A baseline budget establishes a fixed framework for tracking income and expenses, providing a clear financial plan that enhances control over spending. In contrast, a no-budget budget approach emphasizes flexibility by monitoring cash flow without strict allocations, promoting adaptability to changing financial circumstances. Choosing between these methods depends on personal discipline and preference for structured guidance versus dynamic spending.
Table of Comparison
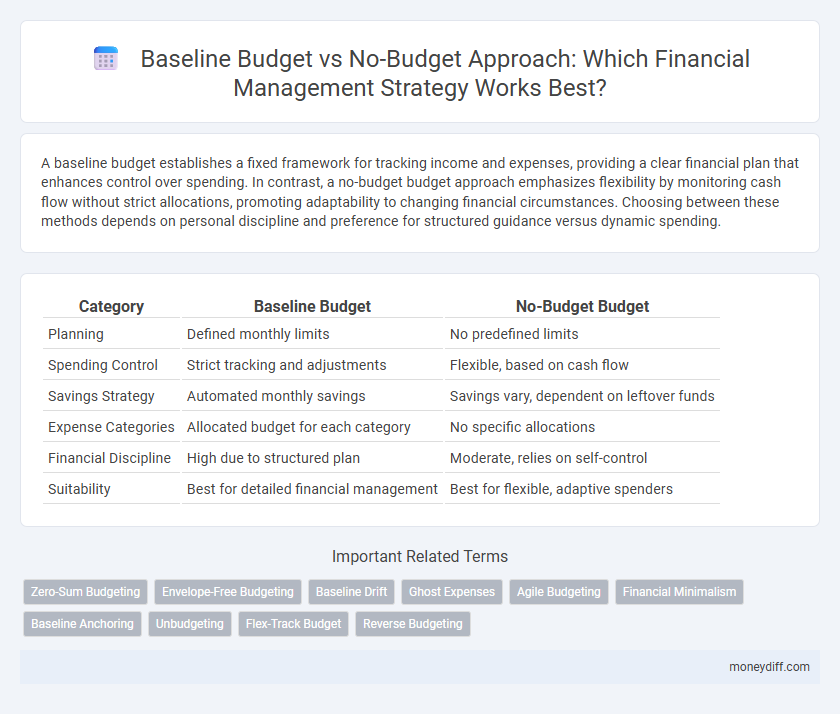
| Category | Baseline Budget | No-Budget Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Defined monthly limits | No predefined limits |
| Spending Control | Strict tracking and adjustments | Flexible, based on cash flow |
| Savings Strategy | Automated monthly savings | Savings vary, dependent on leftover funds |
| Expense Categories | Allocated budget for each category | No specific allocations |
| Financial Discipline | High due to structured plan | Moderate, relies on self-control |
| Suitability | Best for detailed financial management | Best for flexible, adaptive spenders |
Understanding Baseline Budgeting
Baseline budgeting involves using the previous period's expenditures as a reference point to allocate funds for the upcoming budget cycle, ensuring consistency and control over spending. This approach helps organizations maintain financial stability by adjusting only for predictable changes like inflation or contractual obligations. It contrasts with zero-based budgeting, which requires justifying all expenses without relying on past budgets, promoting a more flexible but time-intensive financial management process.
What is a No-Budget Budget Approach?
A No-Budget Budget approach simplifies financial management by eliminating traditional categories and spending limits, allowing individuals to allocate funds based solely on actual income and expenses. This method contrasts with baseline budgeting, which sets fixed amounts for different categories and tracks variance against these targets. By focusing on real-time cash flow rather than preset allocations, the No-Budget Budget approach encourages flexible spending and prioritizes debt repayment and savings without intensive tracking.
Key Differences Between Baseline and No-Budget Budgets
Baseline budgets establish a fixed financial plan based on historical data to set spending limits and targets, promoting stability and predictability. No-budget budgets eliminate formal budgeting constraints, encouraging flexibility and real-time adjustment of expenses according to current needs. Key differences include the structured control of baseline budgets versus the adaptive freedom in no-budget approaches, impacting financial discipline and responsiveness.
Advantages of a Baseline Budget
A baseline budget provides a clear financial framework by establishing fixed expenditure limits based on historical data, ensuring disciplined spending and better resource allocation. It enables organizations to forecast cash flows accurately, reduce financial risks, and maintain fiscal stability through consistent monitoring. By using a baseline budget, decision-makers can identify variances promptly and implement corrective measures to optimize overall financial performance.
Pros and Cons of the No-Budget Budget Method
The No-Budget Budget method simplifies financial management by eliminating rigid budget categories, allowing greater flexibility and reducing time spent on tracking expenses. It promotes natural spending habits that can prevent frustration associated with strict budget limits but may lead to overspending without clear spending boundaries. This approach works best for those with steady incomes and strong self-discipline, while it poses risks for individuals needing concrete guidelines to control expenses effectively.
Suitability: Who Should Use Each Method?
Baseline budgets suit organizations with stable revenue streams and predictable expenses, providing a clear financial framework for consistent operations. No-budget budgets are ideal for startups or highly flexible businesses needing adaptive financial strategies without rigid allocations. Companies should assess their operational predictability and financial stability to determine the appropriate budgeting approach for effective management.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a Baseline Budget
Creating a baseline budget involves identifying all sources of income and recording fixed and variable expenses to establish a clear financial snapshot. Track spending patterns over a month to differentiate essential costs from discretionary expenses, providing accuracy in allocation. This method contrasts with a no-budget budget that relies on flexible spending without predefined limits, leading to less financial control and predictability.
How to Implement a No-Budget Budget in Real Life
Implementing a no-budget budget involves tracking income and expenses without predefined categories, emphasizing real-time spending awareness through tools like expense tracking apps and bank alerts. Prioritize saving any unspent income at the end of the month, adjusting spending habits naturally rather than enforcing strict limits. Consistent monitoring and mindful spending decisions foster financial control without the rigidity of traditional baseline budgets.
Tracking Progress: Measuring Financial Success
Tracking progress in a baseline budget involves comparing actual expenses against predetermined financial targets, enabling precise measurement of financial success and early identification of deviations. In contrast, a no-budget budget relies on monitoring cash flow and spending patterns without fixed categories, emphasizing flexibility but requiring frequent review to gauge financial health effectively. Utilizing detailed financial reports and key performance indicators (KPIs) enhances the accuracy of progress tracking in both budgeting approaches.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Strategy for Your Goals
Choosing the right budgeting strategy depends on your financial goals and spending habits. A baseline budget allocates fixed amounts based on historical expenses, providing stability and predictability, while a no-budget budget promotes flexibility by focusing on saving a predetermined percentage rather than tracking every expense. Understanding whether you prioritize control or adaptability will help select the most effective approach for managing your finances.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Sum Budgeting
Baseline budgets allocate fixed amounts based on historical spending patterns to maintain financial stability, while no-budget budgets, such as zero-sum budgeting, assign every dollar a specific purpose ensuring income minus expenses equals zero for precise cash flow management. Zero-sum budgeting enhances accountability by requiring detailed tracking of all income and expenses, minimizing overspending and maximizing savings potential.
Envelope-Free Budgeting
Baseline budgets establish fixed spending limits based on historical expenses to control costs and maintain financial goals, while no-budget budgets, such as envelope-free budgeting, allocate funds dynamically without strict categories to foster flexibility and encourage mindful spending. Envelope-free budgeting leverages real-time tracking and adaptable fund allocation, reducing rigid constraints and promoting financial discipline through behavioral awareness rather than fixed spending envelopes.
Baseline Drift
Baseline budget establishes fixed financial parameters critical for tracking expenditures, yet is susceptible to baseline drift, where unrealistic targets gradually shift, undermining budget accuracy over time. No-budget budget strategies promote flexibility by avoiding preset limits, reducing risks of baseline drift but require vigilant real-time financial monitoring to prevent overspending.
Ghost Expenses
Baseline budget tracks fixed and variable costs to provide a clear financial framework, helping identify ghost expenses--unnoticed or recurring charges that drain resources. No-budget budget approach relies on real-time spending awareness, minimizing ghost expenses by promoting mindful transaction monitoring without preset spending limits.
Agile Budgeting
Baseline Budget establishes a fixed financial framework based on historical data, providing clear cost expectations and control, whereas No-Budget Budget in Agile Budgeting embraces flexibility, allowing iterative adjustments aligned with evolving project priorities and value delivery. Agile Budgeting optimizes resource allocation and responsiveness, reducing waste and enabling adaptive financial planning in dynamic business environments.
Financial Minimalism
Baseline Budget establishes fixed spending limits based on essential expenses, promoting disciplined financial minimalism by preventing unnecessary expenditures. No-Budget Budget relies on tracking income and spending without preset limits, encouraging mindful money management through simplicity and adaptability.
Baseline Anchoring
Baseline Budget anchoring establishes a fixed financial reference point, ensuring consistent expenditure tracking and preventing overspending by aligning future budgets with historical spending patterns. This method contrasts with No-Budget Budget approaches, which lack predefined limits and rely on flexible, less structured financial management, often leading to unpredictable cash flow and resource allocation.
Unbudgeting
Baseline budgets establish fixed financial targets based on historical data, while no-budget budgets embrace unbudgeting by focusing on dynamic cash flow and prioritizing actual expenses over rigid allocations. This lean approach enhances financial agility and responsiveness, reducing the constraints of traditional budgetary controls.
Flex-Track Budget
A Flex-Track Budget integrates elements of both Baseline Budget and No-Budget Budget approaches by setting an initial financial plan while allowing real-time adjustments based on actual spending and income fluctuations. This adaptive budgeting method enhances cash flow management and financial responsiveness, optimizing resource allocation without the rigidity of a fixed baseline or the unpredictability of a no-budget system.
Reverse Budgeting
Reverse budgeting prioritizes saving and spending goals by allocating funds only after setting aside a predetermined savings amount, contrasting with baseline budgeting that starts with fixed expense allocations. This approach enhances financial discipline and flexibility by ensuring priorities like emergency funds or investments are met before discretionary spending.
Baseline Budget vs No-Budget Budget for managing finances. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com