Commercial banks offer extensive branch networks, a wide range of financial products, and established trust, making them ideal for customers seeking traditional banking services and face-to-face interactions. Challenger banks operate primarily online, providing innovative digital experiences, lower fees, and faster account setup, appealing to tech-savvy users looking for convenience and cost efficiency. Choosing between commercial and challenger banks depends on preferences for personalized service versus digital-first solutions.
Table of Comparison
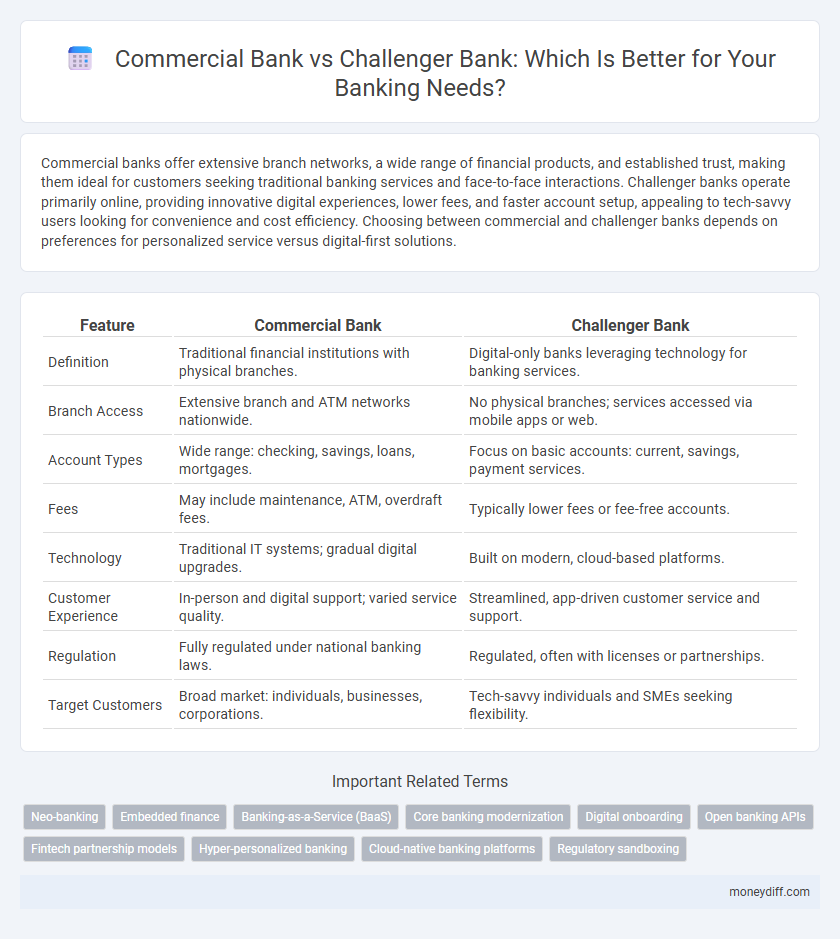
| Feature | Commercial Bank | Challenger Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional financial institutions with physical branches. | Digital-only banks leveraging technology for banking services. |
| Branch Access | Extensive branch and ATM networks nationwide. | No physical branches; services accessed via mobile apps or web. |
| Account Types | Wide range: checking, savings, loans, mortgages. | Focus on basic accounts: current, savings, payment services. |
| Fees | May include maintenance, ATM, overdraft fees. | Typically lower fees or fee-free accounts. |
| Technology | Traditional IT systems; gradual digital upgrades. | Built on modern, cloud-based platforms. |
| Customer Experience | In-person and digital support; varied service quality. | Streamlined, app-driven customer service and support. |
| Regulation | Fully regulated under national banking laws. | Regulated, often with licenses or partnerships. |
| Target Customers | Broad market: individuals, businesses, corporations. | Tech-savvy individuals and SMEs seeking flexibility. |
Introduction to Commercial Banks and Challenger Banks
Commercial banks serve as traditional financial institutions offering a full range of services such as savings and checking accounts, loans, and mortgages, catering to individuals and businesses through physical branches. Challenger banks operate primarily online with a focus on innovative technology, streamlined user experiences, and lower fees, targeting tech-savvy customers and underserved markets. The evolving banking landscape sees challenger banks challenging the established dominance of commercial banks by prioritizing digital accessibility and personalized financial solutions.
Core Differences Between Commercial and Challenger Banks
Commercial banks are traditional financial institutions offering a wide range of services including loans, deposits, and wealth management, operating through extensive branch networks. Challenger banks are digital-first entities leveraging technology to provide streamlined, user-friendly banking experiences with lower fees and faster account setups. The core differences lie in operational models, customer engagement strategies, and regulatory approaches, with commercial banks prioritizing established infrastructure and challenger banks emphasizing innovation and agility.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Commercial banks operate under comprehensive regulatory frameworks established by central banks and financial authorities, ensuring strict compliance with capital adequacy, anti-money laundering (AML), and consumer protection laws. Challenger banks, often licensed as fintech institutions or under specialized banking licenses, face evolving regulatory environments that demand agility in compliance systems but typically benefit from lighter regulatory burdens compared to traditional commercial banks. Both must maintain rigorous standards, yet commercial banks are subject to more extensive audits, reserve requirements, and systemic risk oversight due to their size and market impact.
Technology and Innovation in Banking Services
Commercial banks leverage established technology infrastructures to offer comprehensive banking services, integrating advanced security protocols and extensive branch networks for customer convenience. Challenger banks prioritize cutting-edge digital innovation, utilizing AI-driven platforms and mobile-first solutions to deliver seamless, user-friendly experiences with lower operational costs. Both models drive technological advancement, but challenger banks excel in agility and rapid deployment of new fintech features.
Customer Experience and Accessibility
Commercial banks provide extensive branch networks and a wide range of financial services, ensuring personalized customer support and reliable in-person access. Challenger banks leverage digital platforms to offer seamless, user-friendly mobile banking experiences with faster account setup and lower fees. Accessibility is enhanced by 24/7 online services in challenger banks versus traditional banking hours and physical presence limitations in commercial banks.
Products and Services Offered
Commercial banks provide a wide range of products and services, including savings and checking accounts, mortgages, personal and business loans, credit cards, and wealth management services. Challenger banks primarily focus on digital-first solutions with streamlined checking and savings accounts, payment services, and budgeting tools, often targeting tech-savvy customers. Both types offer competitive financial products, but commercial banks typically deliver more comprehensive services, including extensive branch networks and personalized advisory options.
Security and Risk Management
Commercial banks implement extensive security protocols and regulatory compliance frameworks, leveraging legacy systems combined with advanced fraud detection technologies to mitigate risks effectively. Challenger banks prioritize innovative cybersecurity measures, including biometric authentication and real-time transaction monitoring, to enhance user protection while adapting rapidly to emerging threats. Both models face distinct challenges in managing operational risks, with commercial banks emphasizing stability and challenger banks focusing on agility in security response.
Cost Structure and Fees Comparison
Commercial banks typically have higher overhead costs due to their extensive branch networks and legacy systems, leading to increased fees for services like account maintenance, wire transfers, and overdrafts. Challenger banks operate primarily online with streamlined technology platforms, resulting in lower operational costs and more competitive fee structures, often offering free or minimal-fee checking accounts and lower transaction charges. The cost structure of challenger banks appeals to customers seeking affordable banking solutions without sacrificing digital convenience.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Commercial banks maintain dominance with expansive physical networks and diversified financial services, yet challenger banks rapidly capture market share through digital innovation and customer-centric platforms tailored to tech-savvy consumers. Market trends indicate accelerated adoption of AI-driven personalized banking, open banking APIs, and seamless mobile experiences, which empower challenger banks to disrupt traditional services effectively. The future outlook foresees intensified competition as regulatory environments evolve, with challenger banks poised for growth by leveraging agile technology and commercial banks investing heavily in digital transformation to retain customer loyalty.
Choosing the Right Bank for Your Needs
Choosing the right bank depends on your specific financial needs and preferences, with commercial banks offering extensive branch networks, a wide range of services, and established customer trust. Challenger banks provide innovative digital experiences, lower fees, and faster account setup, appealing to tech-savvy customers seeking convenience and cost-efficiency. Evaluating factors such as service accessibility, technology integration, and fees is essential for selecting between traditional commercial banks and digital-focused challenger banks.
Related Important Terms
Neo-banking
Commercial banks offer extensive branch networks and traditional financial services, while challenger banks focus on digital-first, app-based neo-banking experiences that prioritize user-friendly interfaces and lower fees. Challenger banks leverage innovative technology and agile platforms to provide faster account setup, personalized financial tools, and seamless online transactions, appealing to tech-savvy customers.
Embedded finance
Commercial banks leverage extensive branch networks and regulatory experience to integrate embedded finance solutions, offering businesses seamless access to credit, payments, and treasury services within their existing platforms. Challenger banks prioritize agile digital platforms and innovative APIs, enabling faster deployment of embedded finance products that enhance customer experiences through personalized, real-time financial services.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Commercial banks leverage robust regulatory frameworks and extensive branch networks to offer comprehensive Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) solutions, enabling enterprises to integrate traditional banking services with high levels of security and compliance. Challenger banks focus on agile, technology-driven BaaS platforms that prioritize seamless digital integration and personalized customer experiences, often streamlining onboarding processes and reducing operational costs.
Core banking modernization
Commercial banks emphasize robust core banking modernization through legacy system upgrades and integration of advanced enterprise platforms to enhance security and compliance. Challenger banks leverage cloud-native core banking solutions to enable rapid innovation, seamless digital experiences, and cost-effective scalability.
Digital onboarding
Commercial banks generally offer digital onboarding processes integrated with extensive legacy systems, providing robust security features and broad service access, while challenger banks leverage agile technology platforms to deliver faster, more user-friendly digital onboarding experiences with minimal paperwork and instant account setup. Both models prioritize compliance with regulatory standards but challenger banks emphasize innovation and customer experience in digital onboarding to attract tech-savvy clients.
Open banking APIs
Commercial banks leverage extensive Open Banking APIs to provide a wide range of integrated financial services, ensuring robust security and compliance with regulatory standards. Challenger banks prioritize agile Open Banking APIs for seamless third-party app integrations, enabling faster innovation and personalized customer experiences within the digital banking ecosystem.
Fintech partnership models
Commercial banks leverage established fintech partnership models to enhance their product offerings and expand digital services, often integrating fintech solutions through APIs and joint ventures to deliver seamless customer experiences. Challenger banks predominantly build their platforms around fintech collaborations, utilizing agile, technology-driven models and open banking frameworks to rapidly innovate and personalize banking solutions for niche markets.
Hyper-personalized banking
Commercial banks typically offer standardized financial products with limited customization, while challenger banks leverage advanced AI and data analytics to deliver hyper-personalized banking experiences tailored to individual customer needs. This hyper-personalization enhances customer engagement by providing real-time insights, customized recommendations, and seamless digital interactions.
Cloud-native banking platforms
Commercial banks leverage established infrastructure and regulatory frameworks to support cloud-native banking platforms, enabling scalable and secure financial services with extensive branch networks. Challenger banks prioritize cloud-native architectures to offer agile, customer-centric digital banking experiences, benefiting from lower overhead and rapid innovation cycles.
Regulatory sandboxing
Commercial banks comply with stringent regulatory frameworks established by central banks to ensure financial stability, while challenger banks leverage regulatory sandboxing to test innovative financial products in a controlled environment with temporary regulatory relaxations. Regulatory sandboxing enables challenger banks to accelerate product development and enhance customer experience without compromising compliance, fostering competition and innovation within the banking sector.
Commercial bank vs Challenger bank for banking. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com