Car insurance typically offers fixed premiums based on general risk factors, while usage-based insurance calculates rates according to actual driving behavior and mileage. Usage-based insurance provides personalized coverage that can reward safe driving habits and potentially lower costs for infrequent drivers. Choosing between traditional and usage-based policies depends on individual driving patterns and preferences for premium stability versus behavior-based savings.
Table of Comparison
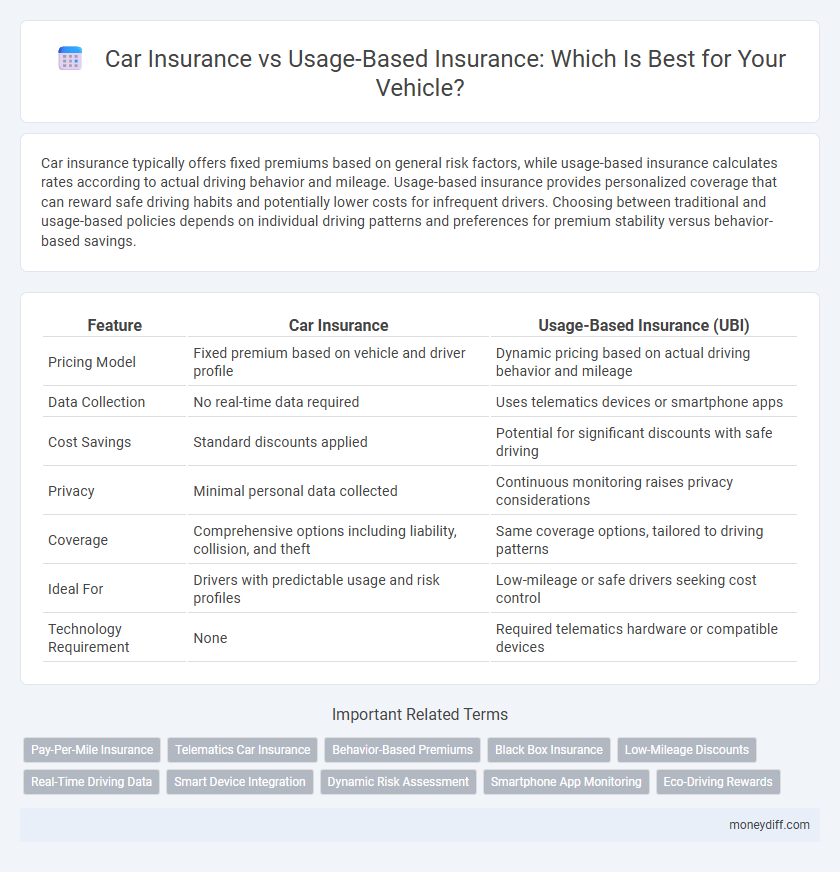
| Feature | Car Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Fixed premium based on vehicle and driver profile | Dynamic pricing based on actual driving behavior and mileage |
| Data Collection | No real-time data required | Uses telematics devices or smartphone apps |
| Cost Savings | Standard discounts applied | Potential for significant discounts with safe driving |
| Privacy | Minimal personal data collected | Continuous monitoring raises privacy considerations |
| Coverage | Comprehensive options including liability, collision, and theft | Same coverage options, tailored to driving patterns |
| Ideal For | Drivers with predictable usage and risk profiles | Low-mileage or safe drivers seeking cost control |
| Technology Requirement | None | Required telematics hardware or compatible devices |
Understanding Car Insurance: Traditional Coverage Explained
Traditional car insurance provides coverage based on factors such as vehicle type, driver history, and location, offering a fixed premium regardless of actual driving behavior. Policies typically include liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage, protecting against accidents, theft, and damage. This standard model relies on actuarial data to assess risk and determine pricing without real-time driving data integration.
What is Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)?
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) is a type of car insurance that calculates premiums based on actual driving behavior and mileage tracked through telematics devices or mobile apps. This model provides personalized rates by analyzing factors such as speed, braking patterns, and distance driven, promoting safer driving habits. UBI offers potential cost savings for low-mileage or careful drivers compared to traditional flat-rate car insurance policies.
Cost Comparison: Standard Car Insurance vs UBI
Standard car insurance typically charges premiums based on fixed factors such as age, location, and driving history, often resulting in higher base costs for average drivers. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) calculates premiums dynamically by monitoring actual driving behavior, potentially lowering costs for low-mileage or safe drivers. For consumers aiming to minimize expenses, UBI offers a cost-efficient alternative by aligning insurance rates directly with individual driving patterns and risk profiles.
How Premiums are Calculated: Risk Factors and Data
Car insurance premiums are traditionally calculated using demographic factors such as age, gender, location, driving history, and vehicle type to assess risk. Usage-based insurance (UBI) calculates premiums dynamically based on real-time data collected from telematics devices, including mileage, driving behavior, speed, and braking patterns. This data-driven approach allows UBI to personalize premiums more accurately by directly correlating risk with actual driving habits.
Flexibility and Customization in Coverage
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) offers greater flexibility by tailoring premiums based on real-time driving behavior and mileage, allowing for more personalized coverage compared to traditional Car Insurance. Traditional policies provide fixed coverage options and rates that may not reflect individual driving habits, whereas UBI enables dynamic customization, rewarding safe drivers with lower costs. This adaptability in usage-based plans enhances customer control over coverage specifics, promoting cost-effectiveness and risk-sensitive pricing.
Pros and Cons of Car Insurance
Traditional car insurance offers predictable premiums and broad coverage, providing financial protection against accidents, theft, and liability. However, it can be costly for low-mileage drivers and may not reward safe driving habits. Fixed rates often lack flexibility, potentially leading to overpayment for those who drive infrequently or maintain excellent driving records.
Pros and Cons of Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based car insurance offers personalized premiums by tracking driving behavior through telematics devices, which can lead to cost savings for safe drivers but may raise privacy concerns due to continuous data monitoring. It incentivizes responsible driving with potential discounts and real-time feedback but can result in higher costs for riskier drivers whose habits increase the likelihood of claims. The choice between traditional car insurance and usage-based insurance depends on driver habits, data privacy preferences, and the willingness to share detailed driving information.
Impact on Safe Driving and Rewards
Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages telematics technology to monitor driving behaviors such as speed, acceleration, and braking, directly influencing premiums based on safety performance. Car insurance policies with UBI reward safe driving habits through discounts, incentivizing reduced risk on roads and promoting vigilant vehicle operation. Traditional car insurance typically assesses risk through historical data and demographic factors, offering fewer immediate rewards for day-to-day safe driving behaviors.
Data Privacy Concerns with Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) for vehicles raises significant data privacy concerns due to continuous tracking of driving behavior and location through telematics devices or smartphone apps. Insurers collect granular data including speed, braking patterns, and routes, which can potentially be shared with third parties or exposed in data breaches. Consumers must carefully evaluate privacy policies and the extent of data collected before opting for UBI, balancing potential cost savings against risks to personal information security.
Choosing the Right Insurance: Which is Best for You?
Choosing the right car insurance depends on your driving habits and financial goals, with traditional car insurance offering fixed premiums based on general risk factors, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) adjusts rates according to real-time driving behavior tracked via telematics. UBI benefits safe drivers by potentially lowering premiums through data on mileage, speed, and braking patterns, making it ideal for low-mileage or cautious drivers seeking personalized coverage. Conventional insurance may better suit those who prefer predictability in premiums without sharing driving data, highlighting the importance of evaluating your driving profile and privacy preferences when selecting between these options.
Related Important Terms
Pay-Per-Mile Insurance
Pay-per-mile car insurance offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional policies by charging based on actual miles driven, making it ideal for low-mileage drivers seeking personalized premiums. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics to monitor driving behavior, but pay-per-mile specifically emphasizes distance traveled, providing transparent pricing and potential savings for infrequent drivers.
Telematics Car Insurance
Telematics car insurance uses real-time data from vehicle sensors to tailor premiums based on driving behavior, offering personalized rates and potential savings compared to traditional car insurance's static policy structure. This usage-based insurance model promotes safer driving habits by monitoring speed, braking, and mileage, ultimately benefiting both insurers and policyholders with more accurate risk assessments.
Behavior-Based Premiums
Behavior-based premiums in car insurance leverage telematics data to assess driving habits such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage, resulting in personalized rates that reward safe drivers with lower costs. This contrasts with traditional car insurance, which relies on demographic and historical data, making usage-based insurance a more accurate and fair method for determining vehicle insurance premiums.
Black Box Insurance
Black Box Insurance, a type of Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), leverages telematics devices to monitor driving behavior, offering personalized premiums based on factors like speed, acceleration, and braking patterns. Traditional car insurance relies on static factors such as age, location, and driving history, whereas Black Box Insurance provides dynamic pricing and potential cost savings by rewarding safer driving habits.
Low-Mileage Discounts
Car insurance policies often provide low-mileage discounts to drivers who use their vehicles less frequently, reducing premiums based on annual mileage thresholds. Usage-based insurance (UBI) enhances this approach by leveraging telematics data to offer personalized rates, rewarding safe driving habits and further optimizing savings for low-mileage drivers.
Real-Time Driving Data
Real-time driving data in usage-based insurance (UBI) allows insurers to assess risk more accurately by monitoring factors such as speed, acceleration, braking, and mileage, leading to personalized premiums based on actual driving behavior. Traditional car insurance relies on static factors like age, location, and vehicle type, whereas UBI leverages telematics technology to offer dynamic pricing and incentivize safer driving habits.
Smart Device Integration
Usage-based insurance leverages smart device integration by collecting real-time driving data through telematics devices, enabling personalized policy pricing based on individual behavior. Traditional car insurance relies on historical data and general risk factors, lacking the dynamic adaptability offered by smart sensors and mobile apps that enhance usage tracking and risk assessment.
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics technology to enable dynamic risk assessment by analyzing real-time driving behavior, such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage, resulting in personalized premium adjustments. Traditional car insurance relies on static factors like age, driving history, and vehicle type, often lacking the granularity and accuracy provided by continuous data collection in UBI models.
Smartphone App Monitoring
Car insurance using smartphone app monitoring leverages real-time data on driving behavior, such as speed, braking patterns, and distance, to tailor premiums more accurately than traditional policies. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) offers personalized rates by analyzing this sensor data, rewarding safe driving habits and potentially lowering costs for low-mileage drivers.
Eco-Driving Rewards
Car insurance traditionally bases premiums on factors like driver history and vehicle type, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics to monitor real-time driving behaviors, offering eco-driving rewards that incentivize fuel-efficient habits and reduce carbon emissions. These eco-driving rewards in UBI programs can lead to significant premium discounts by encouraging smoother acceleration, consistent speeds, and reduced idling, aligning cost savings with environmental benefits.
Car Insurance vs Usage-Based Insurance for vehicles. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com