Wire transfers provide a traditional, reliable method for moving money across banks but often involve higher fees and longer processing times. Blockchain remittance offers faster, more cost-effective transactions with increased transparency and security through decentralized technology. Choosing between the two depends on priorities such as speed, cost, and ease of tracking payments.
Table of Comparison
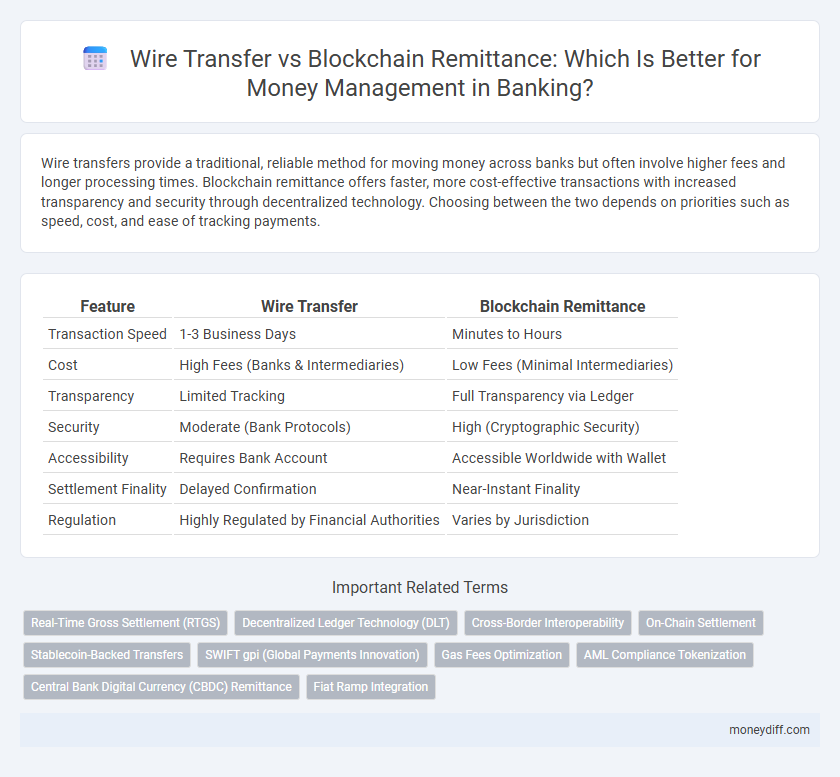
| Feature | Wire Transfer | Blockchain Remittance |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | 1-3 Business Days | Minutes to Hours |
| Cost | High Fees (Banks & Intermediaries) | Low Fees (Minimal Intermediaries) |
| Transparency | Limited Tracking | Full Transparency via Ledger |
| Security | Moderate (Bank Protocols) | High (Cryptographic Security) |
| Accessibility | Requires Bank Account | Accessible Worldwide with Wallet |
| Settlement Finality | Delayed Confirmation | Near-Instant Finality |
| Regulation | Highly Regulated by Financial Authorities | Varies by Jurisdiction |
Understanding Wire Transfers in Modern Banking
Wire transfers in modern banking remain a trusted method for securely sending funds domestically and internationally through established financial institutions, utilizing the SWIFT network or Fedwire system. These electronic transfers are known for their reliability, regulated compliance, and ability to handle large sums efficiently, making them a cornerstone of traditional money management. Despite longer processing times and higher fees compared to blockchain remittance, wire transfers provide a clear audit trail and widespread acceptance across banks worldwide.
Blockchain Remittance: The New Frontier in Money Transfers
Blockchain remittance revolutionizes money management by enabling near-instantaneous, low-cost international transfers without reliance on traditional banking intermediaries. Enhanced security through decentralized ledger technology minimizes fraud risks and ensures transparent transaction tracking. This paradigm shift reduces dependency on SWIFT-based wire transfers, providing greater accessibility and efficiency in cross-border payments.
Speed of Transactions: Wire Transfer vs Blockchain
Wire transfers typically take 1 to 3 business days to process due to banking hours and intermediary verification steps, which can delay transaction completion. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledgers to enable near-instantaneous fund transfers, often clearing within minutes regardless of geographic location. The speed advantage of blockchain technology enhances liquidity and allows for more efficient global money management compared to traditional wire transfers.
Global Accessibility and Reach Comparison
Wire transfers offer widespread global accessibility through established banking networks, enabling cross-border transactions in multiple currencies with regulatory compliance tailored to each region. Blockchain remittance enhances reach by leveraging decentralized networks that bypass traditional banking infrastructure, providing near-instantaneous transfers and access to unbanked populations worldwide. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as speed, cost, and the recipient's access to digital wallets or traditional bank accounts.
Security Measures: Traditional vs Blockchain Methods
Traditional wire transfers rely on robust bank security protocols, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regulatory oversight, to prevent fraud and unauthorized access. Blockchain remittance enhances security by utilizing decentralized ledgers, cryptographic validation, and tamper-proof transaction records, reducing risks associated with central points of failure. However, blockchain's security depends on network consensus mechanisms and smart contract integrity, which differ significantly from traditional banking safeguards.
Cost Efficiency: Banking Fees vs Crypto Fees
Wire transfers typically incur higher banking fees including intermediary charges and currency conversion costs, making them less cost-efficient for frequent or international money management. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized networks to significantly reduce transaction fees, often bypassing traditional banking costs and enabling near-instant settlements. Cost efficiency in blockchain remittance is enhanced by lower overhead, minimal intermediaries, and transparent fee structures compared to the variable and sometimes hidden charges of wire transfers.
User Experience: Ease of Use and Process Transparency
Wire transfers offer familiarity and clear transaction records but often involve multiple intermediaries and delayed processing times, affecting overall user experience. Blockchain remittance enhances ease of use through decentralized platforms and real-time tracking, providing greater process transparency and reduced dependency on banks. Users benefit from faster settlements and more control over their funds, making blockchain a compelling alternative for money management.
Regulations and Compliance in Cross-Border Transfers
Wire transfers are heavily regulated by institutions such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and require compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, ensuring transparency and security in cross-border payments. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology but still faces regulatory uncertainties and varying compliance standards across jurisdictions, which can complicate adherence to international sanctions and AML policies. Financial institutions must navigate evolving regulatory frameworks to balance innovation in blockchain with stringent compliance mandates for secure and legal cross-border money management.
Risks and Fraud Prevention Strategies
Wire transfers pose risks such as interception, identity theft, and unauthorized access, requiring banks to implement strong authentication and transaction monitoring systems to prevent fraud. Blockchain remittance reduces these risks by leveraging decentralized ledgers and cryptographic validation, enhancing transparency and tamper-resistance. Fraud prevention strategies include employing multi-factor authentication, real-time anomaly detection, and continuous blockchain audits to ensure secure and compliant money management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Effective Money Management
Wire transfers offer a traditional, widely accessible method for sending funds with established regulatory safeguards and predictable processing times. Blockchain remittance provides faster settlements, lower fees, and enhanced transparency through decentralized ledger technology, ideal for cross-border transactions. Selecting the right solution depends on priorities like transaction speed, cost-efficiency, security, and the geographical reach of the payment.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems provide instantaneous, high-value wire transfers directly between banks, enhancing liquidity management and reducing settlement risk compared to blockchain remittance, which relies on decentralized validation and may experience delays due to network consensus processes. RTGS's centralized infrastructure ensures compliance with regulatory standards and supports large-scale interbank transactions, while blockchain offers transparency and lower costs but faces scalability challenges impacting real-time fund availability.
Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT)
Wire transfers rely on centralized banking networks with longer processing times and higher fees, whereas blockchain remittance leverages Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT) to enable faster, secure, and cost-effective cross-border money management without intermediaries. DLT enhances transparency and traceability in financial transactions, reducing fraud risk and improving reconciliation efficiency.
Cross-Border Interoperability
Wire transfers rely on established banking networks with limited cross-border interoperability, often causing delays and high fees due to intermediary banks and differing regulatory frameworks. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledgers and standardized protocols, enabling seamless, near-instant cross-border transactions with enhanced transparency and reduced costs.
On-Chain Settlement
Wire transfers rely on traditional banking networks with delayed settlement times and higher fees, while blockchain remittance leverages on-chain settlement to enable near-instant, transparent transactions with lower costs and enhanced security. On-chain settlement records every transaction on a decentralized ledger, reducing fraud risk and increasing auditability compared to conventional wire transfer systems.
Stablecoin-Backed Transfers
Stablecoin-backed transfers leverage blockchain technology to provide faster, cost-effective, and transparent cross-border money management compared to traditional wire transfers. These transfers minimize exchange rate volatility and reduce intermediary fees by using digital assets pegged to stable currencies, enhancing liquidity and security in global banking transactions.
SWIFT gpi (Global Payments Innovation)
SWIFT gpi revolutionizes wire transfers by enabling faster, transparent, and traceable cross-border payments, enhancing traditional banking systems with real-time tracking and same-day settlement capabilities. Compared to blockchain remittance, SWIFT gpi integrates seamlessly with existing financial infrastructures, offering widespread global adoption and regulatory compliance critical for efficient money management.
Gas Fees Optimization
Wire transfers typically incur fixed processing fees that can escalate with international transactions, while blockchain remittance leverages decentralized networks to minimize gas fees through optimized transaction batching and smart contract efficiency. Prioritizing blockchain solutions enhances gas fees optimization, reducing overall costs and expediting cross-border money management compared to traditional banking wire transfers.
AML Compliance Tokenization
Wire transfers rely on traditional banking networks with established AML compliance frameworks, ensuring regulated oversight and traceability. Blockchain remittance leverages tokenization to enhance transaction transparency and security but requires robust AML protocols to address decentralized risks effectively.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Remittance
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) remittance offers faster settlement times and enhanced transparency compared to traditional wire transfers, reducing counterparty risk and transaction costs in cross-border payments. CBDC-based remittance leverages blockchain technology for secure, real-time fund transfers while enabling central banks to maintain regulatory oversight and monetary control.
Fiat Ramp Integration
Wire transfers provide a traditional fiat ramp allowing direct bank-to-bank fiat currency movement, ensuring regulatory compliance and widespread acceptance for international money management. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledgers to facilitate faster and lower-cost cross-border fiat ramps by converting digital assets back to local currencies, enhancing liquidity and real-time transaction visibility.
Wire Transfer vs Blockchain Remittance for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com