Fixed budgets provide a set financial plan for a specific period, offering stability and clear targets but limited flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. Rolling budgets are continuously updated, allowing forecasts to reflect the latest data and trends, enhancing responsiveness and accuracy. Choosing between fixed and rolling budgets depends on an organization's need for stability versus adaptability in financial planning.
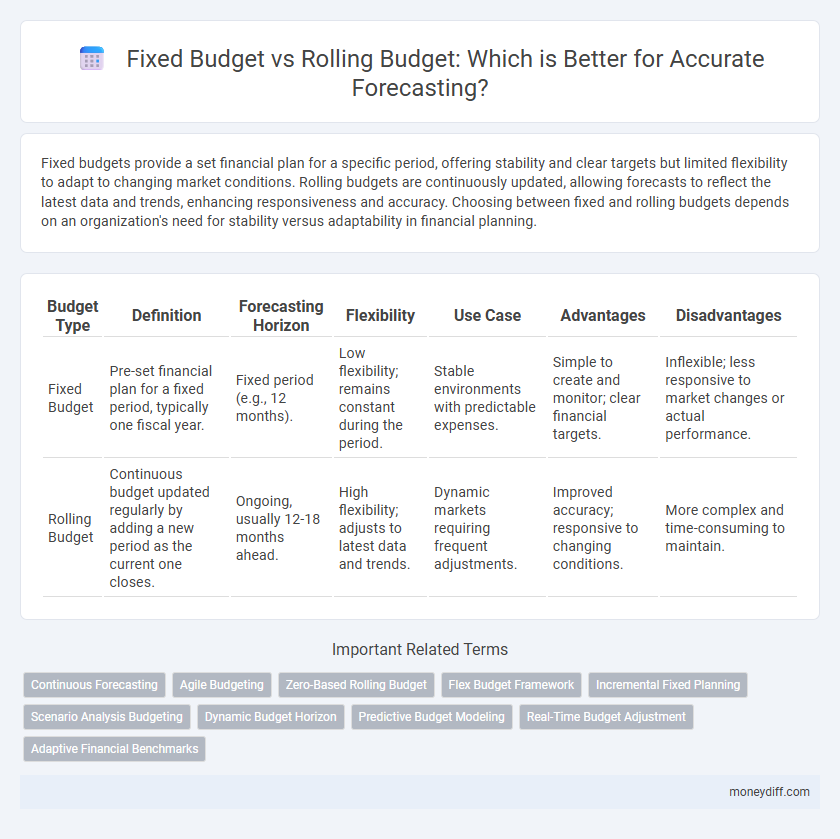
Table of Comparison
| Budget Type | Definition | Forecasting Horizon | Flexibility | Use Case | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Budget | Pre-set financial plan for a fixed period, typically one fiscal year. | Fixed period (e.g., 12 months). | Low flexibility; remains constant during the period. | Stable environments with predictable expenses. | Simple to create and monitor; clear financial targets. | Inflexible; less responsive to market changes or actual performance. |
| Rolling Budget | Continuous budget updated regularly by adding a new period as the current one closes. | Ongoing, usually 12-18 months ahead. | High flexibility; adjusts to latest data and trends. | Dynamic markets requiring frequent adjustments. | Improved accuracy; responsive to changing conditions. | More complex and time-consuming to maintain. |
Introduction to Budgeting Approaches
Fixed budgets establish a predetermined allocation of resources based on historical data, providing stability but limiting flexibility in response to market changes. Rolling budgets update forecasts regularly, typically monthly or quarterly, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to evolving financial conditions. This dynamic approach enhances accuracy and responsiveness in financial planning compared to the static nature of fixed budgets.
Defining Fixed Budget: An Overview
A fixed budget sets predetermined financial limits based on projected revenues and expenses for a specific period, typically a fiscal year, providing clear benchmarks for performance evaluation. Its static nature restricts adjustments once the budget is approved, which can limit flexibility in responding to unexpected changes or opportunities. Organizations favor fixed budgets for stability and control, ensuring disciplined spending aligned with strategic objectives.
Understanding Rolling Budget Systems
Rolling budget systems continuously update financial forecasts by extending the budget period as time progresses, enhancing adaptability to changing market conditions. Unlike fixed budgets with static allocations, rolling budgets provide more accurate and timely insights for decision-making by incorporating real-time data and performance adjustments. This flexibility helps organizations maintain financial control while responding proactively to fluctuations in revenue and expenses.
Key Differences between Fixed and Rolling Budgets
Fixed budgets are static financial plans established for a specific period, typically a fiscal year, without adjustments for changes in business conditions. Rolling budgets, updated regularly--usually monthly or quarterly--incorporate recent financial data and forecasts to adapt to evolving market trends. Key differences include flexibility, with rolling budgets allowing agile response to fluctuations, whereas fixed budgets provide stable, predetermined targets.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Budget Forecasting
Fixed budgets establish a predetermined allocation of resources based on historical data and projected expenses, providing stability but limiting flexibility in responding to market changes. Rolling budgets continuously update financial plans by incorporating actual performance and new information, enhancing adaptability to evolving conditions. This dynamic approach supports more accurate forecasting and agile decision-making in uncertain business environments.
Accuracy of Forecasts: Fixed vs Rolling Budgets
Fixed budgets provide a set financial plan for a specific period, often resulting in less adaptability to market changes and potentially lower forecast accuracy. Rolling budgets continuously update projections based on actual performance and recent trends, enhancing the precision of forecasts by incorporating real-time data. Organizations using rolling budgets can better anticipate fluctuations and adjust financial plans more responsively compared to the static nature of fixed budgets.
Resource Allocation and Control Mechanisms
Fixed budgets establish predetermined resource allocation limits, ensuring strict control mechanisms but often lacking flexibility to adapt to changing business conditions. Rolling budgets update forecast allocations continuously, allowing dynamic resource reallocation and enhanced control through regular performance reviews. This adaptive approach optimizes capital utilization and mitigates risks associated with unexpected market fluctuations.
Implementation Challenges in Both Budget Types
Fixed budgets face challenges in adapting to market fluctuations, often leading to rigidity and outdated forecasts that hinder timely decision-making. Rolling budgets require continuous data updates and extensive collaboration across departments, which can strain resources and complicate implementation. Both budget types demand significant time investment and strong management commitment to maintain accuracy and relevance during forecasting.
Industry Applications: Which Budget Suits Your Business?
Fixed budgets provide stability and clear financial targets, making them ideal for industries with predictable costs such as manufacturing and utilities. Rolling budgets offer continuous updates and flexibility, suited for dynamic sectors like technology and retail that require frequent adaptations to market changes. Businesses with stable operational environments benefit from fixed budgets, while enterprises facing rapid market fluctuations gain advantages from rolling budget forecasts.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method for Effective Money Management
Fixed budgets provide a preset allocation based on historical data and expected expenses, ideal for organizations with stable financial conditions and predictable cash flows. Rolling budgets continuously update forecasts by adding a new period as the previous one concludes, enabling adaptive responses to market fluctuations and more accurate short-term planning. Selecting the right budgeting method depends on the organization's flexibility needs, financial stability, and the accuracy required for effective money management.
Related Important Terms
Continuous Forecasting
Fixed budgets provide a static financial plan based on set assumptions, limiting flexibility in adapting to market changes, while rolling budgets enable continuous forecasting by regularly updating projections to reflect real-time data and shifting business conditions. Continuous forecasting through rolling budgets enhances decision-making accuracy and resource allocation by integrating ongoing performance insights and external factors.
Agile Budgeting
Fixed budgets provide a predetermined allocation of resources based on historical data, limiting flexibility in adapting to market fluctuations. Rolling budgets enable continuous updates and revisions, supporting agile budgeting by allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing forecasts and financial conditions.
Zero-Based Rolling Budget
Zero-based rolling budgets enhance forecasting accuracy by continuously updating financial plans based on current data rather than relying on static figures from previous periods. This dynamic approach allocates resources efficiently by justifying expenses from zero each cycle, contrasting the fixed budget's rigid structure and promoting agility in financial management.
Flex Budget Framework
A Fixed Budget sets predetermined financial targets for a specific period, limiting adaptability to market changes, while a Rolling Budget continuously updates projections based on real-time data, enhancing accuracy and responsiveness. The Flex Budget Framework integrates elements from both approaches, allowing adjustments to budgetary allocations in response to actual activity levels, thereby optimizing resource management and forecasting precision.
Incremental Fixed Planning
Incremental fixed planning in budgeting involves adjusting prior budget figures by a predetermined percentage to account for expected changes, providing stability and ease of control. This method contrasts with rolling budgets, which are continuously updated to reflect real-time business conditions, making incremental fixed budgets less flexible but simpler for short-term forecasting.
Scenario Analysis Budgeting
Scenario analysis budgeting enables businesses to compare fixed budgets, which set predetermined financial constraints, against rolling budgets that continuously update forecasts based on real-time data. This approach enhances forecasting accuracy by allowing organizations to simulate multiple financial outcomes and adapt strategies proactively.
Dynamic Budget Horizon
A fixed budget establishes financial targets for a predetermined period, limiting flexibility in adjusting forecasts despite changing market conditions. Rolling budgets extend the planning horizon by continuously updating forecasts, enabling dynamic budget adjustments that enhance accuracy and responsiveness to evolving business environments.
Predictive Budget Modeling
Fixed budgets provide a static financial plan based on historical data, limiting adaptability in dynamic market conditions. Rolling budgets enhance predictive budget modeling by continuously updating forecasts with real-time data, allowing more accurate and flexible financial planning.
Real-Time Budget Adjustment
A rolling budget enables real-time budget adjustment by continuously updating forecasts based on actual performance and market conditions, providing greater flexibility and accuracy compared to fixed budgets. Fixed budgets, set for a specific period without changes, often lack responsiveness to dynamic business environments, potentially leading to outdated financial plans.
Adaptive Financial Benchmarks
Fixed budgets establish predetermined financial targets for a specific period, offering stability but limited flexibility in response to market changes. Rolling budgets continuously update financial forecasts based on real-time data, enhancing adaptive financial benchmarks and enabling more precise resource allocation.
Fixed Budget vs Rolling Budget for forecasting. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com