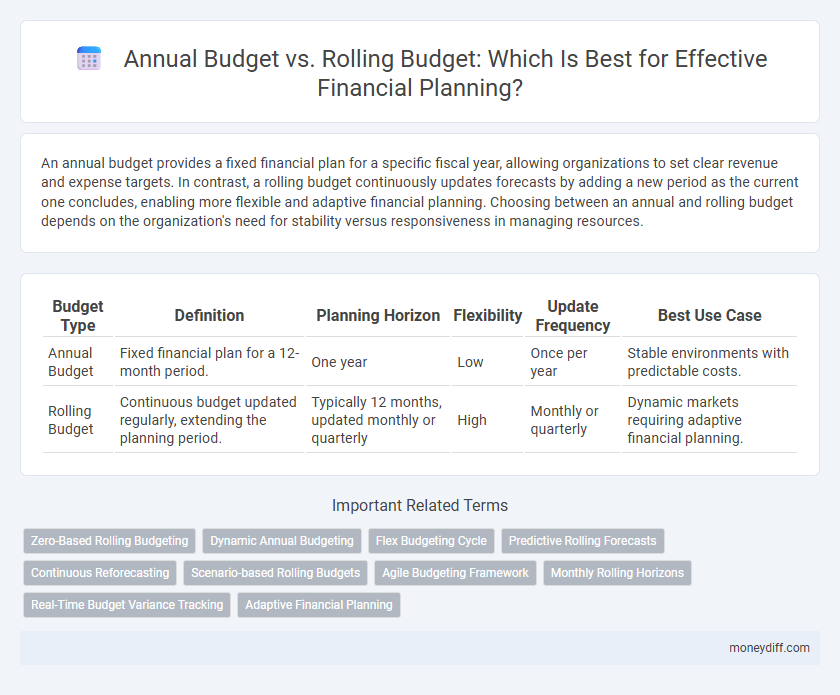
An annual budget provides a fixed financial plan for a specific fiscal year, allowing organizations to set clear revenue and expense targets. In contrast, a rolling budget continuously updates forecasts by adding a new period as the current one concludes, enabling more flexible and adaptive financial planning. Choosing between an annual and rolling budget depends on the organization's need for stability versus responsiveness in managing resources.
Table of Comparison
| Budget Type | Definition | Planning Horizon | Flexibility | Update Frequency | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Budget | Fixed financial plan for a 12-month period. | One year | Low | Once per year | Stable environments with predictable costs. |
| Rolling Budget | Continuous budget updated regularly, extending the planning period. | Typically 12 months, updated monthly or quarterly | High | Monthly or quarterly | Dynamic markets requiring adaptive financial planning. |
Understanding Annual Budgets in Financial Planning
An annual budget in financial planning establishes a fixed financial framework for a 12-month period, enabling organizations to allocate resources and set precise financial targets. This method promotes accountability through clearly defined fiscal goals and performance benchmarks tied to specific timelines. Annual budgets facilitate detailed forecasting and variance analysis, essential for effective financial control and strategic decision-making.
Key Concepts of Rolling Budgets
Rolling budgets continuously update financial forecasts by extending the budget period forward, allowing organizations to adapt to changing economic conditions and operational needs. Key concepts of rolling budgets include regular revision intervals, typically monthly or quarterly, which enhance accuracy and flexibility in resource allocation. This dynamic approach contrasts with fixed annual budgets by providing a more responsive and forward-looking financial planning framework.
Major Differences Between Annual and Rolling Budgets
Annual budgets set fixed financial goals and limits for a 12-month period, providing a clear framework for resource allocation and performance evaluation. Rolling budgets continuously update forecasts by adding a new budget period as the current period ends, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness to changing market conditions. The major difference lies in the adaptability: annual budgets offer stability and simplicity, while rolling budgets ensure ongoing adjustments for more accurate financial planning.
Advantages of Annual Budgeting
Annual budgeting provides a clear financial framework with fixed targets, enhancing organizational discipline and simplifying performance evaluation. It facilitates precise resource allocation and cost control aligned with fiscal year goals, improving accountability. This method supports strategic planning by setting definitive budget limits, enabling efficient monitoring and timely decision-making.
Benefits of Rolling Budgeting
Rolling budgets offer enhanced flexibility by continuously updating financial forecasts to reflect real-time business conditions, improving accuracy and responsiveness. This dynamic approach allows organizations to better manage cash flow and allocate resources efficiently, reducing the risk of budget overruns. Compared to annual budgets, rolling budgets support proactive decision-making through regular performance reviews and adjustments.
Limitations of Annual Budgets
Annual budgets often lack flexibility, making it challenging to adapt to unexpected changes in market conditions or business operations. They can lead to outdated financial plans as they are typically fixed for an entire fiscal year without periodic adjustments. This rigidity limits an organization's ability to respond quickly to new opportunities or risks, potentially impacting overall financial performance.
Challenges with Rolling Budgets
Rolling budgets present challenges such as increased complexity and the need for continuous data updates, which can strain financial resources and staff time. The frequent revisions may lead to forecasting inaccuracies if market conditions rapidly change or if assumptions used are outdated. Maintaining consistency in long-term strategic goals becomes difficult as constant budget adjustments can shift focus away from original financial plans.
Selecting the Right Budget Type for Your Organization
Choosing the right budget type is crucial for effective financial planning and organizational growth. An annual budget provides a fixed financial plan based on predicted revenues and expenses for a fiscal year, offering stability and clear targets. In contrast, a rolling budget continuously updates projections by adding a new period, allowing flexibility to adapt to market changes and improve decision-making accuracy.
Adapting Budget Strategies to Changing Financial Goals
Annual budgets provide a fixed financial plan for a specific fiscal year, offering clear targets and control but limited flexibility. Rolling budgets continuously update projections by incorporating the latest financial data, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing financial goals and market conditions. Implementing a rolling budget strategy enhances responsiveness and alignment with dynamic organizational priorities, supporting more effective decision-making and resource allocation.
Best Practices for Implementing Effective Budget Systems
Annual budgets provide a fixed financial plan based on projected revenues and expenses for a specific fiscal year, promoting stability and clear targets for departments. Rolling budgets continuously update forecasts by extending the planning horizon, enabling organizations to adapt promptly to market fluctuations and operational changes. Best practices include integrating real-time data analytics, fostering cross-departmental collaboration, and establishing regular review cycles to enhance accuracy and responsiveness in budgeting processes.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Rolling Budgeting
Zero-based rolling budgeting enhances financial planning by continuously updating budget assumptions and allocations from a zero base each period, promoting flexibility and resource optimization in a dynamic business environment. Unlike traditional annual budgets, this method prevents budgetary slack and aligns spending with current strategic priorities, improving cost control and financial agility.
Dynamic Annual Budgeting
Annual budget sets fixed financial targets for a specific fiscal year, providing clear benchmarks but limited flexibility, while a rolling budget continuously updates projections by adding a new period as the current one concludes, enhancing adaptability in financial planning. Dynamic annual budgeting integrates the structured framework of annual budgets with rolling adjustments, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to market changes and optimize resource allocation throughout the year.
Flex Budgeting Cycle
Annual budgets provide a fixed financial framework for a 12-month period, while rolling budgets continuously update forecasts by adding new periods as the previous ones close, enabling more adaptive financial planning. The flex budgeting cycle leverages rolling budgets to adjust resource allocation dynamically, ensuring responsiveness to market changes and operational variations.
Predictive Rolling Forecasts
Annual budgets set fixed financial targets for a specific fiscal year, often limiting adaptability in dynamic markets, while rolling budgets utilize predictive rolling forecasts that update financial projections continuously, enhancing responsiveness and accuracy in financial planning. Rolling budgets integrate real-time data and trends, enabling organizations to adjust strategies proactively and optimize resource allocation throughout the year.
Continuous Reforecasting
Annual budgets set fixed financial targets for a fiscal year, limiting flexibility in responding to market changes, while rolling budgets enable continuous reforecasting by updating projections regularly, improving agility and accuracy in financial planning. Continuous reforecasting in rolling budgets allows organizations to adapt quickly to economic fluctuations, optimize resource allocation, and enhance strategic decision-making throughout the year.
Scenario-based Rolling Budgets
Scenario-based rolling budgets enhance financial planning by continuously adjusting projections based on real-time data and multiple potential future conditions, providing greater flexibility than traditional annual budgets. This dynamic approach allows organizations to respond proactively to market fluctuations, improving accuracy in resource allocation and risk management throughout the fiscal year.
Agile Budgeting Framework
An annual budget provides a fixed financial plan for the fiscal year, limiting flexibility in adapting to market changes, while a rolling budget continuously updates projections, allowing agile financial planning aligned with real-time business performance. Agile budgeting frameworks leverage rolling budgets to enhance responsiveness, improve resource allocation, and support dynamic decision-making in volatile economic environments.
Monthly Rolling Horizons
Monthly rolling horizons in financial planning offer more precise control over cash flow and resource allocation compared to annual budgets, enabling continuous adjustments based on real-time data. This dynamic approach reduces forecasting errors and enhances responsiveness to market fluctuations, improving overall financial performance.
Real-Time Budget Variance Tracking
Rolling budgets enable real-time budget variance tracking by continuously updating financial projections based on actual performance, enhancing responsiveness to changing business conditions. In contrast, annual budgets provide fixed financial plans that limit timely adjustments, often resulting in delayed identification of variances and reduced agility in financial planning.
Adaptive Financial Planning
Annual budgets provide a fixed financial framework based on historical data, limiting flexibility in responding to market changes, while rolling budgets continuously update projections, enabling adaptive financial planning that aligns with dynamic business environments. Implementing rolling budgets enhances accuracy in resource allocation and supports strategic decision-making by incorporating real-time financial performance and market trends.
Annual Budget vs Rolling Budget for Financial Planning Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com