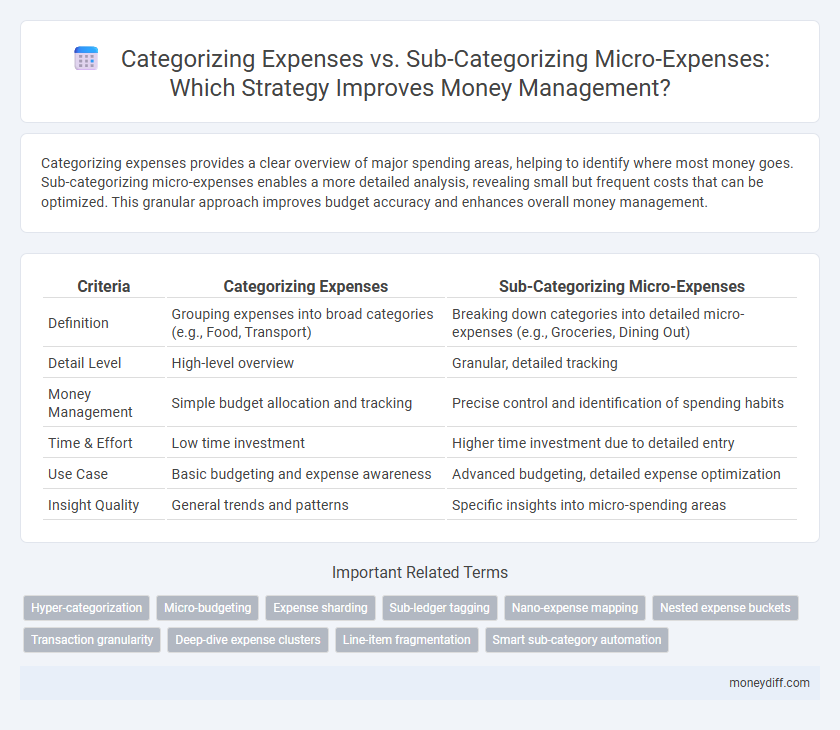
Categorizing expenses provides a clear overview of major spending areas, helping to identify where most money goes. Sub-categorizing micro-expenses enables a more detailed analysis, revealing small but frequent costs that can be optimized. This granular approach improves budget accuracy and enhances overall money management.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Categorizing Expenses | Sub-Categorizing Micro-Expenses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grouping expenses into broad categories (e.g., Food, Transport) | Breaking down categories into detailed micro-expenses (e.g., Groceries, Dining Out) |
| Detail Level | High-level overview | Granular, detailed tracking |
| Money Management | Simple budget allocation and tracking | Precise control and identification of spending habits |
| Time & Effort | Low time investment | Higher time investment due to detailed entry |
| Use Case | Basic budgeting and expense awareness | Advanced budgeting, detailed expense optimization |
| Insight Quality | General trends and patterns | Specific insights into micro-spending areas |
Understanding Expense Categorization in Money Management
Effective money management relies on clear expense categorization to track spending patterns accurately. Categorizing expenses into broad groups like housing, food, and transportation simplifies budgeting while sub-categorizing micro-expenses--such as dining out, groceries, or ride-sharing--provides granular insights for identifying saving opportunities. This dual-layer approach enhances financial awareness by balancing overview clarity with detailed analysis for informed decision-making.
The Basics of Expense Categories
Expense categories organize financial outflows into broad groups such as housing, transportation, and food, providing a clear overview of spending patterns. Sub-categorizing micro-expenses involves breaking down these broad groups into finer details like utilities within housing or dining out under food, allowing for more granular tracking and control. Understanding the basics of expense categories facilitates efficient budgeting and highlights areas for potential savings.
What Are Micro-Expenses?
Micro-expenses refer to small, frequent purchases that may seem insignificant individually but accumulate to impact overall financial health. Categorizing expenses involves grouping larger expense types, while sub-categorizing micro-expenses breaks down these groups into detailed, specific transactions to improve budget precision. Tracking micro-expenses enables better money management by highlighting overlooked spending patterns and identifying opportunities for savings.
Benefits of Sub-Categorizing Micro-Expenses
Sub-categorizing micro-expenses offers precise insight into spending patterns, enhancing budget accuracy and financial control. By breaking down large expense categories into detailed sub-categories, individuals can identify small, habitual costs that often go unnoticed but significantly impact overall savings. This granular approach facilitates targeted cost-cutting strategies and improves long-term money management effectiveness.
Expense Categories vs. Sub-Categories: Key Differences
Expense categories group broad spending areas such as housing, transportation, and food, providing a high-level overview for budgeting and financial analysis. Sub-categories break down these groups into specific micro-expenses like rent, utilities, groceries, and dining out, enabling more precise tracking and better control over spending habits. Understanding the key differences between expense categories and sub-categories enhances money management by offering both a structured framework and detailed insights into financial behavior.
Improved Budgeting with Expense Sub-Categorization
Expense sub-categorization enhances money management by providing granular insight into spending patterns beyond broad categories. This detailed breakdown enables precise tracking of micro-expenses, facilitating targeted budget adjustments and reducing unnecessary expenditures. Improved budgeting accuracy supports better financial goals alignment and optimized resource allocation.
Tracking Spending Patterns: Macro vs. Micro-View
Categorizing expenses provides a macro-view of spending patterns, allowing for broad analysis across major areas like housing, food, and transportation. Sub-categorizing micro-expenses reveals detailed insights into specific spending behaviors, such as dining out frequently or purchasing premium coffee, which helps identify opportunities for saving. Combining both approaches enhances money management by offering a comprehensive understanding of financial habits and enabling targeted budgeting strategies.
Tools for Managing Sub-Categorized Expenses
Tools for managing sub-categorized expenses offer granular tracking that enhances budget accuracy by breaking down micro-expenses into detailed segments. Applications like Mint and YNAB allow users to create customizable sub-categories, enabling precise monitoring of spending patterns and helping identify savings opportunities. Integrating automated transaction classification with AI-powered analytics optimizes financial insights and supports effective money management strategies.
Common Challenges in Micro-Expense Sub-Categorization
Common challenges in micro-expense sub-categorization include accurately distinguishing between similar small transactions and avoiding overly complex classification systems that hinder efficient tracking. Frequent minor expenses often lack clear descriptions, making it difficult to assign them to precise sub-categories without causing confusion or errors. Maintaining consistency in categorizing these micro-expenses requires disciplined record-keeping and can lead to time-consuming adjustments during financial reviews.
Best Practices for Effective Expense Management
Effectively categorizing expenses enhances clarity in financial tracking and budget adherence by grouping related costs like utilities, groceries, or transportation. Sub-categorizing micro-expenses, such as breaking down dining into coffee, fast food, and restaurants, enables pinpoint analysis and refined control over spending habits. Employing digital tools that support multi-level categorization optimizes expense management, ensuring accurate reporting and informed decision-making.
Related Important Terms
Hyper-categorization
Hyper-categorization in money management enhances precision by breaking down expenses into detailed sub-categories, allowing for granular tracking of micro-expenses. This method improves budget accuracy and reveals specific spending patterns that broad categories might overlook.
Micro-budgeting
Micro-budgeting enhances money management by breaking down broad expense categories into detailed sub-categories, allowing precise tracking of micro-expenses. This granular approach improves financial control, revealing spending patterns and enabling targeted budget adjustments for optimized resource allocation.
Expense sharding
Categorizing expenses into broad groups streamlines tracking and budgeting by consolidating similar costs, while sub-categorizing micro-expenses allows for granular analysis and precise financial insights. Expense sharding divides financial outflows into detailed segments, enhancing money management accuracy and enabling targeted spending adjustments.
Sub-ledger tagging
Sub-ledger tagging enables precise tracking of micro-expenses within broader expense categories, enhancing financial transparency and detailed cost analysis. This granular approach to categorizing expenses supports more accurate budgeting and better-informed money management decisions.
Nano-expense mapping
Categorizing expenses streamlines overall budgeting by grouping major spending areas, while sub-categorizing micro-expenses through nano-expense mapping enhances precision in tracking small, frequent transactions. Nano-expense mapping allows for granular analysis of spending habits, enabling improved money management and optimized financial decision-making.
Nested expense buckets
Nested expense buckets enhance money management by organizing broad categories into detailed sub-categories, allowing precise tracking of micro-expenses for better budget control. This hierarchical approach improves financial insights and helps identify specific spending patterns within larger expense groups.
Transaction granularity
Categorizing expenses provides a broad overview of spending patterns, while sub-categorizing micro-expenses enhances transaction granularity, enabling more precise tracking and analysis of cash flow. Detailed sub-categories improve budget accuracy and help identify specific areas for cost reduction in money management.
Deep-dive expense clusters
Deep-dive expense clusters enable precise tracking by grouping broad categories like housing or transportation into detailed sub-categories such as utilities, rent, fuel, and maintenance. This granular approach enhances money management by revealing specific spending patterns, allowing for targeted budgeting and optimized financial decision-making.
Line-item fragmentation
Categorizing expenses provides a high-level overview essential for budget tracking, while sub-categorizing micro-expenses addresses line-item fragmentation by breaking down costs into more precise segments, enabling granular analysis and better control over spending patterns. This detailed segmentation helps identify spending inefficiencies and supports targeted financial decision-making for improved money management.
Smart sub-category automation
Smart sub-category automation enhances money management by precisely categorizing micro-expenses, enabling detailed tracking and insightful analysis of spending patterns. This granular approach increases budgeting accuracy and optimizes financial decision-making by leveraging AI-driven algorithms to dynamically update sub-categories based on transaction data.
Categorizing expenses vs Sub-categorizing micro-expenses for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com