Surplus budgeting emphasizes allocating funds to ensure expenses are consistently lower than income, creating a financial cushion for future needs or investments. Guilt-free spending budgeting encourages mindful allocation of money for enjoyable or discretionary expenses without feeling guilty, promoting a balanced approach to financial well-being. Both methods optimize budget management by combining disciplined saving with intentional, guilt-free expenditures for a sustainable financial lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
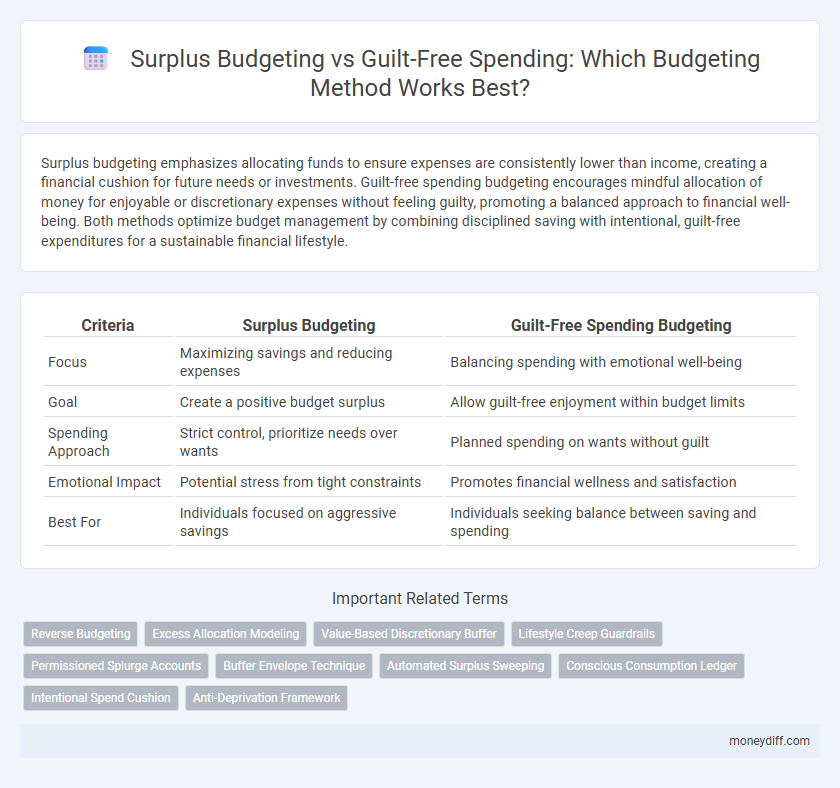
| Criteria | Surplus Budgeting | Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Maximizing savings and reducing expenses | Balancing spending with emotional well-being |
| Goal | Create a positive budget surplus | Allow guilt-free enjoyment within budget limits |
| Spending Approach | Strict control, prioritize needs over wants | Planned spending on wants without guilt |
| Emotional Impact | Potential stress from tight constraints | Promotes financial wellness and satisfaction |
| Best For | Individuals focused on aggressive savings | Individuals seeking balance between saving and spending |
Understanding Surplus Budgeting
Surplus budgeting involves planning expenses to ensure income exceeds expenditures, creating a positive financial balance that supports savings and debt reduction. This approach emphasizes strategic allocation of resources to build financial resilience and long-term stability. Businesses and households employing surplus budgets prioritize sustainable growth by consistently generating excess funds for future investments and emergencies.
What Is Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting?
Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting is a financial strategy that allocates a specific portion of income for discretionary expenses without guilt or overspending worries, promoting a balanced approach to personal finance. Unlike Surplus Budgeting, which focuses on saving excess income after all expenses, Guilt-Free Spending encourages mindful enjoyment of money while maintaining overall budget health. This method supports long-term financial goals by reducing emotional stress related to spending and enhancing sustainable budgeting habits.
Core Principles of Surplus Budgeting
Surplus budgeting prioritizes allocating funds in a way that consistently generates excess revenue beyond expenditures, emphasizing disciplined spending and increased savings to strengthen financial stability. Core principles include strict expense control, prioritizing debt reduction, and setting clear savings targets to ensure long-term fiscal health. This approach contrasts with guilt-free spending budgeting, which centers on spending without financial remorse but may compromise saving goals.
Key Features of Guilt-Free Spending
Guilt-Free Spending budgeting emphasizes mindful allocation of funds towards personal enjoyment while maintaining financial responsibility, ensuring a balanced approach between saving and spending. It incorporates designated discretionary spending categories that promote emotional satisfaction without compromising overall financial goals. This budgeting method reduces stress by allowing intentional splurges without guilt, fostering a healthier relationship with money.
Pros and Cons of Surplus Budgeting
Surplus budgeting ensures fiscal discipline by prioritizing expenditures below revenues, leading to increased savings and debt reduction, which strengthens financial stability. However, this conservative approach may result in underinvestment in essential services or growth opportunities, potentially limiting economic expansion and public welfare. The surplus budget's rigid framework can also restrict flexibility, making it challenging to respond swiftly to emerging needs or emergencies.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Guilt-Free Spending
Guilt-free spending budgeting promotes financial balance by allowing discretionary expenses without stress, enhancing mental well-being and reducing anxiety related to money management. It encourages mindful consumption and better adherence to budgets by differentiating between needs and wants, which can lead to sustained financial discipline. However, the drawback lies in the risk of overspending if limits are not clearly defined, potentially compromising long-term savings and investment goals.
Ideal Situations for Surplus Budgeting
Surplus budgeting is ideal in scenarios where businesses or governments prioritize financial stability and long-term investments, enabling the accumulation of reserves for unexpected expenses or economic downturns. Organizations with fluctuating revenue streams benefit from surplus budgeting as it provides a buffer that supports sustained operations without additional debt. This approach is also suitable when future projects require substantial funding, ensuring resources are available without compromising current financial health.
When to Choose Guilt-Free Spending
Guilt-Free Spending budgeting is ideal when financial stability is established and discretionary income exceeds essential expenses, allowing for purposeful enjoyment without financial stress. It supports mental well-being by balancing saving goals with justified indulgences, reducing guilt associated with spending. Choose this approach when maintaining healthy cash flow and avoiding excessive austerity promotes long-term budgeting success.
How to Combine Both Budgeting Methods
Combining surplus budgeting and guilt-free spending budgeting involves allocating funds to savings and investments while also setting aside a designated amount for guilt-free discretionary expenses. This dual approach ensures financial stability through surplus accumulation while promoting mental well-being by allowing controlled indulgences. Utilizing budgeting tools and tracking expenses helps maintain balance between responsible saving and enjoyable spending.
Which Budgeting Style is Right for You?
Surplus budgeting emphasizes saving excess income to build financial security, while guilt-free spending budgeting allocates funds for enjoyment without remorse, balancing discipline and pleasure. Choosing the right budgeting style depends on your financial goals, personality, and priorities--surplus budgeting suits those focused on long-term savings, whereas guilt-free spending budgeting benefits individuals seeking flexibility and stress-free spending. Evaluating your income stability, spending habits, and emotional relationship with money helps determine the most effective approach for sustainable financial health.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Budgeting
Reverse budgeting prioritizes allocating funds to savings and investments before covering expenses, fostering disciplined financial management and promoting surplus budgeting. This strategy contrasts with guilt-free spending budgeting by ensuring a surplus first, reducing financial stress and enabling controlled discretionary spending.
Excess Allocation Modeling
Surplus budgeting emphasizes allocating excess funds to savings or investments to strengthen financial stability, whereas guilt-free spending budgeting prioritizes intentional, stress-free allocation of surplus toward discretionary expenses that enhance quality of life. Excess allocation modeling identifies optimal distribution of surplus by balancing long-term financial goals with present consumption, maximizing both security and satisfaction.
Value-Based Discretionary Buffer
Surplus budgeting emphasizes allocating excess funds toward savings or debt reduction, creating a financial cushion, whereas guilt-free spending budgeting incorporates a value-based discretionary buffer that allows intentional, guilt-free expenditures aligned with personal priorities. This approach enhances financial well-being by balancing responsible saving with purposeful spending, optimizing budget flexibility and emotional satisfaction.
Lifestyle Creep Guardrails
Surplus Budgeting prioritizes saving and investing the excess income after essential expenses, effectively creating guardrails against lifestyle creep by forcing disciplined financial choices. Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting allocates a portion of income for indulgences without guilt, balancing enjoyment with control to prevent gradual increases in spending that erode financial goals.
Permissioned Splurge Accounts
Surplus budgeting emphasizes allocating funds only after ensuring expenses are covered, promoting financial stability, while guilt-free spending budgeting incorporates permissioned splurge accounts that allow designated discretionary spending without emotional burden. Permissioned splurge accounts empower individuals to enjoy discretionary purchases confidently, supporting balanced financial discipline alongside personal satisfaction.
Buffer Envelope Technique
Surplus budgeting emphasizes setting aside excess funds to build financial security, while guilt-free spending budgeting encourages allocation for enjoyable expenses without remorse. The buffer envelope technique enhances both methods by physically organizing money into designated envelopes, creating a tangible limit that prevents overspending and promotes disciplined saving.
Automated Surplus Sweeping
Automated Surplus Sweeping enhances Surplus Budgeting by systematically redirecting excess funds into savings or investment accounts, optimizing financial resources without manual intervention. This process supports Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting by ensuring discretionary spending aligns with preset limits, allowing for more confident and controlled expenditures.
Conscious Consumption Ledger
Surplus budgeting emphasizes saving excess funds by carefully tracking income and expenses in a conscious consumption ledger, empowering individuals to allocate resources efficiently without guilt. Guilt-free spending budgeting encourages mindful expenditures aligned with personal values, using the consumption ledger to balance enjoyment and financial responsibility for sustainable money management.
Intentional Spend Cushion
Surplus budgeting creates an intentional spend cushion by allocating more income than expenses, ensuring financial stability and reducing the risk of debt. Guilt-free spending budgeting emphasizes mindful allocation of funds for enjoyable expenses, balancing responsible saving with personal satisfaction without compromising long-term goals.
Anti-Deprivation Framework
Surplus budgeting emphasizes allocating funds only after essential expenses are covered, fostering financial stability through an anti-deprivation framework that prevents overspending. Guilt-free spending budgeting prioritizes intentional, value-aligned expenditures without emotional restraint, promoting psychological well-being alongside fiscal responsibility.
Surplus Budgeting vs Guilt-Free Spending Budgeting for Budget Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com