Static budgeting sets a fixed financial plan based on expected revenues and expenses, providing a clear, unchanging framework for money management. Flexible budgeting adjusts allocations dynamically in response to actual financial performance, enhancing adaptability and control. Choosing between static and flexible budgeting depends on the organization's need for predictability versus responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
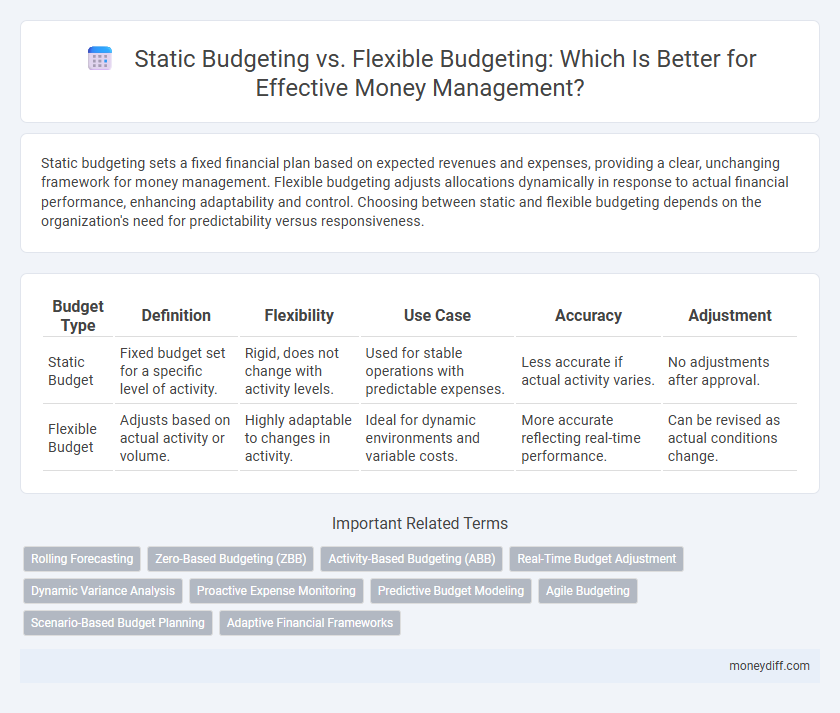
| Budget Type | Definition | Flexibility | Use Case | Accuracy | Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Budget | Fixed budget set for a specific level of activity. | Rigid, does not change with activity levels. | Used for stable operations with predictable expenses. | Less accurate if actual activity varies. | No adjustments after approval. |
| Flexible Budget | Adjusts based on actual activity or volume. | Highly adaptable to changes in activity. | Ideal for dynamic environments and variable costs. | More accurate reflecting real-time performance. | Can be revised as actual conditions change. |
Introduction to Static and Flexible Budgeting
Static budgeting allocates a fixed amount of funds based on projected revenues and expenses, providing a clear financial framework regardless of actual business activity levels. Flexible budgeting adjusts expenditure and revenue targets in response to real-time changes in operational volume, enhancing adaptability and accuracy in financial planning. Both budgeting methods offer distinct approaches to managing resources, where static budgeting emphasizes control, while flexible budgeting prioritizes responsiveness.
Defining Static Budgeting: Key Features
Static budgeting sets a fixed financial plan based on projected revenues and expenses for a specific period without adjusting for actual activity levels. Key features include predetermined budget amounts, consistency in financial targets, and ease of implementation, making it ideal for stable operations with predictable costs. Unlike flexible budgeting, it does not accommodate changes in business volume or unforeseen expenses, which can limit its responsiveness to real-time financial conditions.
Understanding Flexible Budgeting: Core Concepts
Flexible budgeting adjusts expected costs and revenues based on actual activity levels, providing a dynamic framework for money management. It enables businesses to compare real performance against variable budgeted amounts, enhancing accuracy in financial analysis. By reflecting operational changes, flexible budgeting supports more effective cost control and resource allocation than static budgeting.
Pros and Cons of Static Budgeting in Money Management
Static budgeting provides a clear, fixed financial plan that simplifies monitoring and control by setting predetermined expense and revenue targets, beneficial for organizations with stable operations. However, it lacks adaptability to fluctuations in actual activity levels, often resulting in variances that reduce its effectiveness in dynamic business environments. This rigidity can lead to inaccurate financial oversight and missed opportunities for cost optimization during periods of unexpected change.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Flexible Budgeting
Flexible budgeting adapts to varying levels of activity, providing more accurate and realistic financial control compared to static budgeting. Its main advantage is the ability to adjust expenses and revenues dynamically, allowing organizations to respond promptly to operational changes and improve cost management. However, the complexity of creating and maintaining flexible budgets can lead to increased administrative effort and potential inaccuracies if activity levels are incorrectly estimated.
Use Cases: When to Choose Static Budgeting
Static budgeting is ideal for organizations with fixed costs and predictable expenses, such as government agencies and nonprofits, where financial stability is crucial. It provides a clear, unchanging financial framework that simplifies planning and control when sales volumes or operational activities remain constant. Companies with limited variability in production or service delivery benefit from static budgets to maintain tight cost control and ensure disciplined spending.
Situations Favoring Flexible Budgeting
Flexible budgeting excels in dynamic business environments where expenses and revenues fluctuate with changes in activity levels. It allows for real-time adjustments based on actual performance, making it ideal for industries like manufacturing, retail, and hospitality that experience seasonal or unpredictable demand. This adaptability enhances accuracy in financial planning and improves cost control by aligning budgeted expenses with operational realities.
Impact on Financial Decision-Making
Static budgeting, which sets fixed financial targets, limits adaptability to changing business conditions and may lead to less accurate financial decision-making. Flexible budgeting adjusts expenses and revenues based on actual activity levels, providing a more responsive framework for financial planning and control. This dynamic approach enhances decision-making by offering real-time insights and facilitating better resource allocation under varying operational circumstances.
Case Study Comparisons: Static vs Flexible Budget Approaches
Case study comparisons reveal that static budgeting allocates fixed financial targets based on predetermined activity levels, providing simplicity but lacking adaptability to actual performance changes. Flexible budgeting, by contrast, adjusts budgeted costs according to real-time activity or sales volume, enhancing accuracy and responsiveness in financial management. Businesses using flexible budgets in dynamic environments report improved variance analysis and resource allocation compared to those relying solely on static budgets.
Selecting the Right Budgeting Method for Your Needs
Choosing between static budgeting and flexible budgeting depends on the nature of your financial activities and the level of control you require; static budgets set fixed allocations ideal for stable expenses, while flexible budgets adjust according to actual performance, accommodating variable costs. Businesses with predictable revenue streams benefit from static budgeting's simplicity, whereas those facing fluctuating market conditions gain accuracy and responsiveness through flexible budgeting. Evaluating your cash flow patterns and variability in expenses ensures the selection of a budgeting method that best supports effective money management and financial planning.
Related Important Terms
Rolling Forecasting
Static budgeting establishes fixed financial targets based on predetermined assumptions, offering limited adaptability to operational changes, while flexible budgeting adjusts expenses and revenues according to actual activity levels, enhancing accuracy in dynamic environments. Rolling forecasting continuously updates budget projections by integrating real-time financial data and market trends, enabling more responsive money management and improved resource allocation.
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB)
Static budgeting allocates fixed financial resources based on a predetermined level of activity, limiting adaptability to fluctuating business needs, while flexible budgeting adjusts expenses dynamically according to actual performance metrics. Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) enhances money management by requiring each expense to be justified from scratch, promoting cost-efficiency and eliminating redundant expenditures regardless of previous budgets.
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB)
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) allocates resources based on specific activities that drive costs, offering more precise financial control compared to static budgeting, which sets fixed allocations regardless of actual activity levels. Unlike flexible budgeting that adjusts based on volume or output, ABB targets cost drivers to optimize money management by aligning budgets directly with operational activities and business processes.
Real-Time Budget Adjustment
Static budgeting sets fixed financial targets regardless of actual activity levels, often leading to inefficiencies when business conditions change, while flexible budgeting allows real-time budget adjustments by aligning expenses with actual operational performance. This dynamic approach improves financial control and responsiveness, enabling more accurate forecasting and resource allocation in fluctuating economic environments.
Dynamic Variance Analysis
Static budgeting sets fixed financial targets based on projected activity levels, limiting responsiveness to actual performance, whereas flexible budgeting adjusts budgets according to real-time activity, enabling more accurate dynamic variance analysis. Dynamic variance analysis leverages flexible budgets to identify and explain variances caused by changes in volume, price, and efficiency, improving money management decisions and resource allocation.
Proactive Expense Monitoring
Static budgeting sets fixed expense limits based on forecasted activity, offering clear benchmarks but limited adaptability to actual financial fluctuations. Flexible budgeting adjusts expenses in real-time according to revenue changes, enabling more proactive expense monitoring and responsive money management.
Predictive Budget Modeling
Static budgeting sets fixed financial targets based on initial estimates, offering limited adaptability to changing conditions, while flexible budgeting adjusts allocations dynamically according to actual activity levels, enhancing predictive accuracy for cash flow management. Predictive budget modeling leveraging flexible budgets enables businesses to forecast expenses and revenues more precisely, improving decision-making and resource allocation under varying operational scenarios.
Agile Budgeting
Agile budgeting prioritizes flexibility by adjusting financial plans based on real-time data, contrasting with static budgeting's fixed allocations that may not respond to changing business conditions. This approach enhances money management by allowing organizations to reallocate resources dynamically, improving responsiveness and optimizing financial performance.
Scenario-Based Budget Planning
Static budgeting uses a fixed projection of expenses and revenues based on a single scenario, limiting adaptability when actual business conditions vary significantly. Flexible budgeting adjusts financial plans according to real-time activity levels or different scenarios, enhancing accuracy in money management and decision-making under varying operational conditions.
Adaptive Financial Frameworks
Static budgeting sets fixed financial targets based on predetermined assumptions, offering limited adaptability to fluctuating business conditions, whereas flexible budgeting adjusts expense estimates and revenue projections in real time to align with actual activity levels. Adaptive financial frameworks leverage flexible budgeting to enhance precision in money management, enabling organizations to dynamically allocate resources and optimize cash flow under varying economic scenarios.
Static Budgeting vs Flexible Budgeting for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com