Performance budgets emphasize tracking resource allocation and outputs, ensuring efficiency in spending relative to planned activities. Impact budgets prioritize measuring the actual outcomes and long-term effects of expenditures on organizational goals or community well-being. Evaluating both approaches helps balance financial control with meaningful results, optimizing decision-making and resource utilization.
Table of Comparison
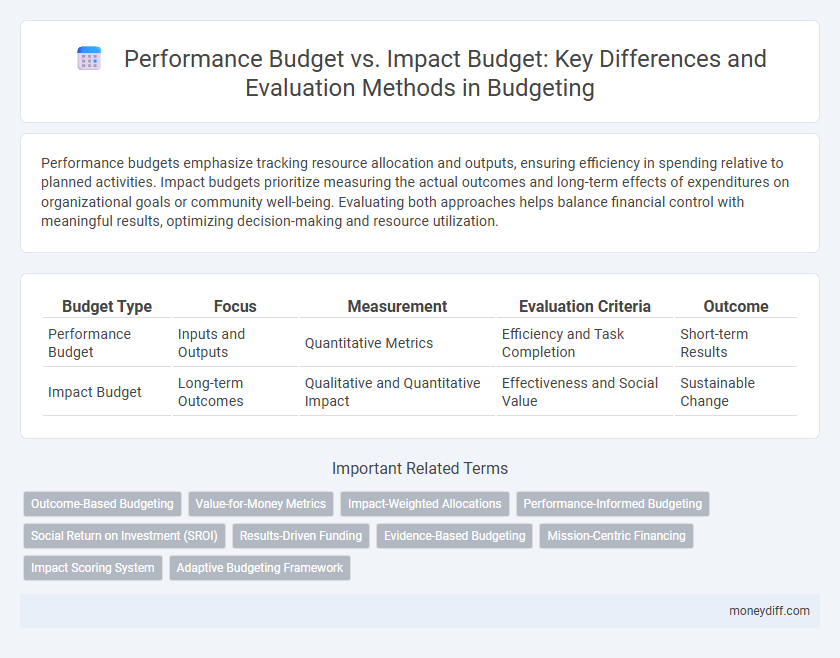
| Budget Type | Focus | Measurement | Evaluation Criteria | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Budget | Inputs and Outputs | Quantitative Metrics | Efficiency and Task Completion | Short-term Results |
| Impact Budget | Long-term Outcomes | Qualitative and Quantitative Impact | Effectiveness and Social Value | Sustainable Change |
Understanding Performance Budgeting
Performance budgeting links financial resources directly to measurable outputs, enabling organizations to track efficiency and effectiveness within specific programs. It emphasizes quantifiable results and cost control, ensuring funds are allocated based on achieving predefined performance targets. This approach contrasts with impact budgeting, which focuses on broader long-term outcomes and societal changes beyond immediate performance metrics.
Defining Impact Budgeting
Impact budgeting emphasizes allocating resources based on measurable outcomes and long-term value rather than merely tracking expenditures or short-term performance indicators. This approach integrates quantifiable social, environmental, or economic benefits into financial planning, ensuring that each dollar spent drives meaningful change aligned with strategic goals. By prioritizing impact metrics, organizations enhance transparency and accountability, facilitating more effective decision-making and resource optimization.
Key Differences: Performance vs Impact Budget
Performance budget focuses on allocating resources based on specific activities or outputs, emphasizing measurable efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Impact budget prioritizes funding according to intended long-term outcomes and overall social or environmental effects, highlighting value creation beyond immediate results. Key differences lie in performance budgeting's concentration on short-term targets versus impact budgeting's alignment with strategic goals and sustainable impact measurement.
Goals and Objectives Alignment
Performance budgets prioritize allocating resources based on measurable outputs linked directly to specific program activities, ensuring goals are quantifiable and objectives are clearly defined. Impact budgets concentrate on the broader outcomes and long-term effects of spending, aligning resources with strategic objectives that reflect the overall mission and desired societal changes. Both approaches require precise alignment of goals and objectives to optimize resource utilization and enhance evaluation accuracy.
Measuring Success: Output vs Outcome
Performance budgets prioritize quantifiable outputs such as units produced or services delivered, emphasizing efficiency and resource allocation. Impact budgets focus on outcomes, assessing the longer-term effects and changes resulting from the budget, such as improved community well-being or increased user satisfaction. Measuring success through output offers immediate, tangible metrics, while outcome measurement provides a deeper understanding of effectiveness and real-world significance.
Resource Allocation Strategies
Performance Budget prioritizes allocating resources based on measurable outputs and efficiency metrics, enabling precise tracking of expenditure against predefined targets. Impact Budget shifts focus towards long-term outcomes and societal benefits, emphasizing qualitative results over quantitative inputs for resource distribution. Strategic resource allocation requires balancing immediate performance indicators with broader impact goals to optimize both accountability and sustainable value creation.
Data and Metrics for Evaluation
Performance Budget emphasizes quantitative data and predefined metrics such as output volume, efficiency rates, and cost per unit to assess operational effectiveness. Impact Budget prioritizes qualitative and long-term outcome metrics, including social return on investment (SROI), behavioral changes, and community well-being indicators for comprehensive evaluation. Integrating both approaches enhances decision-making by balancing immediate performance data with sustainable impact measurement.
Advantages of Performance Budgeting
Performance budgeting enhances resource allocation by linking funds directly to measurable outcomes, improving accountability and transparency in public spending. This approach facilitates more accurate monitoring and evaluation of program effectiveness, enabling timely adjustments and better decision-making. By emphasizing results, performance budgeting promotes efficient use of resources and supports strategic planning aligned with organizational goals.
Benefits of Impact Budgeting
Impact budgeting enhances resource allocation by prioritizing outcomes and long-term value over mere expenditure tracking. This approach drives strategic decision-making, enabling organizations to measure and optimize the social, environmental, or economic effects of their investments. Compared to performance budgeting, impact budgeting offers deeper insights into the effectiveness of programs, fostering accountability and sustainable growth.
Choosing the Right Budget Model
Choosing the right budget model between performance budget and impact budget depends on organizational goals and evaluation criteria. Performance budgets focus on allocating resources based on measurable outputs and efficiency indicators, optimizing short-term operational effectiveness. Impact budgets prioritize long-term outcomes and social or environmental changes, aligning investments with strategic impact objectives for sustainable value creation.
Related Important Terms
Outcome-Based Budgeting
Outcome-based budgeting prioritizes allocating resources based on measurable results and strategic goals, emphasizing performance indicators over traditional expense tracking. Performance budgets focus on inputs and activities, while impact budgets evaluate long-term effects, making outcome-based budgeting essential for aligning expenditures with tangible outcomes and policy effectiveness.
Value-for-Money Metrics
Performance Budget allocates funds based on predefined outputs and efficiency metrics, emphasizing cost control and measurable deliverables, while Impact Budget prioritizes long-term value creation and social outcomes, focusing on effectiveness and return on investment. Value-for-Money Metrics integrate cost-efficiency, quality, and impact measurements to assess how well funds achieve intended results and maximize stakeholder benefits.
Impact-Weighted Allocations
Performance budget focuses on quantifiable outputs and efficiency metrics, whereas impact budget emphasizes Outcome-Based Financing through Impact-Weighted Allocations, integrating social and environmental returns into financial decision-making. Impact-Weighted Allocations prioritize value creation by assigning monetary weights to non-financial impacts, enabling organizations to better assess long-term benefits and allocate resources toward sustainable initiatives.
Performance-Informed Budgeting
Performance-Informed Budgeting allocates resources based on measurable outputs and efficiency metrics, ensuring funds directly support organizational goals and improve accountability. In contrast, Impact Budgeting prioritizes long-term outcomes and social value, focusing on the broader effects and sustainability of funded programs rather than immediate performance indicators.
Social Return on Investment (SROI)
Performance Budget allocates resources based on measurable outputs and activities, focusing on efficiency and immediate results, while Impact Budget emphasizes long-term outcomes and the broader social value created, aligning closely with Social Return on Investment (SROI) metrics. SROI quantifies the economic, social, and environmental impact, providing a comprehensive framework that links budget decisions to tangible social returns beyond traditional performance indicators.
Results-Driven Funding
Performance Budget allocates resources based on measurable outputs and efficiency metrics to ensure accountability, while Impact Budget prioritizes funding tied to long-term outcomes and societal changes, emphasizing value generation. Results-driven funding integrates both approaches by linking budgetary decisions to clear performance targets and tangible impact indicators, maximizing resource effectiveness and strategic goal attainment.
Evidence-Based Budgeting
Performance Budget allocates funds based on measurable outputs and efficiency metrics, emphasizing quantitative results to optimize resource use. Impact Budget prioritizes funding decisions driven by evidence-based outcomes and long-term societal effects, ensuring budget allocation supports meaningful change.
Mission-Centric Financing
Mission-Centric Financing prioritizes Impact Budgets by aligning resources directly with measurable outcomes and mission-driven objectives rather than solely focusing on input metrics typical of Performance Budgets. This approach enhances strategic evaluation by linking funding allocation to the tangible social or organizational impact achieved, ensuring more effective and accountable use of budgetary resources.
Impact Scoring System
Performance Budget emphasizes quantifiable output metrics such as units produced or tasks completed, whereas Impact Budget focuses on qualitative outcomes measured by an Impact Scoring System that assesses significance, reach, and long-term effects. The Impact Scoring System incorporates multi-dimensional criteria including social value, sustainability, and beneficiary feedback to provide a holistic evaluation beyond mere financial efficiency.
Adaptive Budgeting Framework
Performance Budget allocates funds based on specific output metrics to track efficiency, while Impact Budget emphasizes outcomes and long-term effects, aligning resources with strategic goals. The Adaptive Budgeting Framework integrates both approaches by continuously adjusting allocations to optimize both immediate performance and sustainable impact.
Performance Budget vs Impact Budget for evaluation. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com