applied in communities or organizations, prioritizes collective needs and distributes resources to benefit the group, potentially diluting individual financial objectives but fostering shared economic stability. The impact on financial goals varies as personal budgeting drives precise individual progress, while social budgeting promotes broad-based financial health and social welfare.
Tools and Apps for Personal vs Social Budgeting
Personal budgeting tools like YNAB and Mint offer features tailored to individual expense tracking, goal setting, and financial forecasting, enhancing user control over private finances. In contrast, social budgeting apps such as Splitwise and Honeydue facilitate shared expense management among groups or couples, promoting transparency and collaborative decision-making in collective money management. The integration of real-time notifications and flexible payment options in social budgeting tools supports effective communication and accountability within shared financial responsibilities.
Real-Life Examples: Success Stories
Real-life success stories highlight how personal budgeting empowers individuals to achieve financial goals such as debt reduction and emergency fund growth, as seen in cases where disciplined monthly tracking increased savings by 30%. Social budgeting initiatives, like community-based cooperative funds, demonstrate effective collective money management by enabling groups to pool resources for shared projects, resulting in improved local infrastructure and economic resilience. These examples underscore that both personal and social budgeting models enhance financial stability through tailored approaches to resource allocation and accountability.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Strategy for You
Choosing the right budgeting strategy depends on your financial goals and lifestyle; personal budgeting offers tailored control over individual expenses and savings, while social budgeting emphasizes shared financial responsibilities within families or groups. Personal budgeting leverages tools like expense tracking apps and savings plans for customized money management, whereas social budgeting requires clear communication and agreed-upon financial priorities among members. Evaluating your spending habits, income sources, and financial commitments helps determine whether a solo or collective approach best enhances your money management efficiency and financial stability.
Related Important Terms
Digital Envelope Budgeting
Digital Envelope Budgeting enhances personal budgeting by allowing individuals to allocate funds into virtual categories, improving spending discipline and financial control. In contrast, social budgeting leverages shared financial goals within groups, facilitating collaborative money management while maintaining transparency through digital tools.
Social Peer Pressure Savings
Social budgeting leverages peer pressure by encouraging individuals to save through group commitments and shared financial goals, increasing accountability and motivation. Personal budgeting focuses on individual preferences and goals but may lack the external reinforcement found in social savings environments that drive consistent money management behavior.
Crowdsourced Budgeting
Crowdsourced budgeting leverages collective input from multiple individuals to prioritize expenditures and allocate resources more effectively than traditional personal budgeting, which relies on individual decision-making. By integrating diverse financial perspectives, crowdsourced budgeting enhances transparency, accountability, and responsiveness in managing shared funds within communities or organizations.
Finfluencer-Led Budgeting
Finfluencer-led budgeting leverages social media experts to provide personalized money management advice, blending individual financial goals with community-driven insights. This approach enhances personal budgeting by integrating social influence dynamics, fostering accountability, and promoting smarter spending habits through collective financial literacy.
Group Accountability Spending
Personal budgeting allows individuals to track and control their own expenses for financial independence, while social budgeting emphasizes group accountability, promoting shared financial goals and transparent spending among members. Group accountability spending fosters collective responsibility, reduces impulsive purchases, and enhances overall money management efficiency within social or familial settings.
Transparent Budget Journaling
Transparent budget journaling enhances personal budgeting by providing clear, itemized records of income and expenses, fostering accountability and informed decision-making. In social budgeting, transparent journaling facilitates collective financial management by ensuring all participants have access to shared budget information, promoting trust and collaboration.
Social Expense Sharing
Social expense sharing in budgeting enables groups to pool resources, track collective spending, and allocate costs fairly, enhancing transparency and reducing individual financial burdens. This collaborative approach optimizes money management by simplifying expense reconciliation within households, roommates, or communities.
Collaborative Financial Planning
Collaborative financial planning enhances money management by integrating personal budgeting with social budgeting frameworks, enabling individuals to pool resources, set shared financial goals, and track collective expenditures efficiently. This approach leverages group dynamics and transparent communication to optimize savings, debt management, and investment strategies within families, communities, or organizations.
Budget Gamification Communities
Budget gamification communities enhance personal budgeting by incorporating social elements that boost motivation and accountability through shared goals, challenges, and rewards. These platforms leverage collective engagement to improve money management habits, making social budgeting a dynamic complement to individual financial planning.
Shared Wallet Analytics
Personal budgeting centers on managing individual income and expenses, optimizing financial goals through detailed tracking and categorization, while social budgeting leverages Shared Wallet Analytics to provide collective insights, enhancing transparency and collaborative decision-making among group members. Shared Wallet Analytics aggregates transaction data, monitors spending patterns, and identifies common financial priorities, enabling optimized resource allocation and improved accountability within communal money management systems.
Personal Budgeting vs Social Budgeting for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com