A fixed budget sets predetermined spending limits based on past expenses, providing clear boundaries but often lacking flexibility to adapt to changing financial goals. In contrast, a value-based budget aligns spending with personal priorities and values, enabling more intentional allocation of funds toward what truly matters. Choosing between these approaches depends on individual preferences for structure versus adaptability in managing personal finances.
Table of Comparison
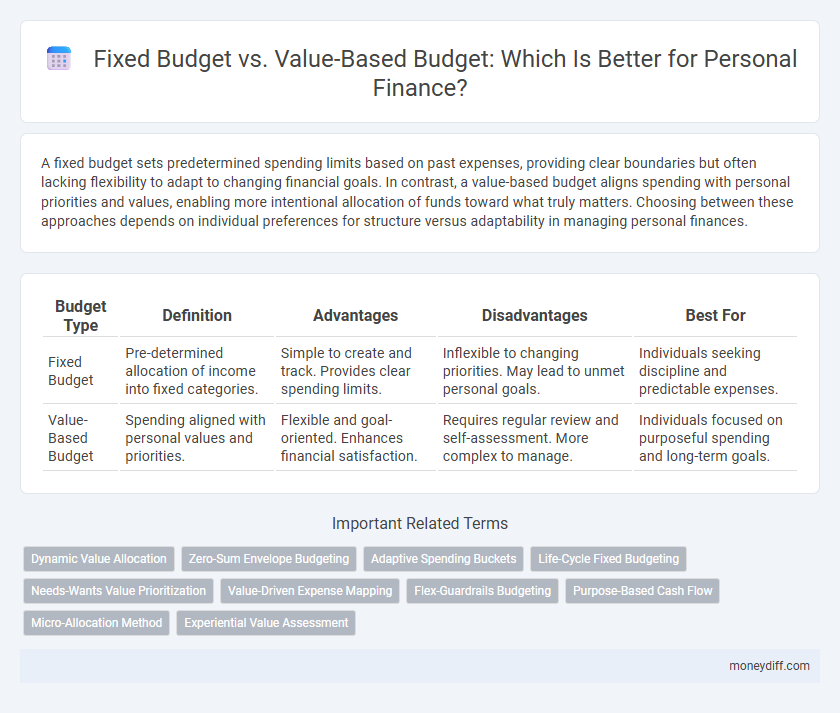
| Budget Type | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Budget | Pre-determined allocation of income into fixed categories. | Simple to create and track. Provides clear spending limits. | Inflexible to changing priorities. May lead to unmet personal goals. | Individuals seeking discipline and predictable expenses. |
| Value-Based Budget | Spending aligned with personal values and priorities. | Flexible and goal-oriented. Enhances financial satisfaction. | Requires regular review and self-assessment. More complex to manage. | Individuals focused on purposeful spending and long-term goals. |
Understanding Fixed Budgeting in Personal Finance
Fixed budgeting in personal finance involves setting a predetermined spending limit for various expense categories, ensuring consistent control over monthly expenditures. This approach simplifies tracking by allocating exact amounts for necessities like rent, groceries, and utilities, minimizing the risk of overspending. While rigid, fixed budgets provide clear financial boundaries, making them ideal for individuals seeking stability and straightforward expense management.
What Is Value-Based Budgeting?
Value-based budgeting prioritizes expenses based on personal values and long-term goals rather than fixed spending limits, aligning financial decisions with what matters most to the individual. Unlike fixed budgets that allocate set amounts to categories, value-based budgeting adapts spending dynamically to support priorities such as experiences, savings, or debt reduction. This approach enhances motivation and flexibility, making personal finance management more meaningful and effective.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Value-Based Budgets
Fixed budgets allocate a set amount of money to each category regardless of changing priorities, ensuring strict spending limits and predictability. Value-based budgets prioritize spending based on personal values and goals, allowing for flexibility and alignment with long-term objectives. The key difference lies in fixed budgets emphasizing control and consistency, while value-based budgets focus on adaptability and purposeful financial decisions.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Budgets
Fixed budgets provide clear spending limits, helping individuals maintain strict control over expenses and avoid overspending. However, they can lack flexibility, making it difficult to adjust for unexpected costs or changes in income. This rigidity may lead to frustration and potential failure to meet financial goals if circumstances evolve.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Value-Based Budgets
Value-based budgets prioritize spending aligned with personal values, enhancing financial satisfaction and motivation to save by focusing on meaningful expenditures. This approach can increase flexibility and adaptability, allowing adjustments based on changing priorities, unlike rigid fixed budgets that might cause frustration. However, value-based budgets may lead to inconsistent saving patterns and require regular evaluation to maintain financial discipline and long-term goals.
Suitability: Who Should Use Fixed Budgets?
Fixed budgets suit individuals with predictable income and expenses seeking strict financial control, such as salaried employees or retirees. This budgeting approach provides clear spending limits, ideal for those who benefit from structured financial discipline and minimal variability. People aiming for consistent savings or debt reduction find fixed budgets particularly effective for maintaining stability and accountability.
Is Value-Based Budgeting Right for You?
Value-based budgeting prioritizes spending aligned with personal values and long-term goals rather than strictly adhering to fixed limits, promoting financial flexibility and purpose-driven decisions. This approach suits individuals seeking to optimize their money for meaningful experiences and priorities, yet it requires discipline to avoid overspending without rigid caps. Assessing your financial habits and goals helps determine if value-based budgeting supports your path to both satisfaction and fiscal responsibility.
How to Transition from Fixed to Value-Based Budgeting
Transitioning from a fixed budget to a value-based budget requires identifying core personal values and aligning spending habits accordingly. Begin by analyzing current fixed expenses, then prioritize expenditures that contribute to those values while cutting or reallocating funds from less meaningful categories. Tracking progress through budgeting apps or spreadsheets helps maintain focus on value-driven financial decisions and promotes intentional money management.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a Budgeting Method
Choosing between a fixed budget and a value-based budget often leads to common mistakes such as underestimating essential expenses in a fixed budget or failing to align spending with personal priorities in a value-based budget. Many individuals overlook the importance of flexibility, causing rigid fixed budgets to create stress when unexpected costs arise. Misjudging personal values can result in misallocated funds, reducing savings efficiency and financial satisfaction.
Which Budgeting Method Maximizes Financial Goals?
A value-based budget maximizes financial goals by aligning expenses with core personal values and long-term priorities, ensuring money is spent meaningfully rather than just tracking fixed limits. Fixed budgets impose strict spending caps on categories, providing structure but often lacking flexibility to adapt to changing needs or opportunities for growth. Prioritizing value-based budgeting leads to improved financial outcomes by focusing resources on what matters most, promoting savings, investments, and overall financial well-being.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Value Allocation
Fixed budgets allocate predetermined amounts to expenses regardless of changing needs, often limiting flexibility and responsiveness. Value-based budgets prioritize dynamic value allocation by adjusting spending according to evolving financial goals and priorities, enhancing personal finance adaptability.
Zero-Sum Envelope Budgeting
Zero-sum envelope budgeting allocates every dollar of income to specific categories, ensuring expenses do not exceed income, which contrasts fixed budgets that set static limits regardless of changing priorities; value-based budgets prioritize spending aligned with personal goals and values rather than rigid categories. This adaptive approach enhances financial discipline by combining the accountability of fixed budgets with the flexibility of value-driven spending, optimizing both control and motivation in personal finance management.
Adaptive Spending Buckets
Fixed Budget allocates set amounts to predefined spending buckets, limiting flexibility in adjusting to fluctuating income or expenses, while Value-Based Budget emphasizes adaptive spending buckets that prioritize essential values and financial goals, allowing dynamic reallocation of funds for greater personal financial control and responsiveness. Embracing adaptive spending buckets enhances financial resilience by continuously aligning expenditures with changing priorities and real-time needs rather than rigid limits.
Life-Cycle Fixed Budgeting
Life-cycle fixed budgeting allocates financial resources based on anticipated income and expenses across different life stages, ensuring stability during fluctuating earning periods. Unlike value-based budgeting which prioritizes spending aligned with personal goals and values, life-cycle fixed budgets emphasize disciplined saving and expenditure patterns to navigate long-term financial obligations effectively.
Needs-Wants Value Prioritization
A fixed budget allocates specific amounts to predefined categories, often limiting flexibility in adjusting for changing priorities, whereas a value-based budget prioritizes spending based on the personal importance of needs and wants, maximizing financial satisfaction. By focusing on value prioritization, individuals can optimize their personal finance strategy to align expenditures with their core values and long-term goals.
Value-Driven Expense Mapping
Value-driven expense mapping in personal finance emphasizes allocating funds based on prioritized goals and measurable outcomes rather than rigid spending limits typical of fixed budgets. This approach enhances financial efficiency by aligning expenditures with individual values, promoting intentional spending that maximizes overall satisfaction and long-term wealth building.
Flex-Guardrails Budgeting
Flex-Guardrails Budgeting combines the structure of a fixed budget with the adaptability of value-based budgeting, allowing for prioritized spending on essential categories while adjusting discretionary expenses based on real-time needs and values. This approach enhances financial control and flexibility, promoting sustainable personal finance management by aligning expenditures with long-term goals and changing priorities.
Purpose-Based Cash Flow
A Fixed Budget allocates a predetermined amount to expenses regardless of changing financial goals, while a Value-Based Budget prioritizes purpose-driven cash flow by aligning expenditures with personal values and long-term objectives. This approach enhances financial flexibility and motivation, ensuring money is spent on areas that directly contribute to individual priorities and overall life satisfaction.
Micro-Allocation Method
Fixed budgets allocate set amounts to each category, providing strict financial boundaries, while value-based budgets prioritize spending aligned with personal values and goals, promoting intentional micro-allocation. Micro-allocation in value-based budgeting enhances financial flexibility by directing funds to high-priority areas, improving overall money management effectiveness.
Experiential Value Assessment
Fixed budgets allocate a set amount to each expense category, providing clear spending limits but often lacking flexibility to capture the true experiential value of purchases. Value-based budgets prioritize spending based on the personal satisfaction and long-term benefits derived from each expense, enabling a more meaningful assessment and optimization of financial resources.
Fixed Budget vs Value-Based Budget for Personal Finance Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com