Living expenses typically cover essential needs such as housing, utilities, food, and transportation, ensuring a comfortable lifestyle. A bare bones budget prioritizes only the most critical costs to minimize spending and maximize savings. Understanding the difference helps individuals identify areas where they can cut non-essential expenses without compromising basic necessities.
Table of Comparison
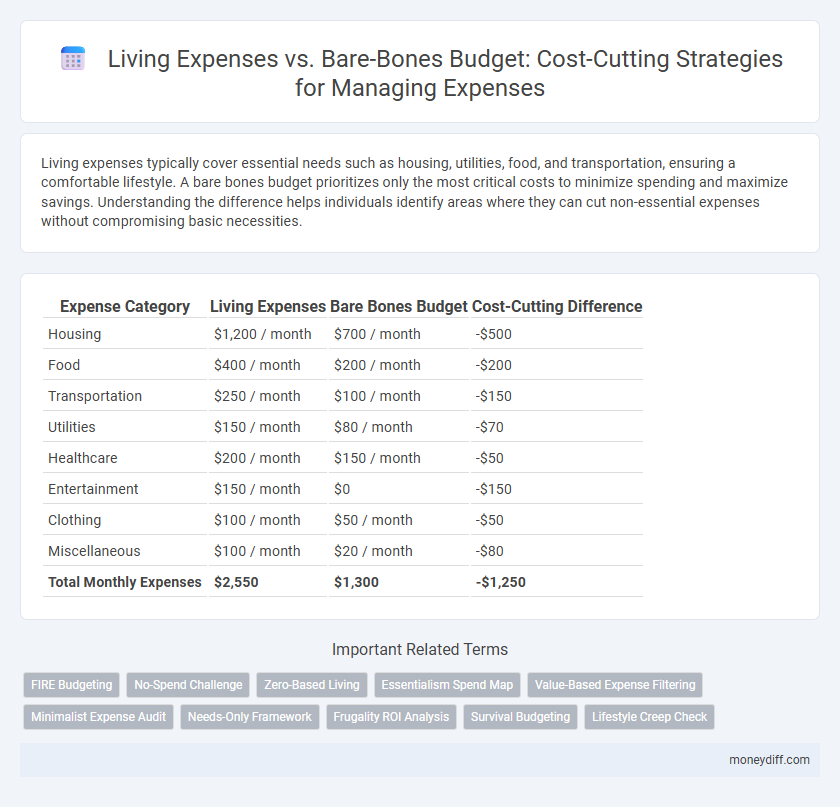
| Expense Category | Living Expenses | Bare Bones Budget | Cost-Cutting Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Housing | $1,200 / month | $700 / month | -$500 |
| Food | $400 / month | $200 / month | -$200 |
| Transportation | $250 / month | $100 / month | -$150 |
| Utilities | $150 / month | $80 / month | -$70 |
| Healthcare | $200 / month | $150 / month | -$50 |
| Entertainment | $150 / month | $0 | -$150 |
| Clothing | $100 / month | $50 / month | -$50 |
| Miscellaneous | $100 / month | $20 / month | -$80 |
| Total Monthly Expenses | $2,550 | $1,300 | -$1,250 |
Introduction to Living Expenses vs Bare Bones Budget
Living expenses encompass all necessary costs to maintain a standard lifestyle, including housing, utilities, food, transportation, and healthcare. A bare bones budget targets the absolute minimum spending required for survival, eliminating non-essential items to optimize cost-cutting efforts. Understanding the difference between living expenses and a bare bones budget helps individuals prioritize spending and make informed financial decisions during economic challenges.
Defining Living Expenses: What’s Included?
Living expenses encompass all regular costs essential for maintaining a standard lifestyle, including housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, healthcare, and personal care. These expenses represent the baseline for financial planning, reflecting everyday needs rather than discretionary spending. Defining living expenses helps distinguish them from a bare bones budget, which targets only the most critical costs required for survival, excluding non-essential items.
What Constitutes a Bare Bones Budget?
A bare bones budget includes only essential living expenses such as rent or mortgage, utilities, groceries, and basic transportation, eliminating discretionary spending like dining out and entertainment. It prioritizes necessities to minimize financial outflows during cost-cutting measures. Understanding what constitutes a bare bones budget helps individuals or families maintain financial stability by focusing solely on unavoidable expenses.
Key Differences Between Living Expenses and Bare Bones Budget
Living expenses encompass all routine costs required to maintain a comfortable lifestyle, including housing, food, transportation, and healthcare. A bare bones budget focuses solely on essential expenditures, stripping away non-necessities to minimize spending during financial constraints. Key differences lie in scope and flexibility, with living expenses covering broader needs while bare bones budgets prioritize survival-level costs for aggressive cost-cutting.
Common Categories in a Standard Living Expense Budget
Common categories in a standard living expense budget include housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, healthcare, insurance, and entertainment. In contrast, a bare bones budget focuses on essential costs like rent, basic food items, minimal utilities, and necessary transportation, eliminating discretionary spending. Understanding these categories helps identify specific areas for cost-cutting without compromising fundamental needs.
Essential Expenses in a Bare Bones Budget
Essential expenses in a bare bones budget prioritize housing, utilities, food, and transportation to maintain basic living standards while minimizing costs. These fundamental costs exclude non-essential items like entertainment, dining out, or subscriptions, focusing solely on necessities for survival and health. By concentrating on essential expenses, individuals can significantly reduce their overall living expenses and improve financial stability during cost-cutting measures.
How to Transition from Living Expenses to a Bare Bones Budget
Transitioning from living expenses to a bare bones budget requires identifying essential costs such as rent, utilities, and groceries while eliminating discretionary spending like dining out and subscriptions. Prioritize fixed expenses to maintain stability and allocate funds strictly for necessities, ensuring a sustainable financial structure during cost-cutting. Regularly tracking and adjusting the budget supports adherence to strict limits while avoiding financial strain.
Cost-Cutting Strategies for Each Budget Type
Living expenses encompass all monthly costs including housing, utilities, food, transportation, and healthcare, requiring cost-cutting strategies such as negotiating bills, meal planning, and using public transportation to reduce overall spending. Bare bones budgets focus only on essential expenses like rent, utilities, and basic groceries, with cost-cutting methods prioritizing eliminating non-essential purchases, seeking lower-cost housing options, and minimizing utility usage to sustain minimal living standards. Tailoring cost-cutting strategies to each budget type ensures effective financial management by targeting reductions in flexible spending for living expenses and strict prioritization of necessities for bare bones budgets.
Pros and Cons: Living Expenses Budget vs Bare Bones Budget
Living expenses budgets provide a realistic view of necessary costs, covering housing, food, utilities, and transportation, which helps maintain a balanced lifestyle but may limit savings potential. Bare bones budgets focus strictly on essential expenditures, maximizing savings and debt repayment but often sacrificing comfort and flexibility, leading to potential stress and reduced quality of life. Choosing between these budgets depends on financial goals, with living expenses budgets supporting sustainability and bare bones budgets enabling rapid debt reduction or emergency fund growth.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Financial Goals
Living expenses encompass all necessary and discretionary costs required for a comfortable lifestyle, while a bare bones budget strips spending down to essentials like housing, food, and utilities to minimize expenses drastically. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on your financial goals, whether prioritizing debt reduction, savings growth, or emergency fund buildup. Analyzing monthly income, fixed obligations, and personal spending habits helps determine if a comprehensive budget or minimalistic cost-cutting strategy aligns best with long-term financial stability.
Related Important Terms
FIRE Budgeting
Living expenses typically cover essential housing, food, transportation, and healthcare costs, while a bare bones budget for FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) focuses strictly on minimal necessities to maximize savings and investment potential. Optimizing a bare bones budget by reducing discretionary spending accelerates financial independence by lowering the required FIRE target amount.
No-Spend Challenge
A No-Spend Challenge drastically reduces living expenses by eliminating all non-essential purchases, helping individuals identify the minimum bare bones budget needed for survival. This practice highlights discretionary spending patterns and encourages financial discipline by focusing only on fixed costs like rent, utilities, and groceries.
Zero-Based Living
Zero-Based Living emphasizes aligning every dollar with specific expenses, optimizing living expenses by eliminating non-essential spending. This approach contrasts with a bare bones budget by focusing on intentional allocation rather than minimal survival costs, enabling more strategic cost-cutting and financial control.
Essentialism Spend Map
Living expenses encompass all necessary costs for daily life, such as housing, food, utilities, and transportation, while a bare bones budget targets only the absolute essentials to maximize savings and reduce financial waste. Using the Essentialism Spend Map helps identify and prioritize core expenditures, enabling individuals to focus spending strictly on critical needs and streamline budgets for effective cost-cutting.
Value-Based Expense Filtering
Living expenses encompass essential costs such as housing, utilities, food, and transportation, whereas a bare bones budget focuses strictly on fundamental needs to minimize spending. Value-based expense filtering prioritizes expenditures that deliver the highest utility and necessity, enabling consumers to eliminate non-essential costs and optimize financial efficiency.
Minimalist Expense Audit
A minimalist expense audit reveals that living expenses often exceed the bare bones budget, which prioritizes essential costs such as housing, utilities, and food, excluding discretionary spending. Implementing this audit helps identify non-essential expenditures, streamlining finances to maintain only critical outflows during cost-cutting efforts.
Needs-Only Framework
Living expenses encompass essential costs such as housing, food, utilities, transportation, and healthcare, reflecting a full but manageable lifestyle. The bare bones budget focuses strictly on the Needs-Only Framework by prioritizing critical expenses necessary for survival, excluding discretionary spending to maximize cost-cutting efficiency.
Frugality ROI Analysis
Analyzing the ROI of frugality reveals that while living expenses cover essential needs and moderate comforts, a bare bones budget eliminates all non-essentials to maximize savings, significantly boosting financial resilience. Prioritizing cost-cutting on discretionary items within living expenses yields the highest return by reducing variable costs without sacrificing critical quality of life factors.
Survival Budgeting
Survival budgeting prioritizes essential living expenses such as housing, food, utilities, and transportation, trimming non-essential costs to maintain financial stability during tough times. Implementing a bare bones budget eliminates discretionary spending, ensuring funds cover only necessary survival expenses for minimal daily living.
Lifestyle Creep Check
Monitoring living expenses against a bare bones budget reveals lifestyle creep, where gradual increases in discretionary spending inflate overall costs without proportional income growth. Implementing strict spending limits and regular budget reviews can effectively counteract lifestyle creep, ensuring sustainable financial health and optimized cost-cutting.
Living expenses vs Bare bones budget for cost-cutting. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com