Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving by automatically setting aside a portion of income before covering expenses, ensuring financial goals are met consistently. Budgeting allocates funds across various spending categories after income is received, helping track and control expenses to avoid overspending. Combining both strategies enhances money management by securing savings upfront while maintaining disciplined spending habits.
Table of Comparison
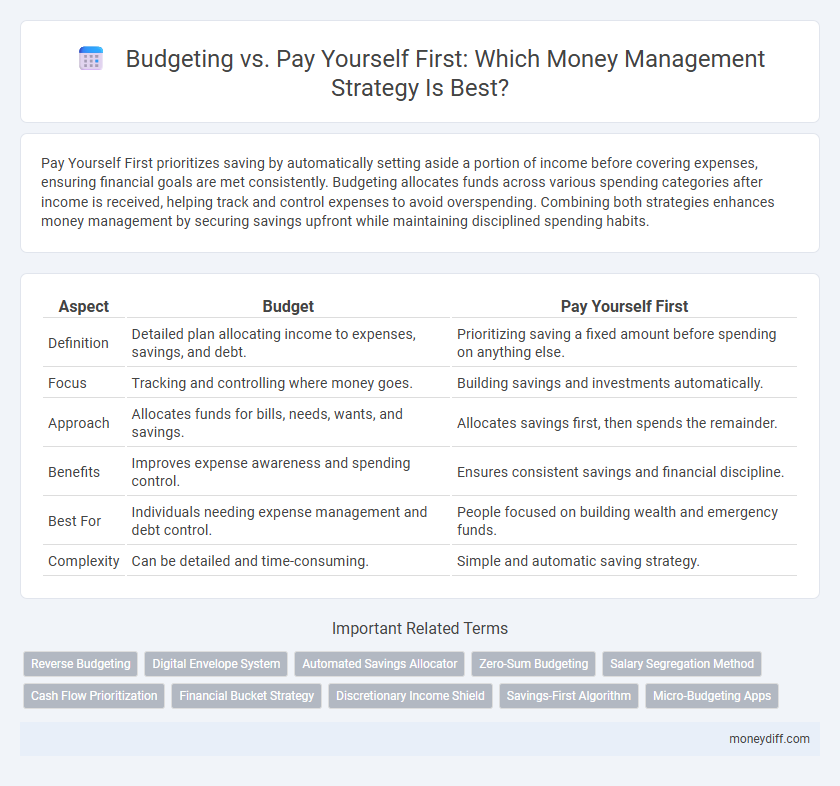
| Aspect | Budget | Pay Yourself First |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detailed plan allocating income to expenses, savings, and debt. | Prioritizing saving a fixed amount before spending on anything else. |
| Focus | Tracking and controlling where money goes. | Building savings and investments automatically. |
| Approach | Allocates funds for bills, needs, wants, and savings. | Allocates savings first, then spends the remainder. |
| Benefits | Improves expense awareness and spending control. | Ensures consistent savings and financial discipline. |
| Best For | Individuals needing expense management and debt control. | People focused on building wealth and emergency funds. |
| Complexity | Can be detailed and time-consuming. | Simple and automatic saving strategy. |
Understanding Budgeting: Core Principles
Budgeting revolves around allocating income to cover essential expenses, savings, and discretionary spending, providing a structured financial plan. The core principle of budgeting is tracking income and expenditures to maintain financial balance and avoid overspending. Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving a fixed portion of income before other expenses, ensuring consistent wealth accumulation within an overall budget framework.
What Does “Pay Yourself First” Mean?
"Pay Yourself First" means setting aside a portion of your income for savings or investments before allocating money to any other expenses or bills. This approach prioritizes building financial security and wealth by ensuring consistent savings regardless of spending habits. Unlike traditional budgeting that focuses on controlling expenses, "Pay Yourself First" emphasizes proactive savings as a foundational money management strategy.
Budgeting vs Pay Yourself First: Key Differences
Budgeting involves tracking all income and expenses to allocate funds efficiently across various categories, ensuring financial obligations are met and goals are prioritized. Pay Yourself First prioritizes saving by automatically setting aside a fixed amount of income for savings or investments before other expenditures. The key difference lies in budgeting's comprehensive control over spending versus Pay Yourself First's focus on consistently building savings upfront.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting provides clear spending limits and helps track expenses, offering structure for managing finances effectively. However, it can be time-consuming to maintain and often leads to rigid constraints that reduce flexibility in spending. Unlike the Pay Yourself First method, which prioritizes savings upfront, traditional budgeting may delay savings and emphasize expense control over wealth building.
Pros and Cons of the Pay Yourself First Method
The Pay Yourself First method prioritizes saving by automatically setting aside a portion of income before expenses, ensuring consistent financial growth and emergency fund buildup. Its pros include fostering disciplined savings habits and reducing the temptation to overspend, while cons involve potential cash flow challenges if fixed expenses are high or unexpected costs arise. Unlike traditional budgeting that tracks and adjusts expenses post hoc, Pay Yourself First requires accurate income and expense forecasting to prevent shortfalls.
Which Method Helps Build Wealth Faster?
Pay Yourself First accelerates wealth building by prioritizing savings and investments before expenses, ensuring consistent wealth accumulation. Budgeting provides a detailed plan to control spending but may delay savings if not disciplined. Combining both strategies maximizes financial growth by securing savings upfront while managing expenditures effectively.
Adapting Money Management to Your Lifestyle
Paying yourself first prioritizes savings by automatically setting aside a portion of income before expenses, promoting financial stability tailored to personal goals. Budgeting offers a comprehensive overview of income and expenditures, enabling tailored adjustments that suit lifestyle needs and spending habits. Combining both strategies ensures adaptive money management, aligning savings with everyday financial responsibilities and lifestyle priorities.
Common Pitfalls in Budgeting and Pay Yourself First
Common pitfalls in budgeting include underestimating expenses and failing to track spending consistently, leading to inaccurate financial planning. Pay Yourself First may be overlooked if priorities are unclear or if automated savings are not set up, reducing the effectiveness of this strategy. Combining both methods ensures disciplined saving while maintaining control over daily expenses.
Combining Budgeting and Pay Yourself First Strategies
Combining budgeting with the Pay Yourself First strategy enhances financial discipline by ensuring savings are prioritized before allocating funds to expenses. Setting aside a fixed percentage of income for savings or investments immediately upon receipt streamlines budget planning and reduces the risk of overspending. This integrated approach boosts long-term wealth accumulation and financial security by balancing expense management with consistent savings growth.
Choosing the Best Approach for Financial Success
Budgeting involves tracking and categorizing all income and expenses to maintain control over spending, while the Pay Yourself First method prioritizes saving a set amount before covering other costs. Financial success depends on selecting the strategy that aligns with individual goals and spending habits, ensuring consistent saving or disciplined expense management. Combining both approaches can optimize money flow management and enhance long-term wealth accumulation.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Budgeting
Reverse budgeting prioritizes saving and investing by paying yourself first, ensuring financial goals are met before allocating funds for expenses. Unlike traditional budgeting, this method directs a fixed amount into savings at the start, enhancing discipline and long-term wealth accumulation.
Digital Envelope System
The Digital Envelope System enhances money management by allocating funds into designated virtual categories, promoting disciplined spending without sacrificing savings goals. This method optimizes cash flow control compared to traditional budgeting, while integrating the Pay Yourself First principle to ensure consistent savings before expense allocation.
Automated Savings Allocator
Automated Savings Allocator streamlines money management by prioritizing Pay Yourself First, automatically directing a set percentage of income into savings before other expenses, ensuring consistent wealth building. This method often outperforms traditional budgeting by reducing reliance on manual tracking and minimizing the temptation to overspend.
Zero-Sum Budgeting
Zero-sum budgeting allocates every dollar of income to specific expenses or savings, ensuring that income minus expenditures equals zero, which aligns with the pay yourself first strategy by prioritizing savings before discretionary spending. This method enforces disciplined money management by creating intentional spending categories, reducing overspending, and maximizing financial goals through proactive allocation.
Salary Segregation Method
The Salary Segregation Method prioritizes allocating a fixed percentage of income to savings before budgeting for expenses, aligning with the "Pay Yourself First" principle to ensure financial goals are met. This approach reduces reliance on traditional budgeting by automating savings and promoting disciplined money management.
Cash Flow Prioritization
Cash flow prioritization through the "Pay Yourself First" strategy ensures that savings are allocated before any expenses, creating a disciplined financial habit that secures future financial goals. In contrast, traditional budgeting allocates funds after expenses are accounted for, which often risks delaying or neglecting savings due to fluctuating spend patterns.
Financial Bucket Strategy
The Financial Bucket Strategy enhances money management by categorizing income into specific allocations before expenses, aligning closely with the Pay Yourself First approach that prioritizes savings and investments. Unlike traditional budgeting, this strategy ensures predetermined financial goals are met by funneling funds directly into dedicated buckets such as emergency savings, retirement, and discretionary spending.
Discretionary Income Shield
Discretionary Income Shield refers to the portion of income reserved for non-essential spending after covering savings and fixed expenses, aligning closely with the Pay Yourself First method where savings take priority. Unlike traditional budgeting that allocates funds based on expenses first, this approach ensures financial security by protecting discretionary income for future goals and unexpected costs.
Savings-First Algorithm
The Savings-First Algorithm prioritizes allocating a fixed percentage of income directly to savings before budgeting for expenses, ensuring consistent wealth growth and financial security. This approach contrasts with traditional budgeting by emphasizing proactive savings rather than adjusting leftover funds, fostering disciplined money management and long-term financial goals.
Micro-Budgeting Apps
Micro-budgeting apps enhance money management by integrating budget tracking with the pay yourself first strategy, automatically allocating funds to savings before expenses. These tools optimize cash flow by categorizing expenses in real time and prioritizing savings goals, improving financial discipline and long-term wealth accumulation.
Budget vs Pay Yourself First for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com