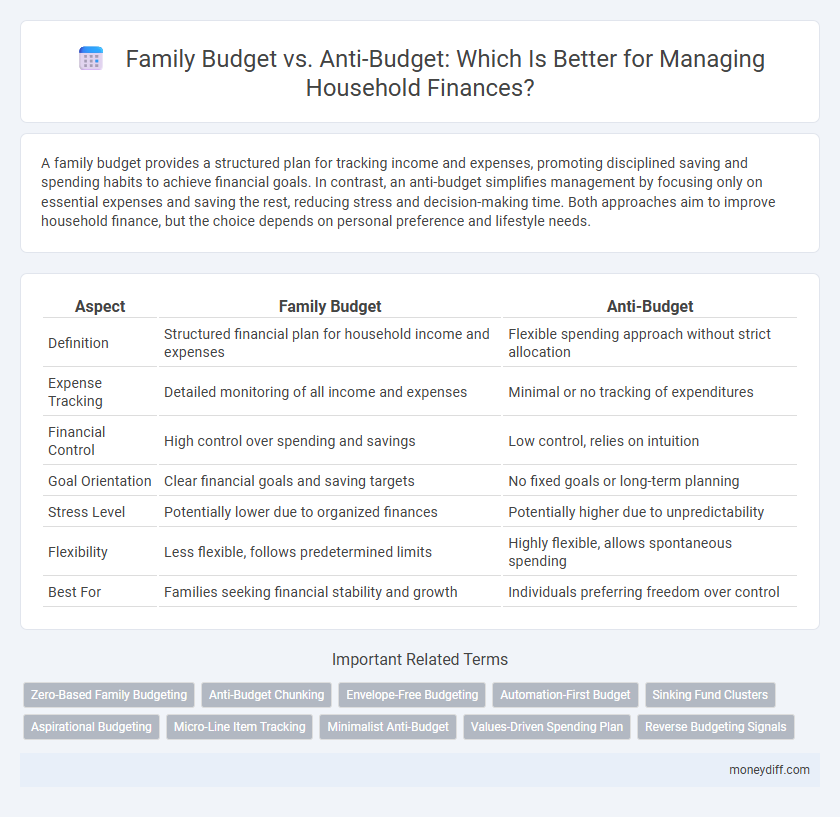
A family budget provides a structured plan for tracking income and expenses, promoting disciplined saving and spending habits to achieve financial goals. In contrast, an anti-budget simplifies management by focusing only on essential expenses and saving the rest, reducing stress and decision-making time. Both approaches aim to improve household finance, but the choice depends on personal preference and lifestyle needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Family Budget | Anti-Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured financial plan for household income and expenses | Flexible spending approach without strict allocation |
| Expense Tracking | Detailed monitoring of all income and expenses | Minimal or no tracking of expenditures |
| Financial Control | High control over spending and savings | Low control, relies on intuition |
| Goal Orientation | Clear financial goals and saving targets | No fixed goals or long-term planning |
| Stress Level | Potentially lower due to organized finances | Potentially higher due to unpredictability |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, follows predetermined limits | Highly flexible, allows spontaneous spending |
| Best For | Families seeking financial stability and growth | Individuals preferring freedom over control |
Understanding Family Budgeting: Key Principles
Family budgeting involves creating a structured plan that allocates income toward essential expenses, savings, and discretionary spending, ensuring financial stability and goal achievement. Key principles include tracking all sources of income, categorizing fixed and variable expenses, and regularly reviewing spending patterns to adjust the budget as needed. This disciplined approach helps households manage cash flow effectively and avoid debt accumulation.
What Is the Anti-Budget Method?
The Anti-Budget method simplifies household finance by focusing solely on savings and essential expenses, ignoring detailed tracking of every dollar spent. This approach allocates a fixed percentage of income directly to savings or investment first, allowing the remaining funds for flexible spending without strict limits. By prioritizing savings upfront, the Anti-Budget helps families avoid financial stress commonly associated with rigid budgets, improving long-term financial stability.
Comparing Family Budget vs Anti-Budget Approaches
Family budget methods emphasize detailed tracking of income and expenses to allocate funds across categories, promoting financial discipline and goal achievement. In contrast, the anti-budget simplifies management by prioritizing essential savings and fixed expenses first, allowing flexible spending with remaining funds, reducing the need for constant monitoring. Comparing these approaches highlights that while family budgets offer structured control, the anti-budget provides stress-free adaptability suited for households valuing simplicity.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Family Budgeting
Traditional family budgeting offers clear financial guidelines and helps control spending by allocating fixed amounts to different expense categories, promoting disciplined money management. However, it can be rigid, limiting flexibility to adapt to unexpected expenses or fluctuating incomes, potentially causing stress or frustration. This approach may also overlook personal spending habits and emotional factors, reducing effectiveness in achieving long-term financial goals.
Advantages and Drawbacks of the Anti-Budget Strategy
The Anti-Budget strategy simplifies household finance by dividing income into fixed spending, savings, and bills categories, reducing the need for detailed tracking compared to a traditional Family Budget. Its advantages include less time spent on managing expenses and a focus on saving first, which can improve financial discipline. However, drawbacks involve limited visibility into discretionary spending habits and potential overspending if categories are not well balanced, making it less effective for those needing granular control.
Which Method Fits Your Household: Key Considerations
Choosing between a family budget and an anti-budget depends on spending habits, financial goals, and discipline levels. A family budget requires detailed tracking and planning to allocate expenses effectively, ideal for households needing structure and control. The anti-budget suits those with stable income and expenses who prefer simplicity by saving first and spending freely within remaining funds.
Impact on Savings and Debt Reduction
A family budget provides a structured approach to managing income and expenses, which enhances savings growth and accelerates debt reduction by identifying spending patterns and setting clear financial goals. In contrast, an anti-budget focuses on financial freedom by prioritizing debt payoff through methods like the debt snowball or avalanche, often leading to quicker elimination of liabilities but less emphasis on detailed savings plans. Both methods impact household finance differently; the family budget fosters consistent savings accumulation while the anti-budget drives aggressive debt repayment strategies.
Managing Unexpected Expenses Effectively
A family budget allocates specific amounts for essential categories, enabling better control over monthly expenses but often struggles with unexpected costs like medical emergencies or urgent repairs. An anti-budget approach, prioritizing flexible savings and variable spending, allows households to manage unforeseen expenses more effectively by distributing leftover funds into adjustable categories. Adopting a mixed strategy that combines structured allocation with flexible saving can enhance financial resilience and reduce stress during unpredictable financial events.
Tools and Apps for Both Budgeting Styles
Family budget tools like YNAB (You Need A Budget) and EveryDollar offer structured frameworks emphasizing expense tracking and financial goal setting, ideal for collaborative household management. Anti-budget apps, such as Simple and Qapital, promote automated saving and spending with minimal user input, appealing to those preferring flexibility and less hands-on control. Integrating these apps with bank accounts and real-time notifications enhances accuracy and user engagement for both budgeting methods.
Choosing the Best Budget Strategy for Your Family
Choosing the best budget strategy for your family depends on your financial goals and spending habits, with traditional family budgets emphasizing detailed tracking of income and expenses to maximize savings. The anti-budget approach simplifies finances by allocating fixed amounts to essentials and savings, allowing more flexibility without constant monitoring. Evaluating factors such as discipline, financial stability, and lifestyle preferences helps determine whether a structured family budget or a more relaxed anti-budget system is ideal for your household finance management.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Family Budgeting
Zero-based family budgeting allocates every dollar of income to specific expenses, savings, or debt repayment, ensuring no money is left unassigned, which enhances financial control and accountability. Compared to anti-budget methods that forgo strict categorization, zero-based budgeting provides a clear roadmap to optimize household finances by preventing overspending and promoting intentional allocation.
Anti-Budget Chunking
Anti-budget chunking simplifies household finance by categorizing expenses into fixed, variable, and occasional chunks, enabling precise tracking and control without rigid line-item budgets. This method enhances flexibility and adaptability in managing family budgets, optimizing savings, and reducing overspending through intuitive financial allocation.
Envelope-Free Budgeting
Envelope-free budgeting enhances household finance by leveraging digital tools to track expenses without physical cash divisions, promoting flexibility and real-time adjustments. This method contrasts with traditional family budgets tied to cash envelopes, enabling more adaptive control over spending and savings goals.
Automation-First Budget
An automation-first budget leverages digital tools and apps to track household expenses and income, reducing manual input and enhancing accuracy compared to traditional family budgets. Utilizing automated categorization and bill payment ensures consistent savings and timely financial decisions, optimizing overall household finance management.
Sinking Fund Clusters
Sinking fund clusters in a family budget organize savings into targeted categories, enabling precise allocation for future expenses such as home repairs, vacations, and education. In contrast, an anti-budget approach emphasizes spending awareness without strict categories, potentially leading to less structured savings but increased flexibility in managing household finances.
Aspirational Budgeting
Aspirational budgeting in family finance emphasizes goal-oriented spending and saving strategies that enhance long-term financial growth, contrasting with anti-budgeting, which relies on flexible, zero-constraint methods to reduce anxiety and improve cash flow management. Prioritizing aspirational budgets helps households align expenses with future objectives like education, retirement, and home ownership, fostering disciplined yet adaptable financial planning.
Micro-Line Item Tracking
Family Budget and Anti-Budget approaches differ significantly in micro-line item tracking, with the Family Budget emphasizing detailed allocation of expenses to individual categories for precise control, while the Anti-Budget simplifies household finance by focusing on overall spending limits without granular tracking. Micro-line item tracking in a Family Budget enhances financial discipline and clarity, enabling households to identify specific spending patterns and optimize resource allocation.
Minimalist Anti-Budget
The minimalist anti-budget simplifies household finance by prioritizing essential expenses and automating savings, contrasting with traditional family budgets that track every dollar. This approach reduces stress and increases financial freedom by focusing only on income, fixed bills, and savings, allowing flexible spending without detailed tracking.
Values-Driven Spending Plan
A values-driven spending plan prioritizes essential expenses and personal financial goals over arbitrary limits, contrasting with traditional family budgets that rigidly allocate funds regardless of individual priorities. This approach enhances household finance management by aligning expenditures with core values, promoting long-term satisfaction and financial resilience.
Reverse Budgeting Signals
Family budgets allocate specific amounts to expenses to control spending, while anti-budgeting encourages prioritizing savings first, allowing flexibility in expenditures. Reverse budgeting signals focus on automating savings and emphasizing financial goals, minimizing the mental load of tracking every expense for improved household finance management.
Family Budget vs Anti-Budget for Household Finance Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com