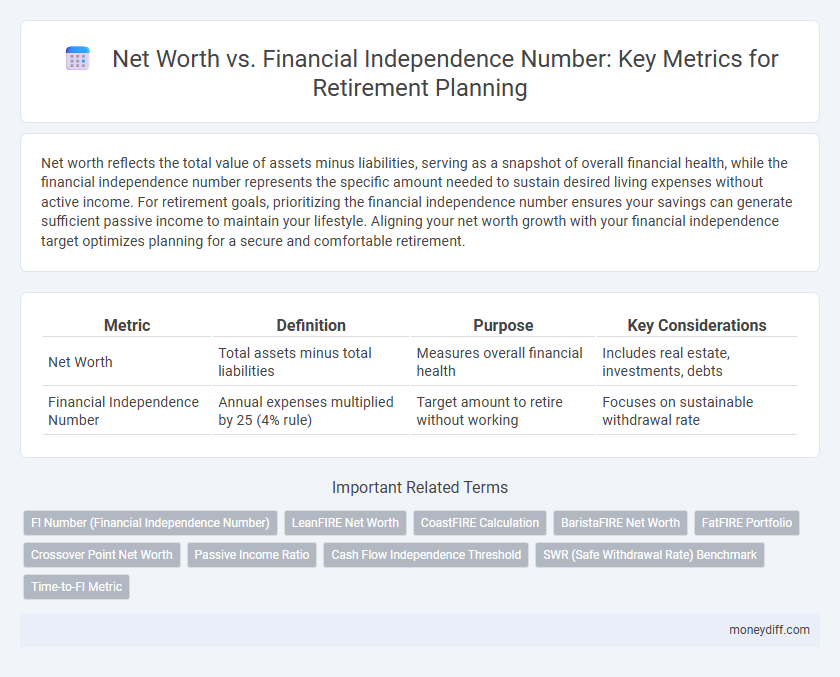
Net worth reflects the total value of assets minus liabilities, serving as a snapshot of overall financial health, while the financial independence number represents the specific amount needed to sustain desired living expenses without active income. For retirement goals, prioritizing the financial independence number ensures your savings can generate sufficient passive income to maintain your lifestyle. Aligning your net worth growth with your financial independence target optimizes planning for a secure and comfortable retirement.
Table of Comparison
| Metric | Definition | Purpose | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Worth | Total assets minus total liabilities | Measures overall financial health | Includes real estate, investments, debts |
| Financial Independence Number | Annual expenses multiplied by 25 (4% rule) | Target amount to retire without working | Focuses on sustainable withdrawal rate |
Understanding Net Worth: The Foundation of Wealth
Net worth represents the total value of assets minus liabilities, serving as a fundamental indicator of financial health and wealth accumulation. It provides a clear snapshot of one's economic standing, essential for setting realistic retirement goals compared to the financial independence number -- the amount needed to sustain desired living expenses without active income. Understanding net worth allows individuals to track progress and make informed decisions toward achieving financial independence and long-term retirement security.
What Is a Financial Independence Number?
A financial independence number represents the specific amount of money needed to cover all living expenses without relying on earned income, serving as a clear retirement goal. Unlike net worth, which is a snapshot of total assets minus liabilities, the financial independence number focuses on sustainable income generation through investments and savings. Calculating this number involves estimating annual expenses and multiplying by a safe withdrawal rate, commonly 25 times annual expenses for a 4% withdrawal rate.
Calculating Your Current Net Worth
Calculating your current net worth involves subtracting your total liabilities from your total assets, providing a clear snapshot of your financial standing. Understanding this number is crucial for comparing it against your financial independence number, which represents the amount needed to sustain your desired retirement lifestyle without active income. Accurately assessing net worth helps set realistic retirement goals and guides strategic planning toward achieving financial independence.
Steps to Determine Your Financial Independence Number
Calculate your current net worth by subtracting total liabilities from total assets to establish a clear financial baseline. Identify your annual retirement expenses and multiply by 25 to estimate your Financial Independence Number, reflecting the amount needed to retire safely. Regularly update these figures to adjust for inflation, lifestyle changes, and investment growth, ensuring accurate retirement planning.
Net Worth vs. Financial Independence: Key Differences
Net worth measures the total value of assets minus liabilities, reflecting overall financial health, while the financial independence number represents the amount of savings and investments required to sustain living expenses indefinitely without employment income. Net worth can fluctuate based on asset values and debts, but financial independence is a targeted threshold critical for retirement planning. Understanding the distinction between net worth and the financial independence number helps prioritize goal-setting for securing a stable and self-sufficient retirement.
Why Net Worth Alone Isn’t Enough for Retirement
Net worth provides a snapshot of total assets minus liabilities but doesn't account for ongoing expenses or income needs essential for retirement. Financial independence number incorporates sustainable withdrawal rates, lifestyle costs, and inflation, offering a more accurate measure of readiness. Relying solely on net worth risks underestimating the funds required to maintain desired retirement living standards over time.
Aligning Retirement Goals with Your FI Number
Aligning your retirement goals with your financial independence (FI) number ensures a clear target for sustainable wealth. Your net worth should be evaluated not just as a static figure, but relative to the FI number, which typically represents 25 to 30 times your expected annual expenses. Prioritizing this alignment helps maintain financial security and guides strategic investment decisions for long-term retirement success.
Tracking Your Progress: Net Worth and FI Milestones
Tracking your net worth alongside your financial independence (FI) number provides clear benchmarks for retirement goals, emphasizing asset growth and expense coverage. Regularly comparing these milestones helps identify savings gaps and allows adjustments to investment strategies to accelerate progress. Monitoring both metrics ensures balanced focus on wealth accumulation and sustainable income for long-term financial security.
Common Pitfalls: Confusing Net Worth with FI Readiness
Confusing net worth with financial independence (FI) readiness often leads to unrealistic retirement goals, as net worth includes illiquid assets that cannot support ongoing expenses. Relying solely on net worth ignores cash flow sustainability and withdrawal strategies critical for maintaining FI status. Evaluating retirement readiness requires analyzing safe withdrawal rates and passive income streams, rather than just asset accumulation.
Action Plan: Bridging the Gap Between Net Worth and FI Number
Develop a detailed action plan by assessing your current net worth and calculating your financial independence (FI) number, which represents the savings needed to retire without additional income. Prioritize increasing savings rate, reducing expenses, and investing strategically to accelerate growth toward your FI target. Regularly monitor net worth progress against the FI number to adjust contributions and investment allocations, ensuring timely achievement of retirement goals.
Related Important Terms
FI Number (Financial Independence Number)
The Financial Independence (FI) Number represents the precise amount of investable assets required to generate passive income that covers all retirement expenses without depleting principal. Unlike net worth, which aggregates total assets minus liabilities, the FI Number specifically targets sustainable cash flow generation, making it a more actionable metric for retirement planning.
LeanFIRE Net Worth
LeanFIRE net worth emphasizes maintaining a modest financial independence number that supports a frugal retirement lifestyle with minimal expenses while still providing sufficient security. Prioritizing LeanFIRE net worth helps individuals achieve early retirement by balancing lower cost of living with sustainable withdrawal rates, maximizing the efficiency of their savings.
CoastFIRE Calculation
The CoastFIRE calculation determines the net worth required at a specific age to achieve financial independence by allowing investments to grow passively until retirement, emphasizing the importance of early savings and compound growth. Comparing net worth to the financial independence number highlights how reaching the CoastFIRE point reduces future savings needs while still ensuring retirement goals are met.
BaristaFIRE Net Worth
BaristaFIRE net worth reflects a strategic balance between passive income and asset accumulation, emphasizing a lower financial independence number tailored for semi-retirement lifestyle goals. This approach contrasts with traditional retirement metrics by prioritizing flexible income streams over fully funded portfolios.
FatFIRE Portfolio
A FatFIRE portfolio typically targets a net worth significantly higher than the standard financial independence number, often requiring $2 million to $5 million to sustain an affluent lifestyle during retirement. This elevated net worth supports increased annual spending, luxury expenses, and greater financial security beyond basic retirement needs.
Crossover Point Net Worth
The Crossover Point Net Worth represents the moment when your assets generate enough passive income to cover your desired retirement expenses, effectively bridging the gap between mere net worth accumulation and achieving financial independence. Understanding this conversion is crucial for setting accurate retirement goals and ensuring sustainable financial freedom without relying on active income.
Passive Income Ratio
Net worth represents the total value of assets minus liabilities, while the financial independence number quantifies the sustainable annual passive income needed to cover living expenses without active employment. Focusing on the Passive Income Ratio--passive income divided by expenses--provides a critical metric for retirement goals, as achieving a ratio of 1.0 or higher signals true financial independence.
Cash Flow Independence Threshold
Net worth represents the total value of assets minus liabilities, while the Financial Independence Number (FIN) specifically targets the Cash Flow Independence Threshold needed to sustain retirement expenses without employment income. Achieving the FIN ensures that passive income streams consistently cover all living costs, making it a more precise metric for retirement planning than net worth alone.
SWR (Safe Withdrawal Rate) Benchmark
Net worth represents total assets minus liabilities, but the financial independence number quantifies the target portfolio size needed to sustain retirement expenses based on the Safe Withdrawal Rate (SWR) benchmark, typically 4% annually. Using the SWR method, retirement goals align more closely with cash flow sustainability than net worth alone, ensuring funds last through market fluctuations and longevity risks.
Time-to-FI Metric
The Time-to-FI metric calculates the number of years required to reach financial independence by comparing current net worth against the financial independence number, which represents the amount needed to sustain retirement expenses without employment income. This metric provides a practical timeline for retirement goals, emphasizing progress towards achieving sufficient assets to cover living costs through investment returns alone.
Net worth vs Financial independence number for retirement goals. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com