Freelancing offers flexible income potential by leveraging personal skills and expertise, allowing individuals to directly control their workload and rates. Dropshipping requires managing e-commerce operations with lower upfront costs but relies heavily on marketing and supplier relationships, often resulting in variable profit margins. Both income streams can be scalable, but freelancing provides more immediate revenue through specialized services while dropshipping demands strategic investment in customer acquisition and inventory management.
Table of Comparison
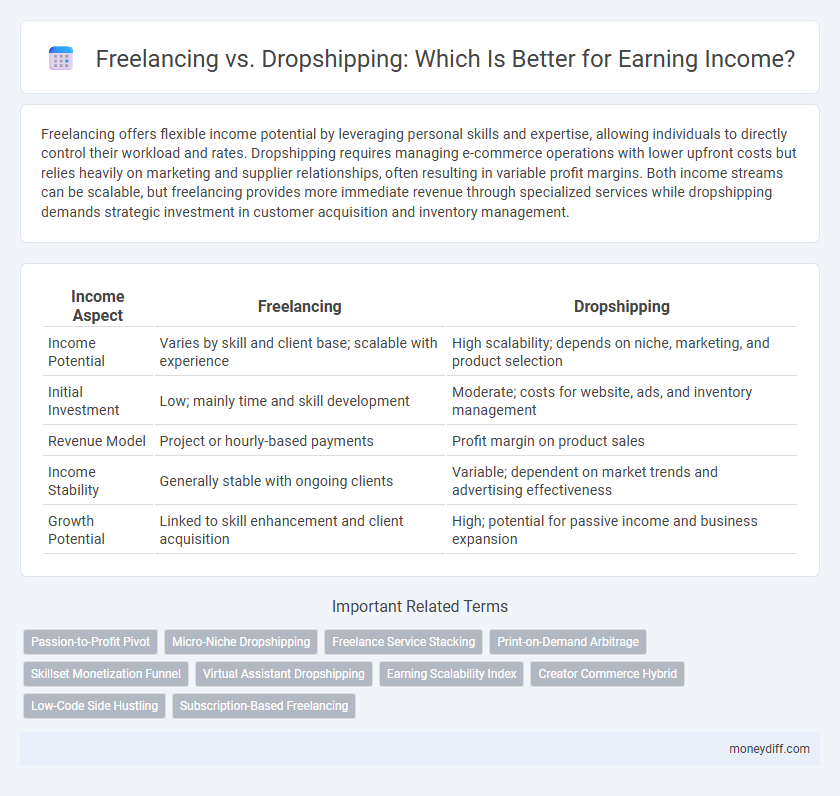
| Income Aspect | Freelancing | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Income Potential | Varies by skill and client base; scalable with experience | High scalability; depends on niche, marketing, and product selection |
| Initial Investment | Low; mainly time and skill development | Moderate; costs for website, ads, and inventory management |
| Revenue Model | Project or hourly-based payments | Profit margin on product sales |
| Income Stability | Generally stable with ongoing clients | Variable; dependent on market trends and advertising effectiveness |
| Growth Potential | Linked to skill enhancement and client acquisition | High; potential for passive income and business expansion |
Introduction: Freelancing vs Dropshipping for Income
Freelancing offers direct income through providing specialized skills or services, allowing flexible work hours and client diversity. Dropshipping generates income by selling products without inventory, relying on supplier partnerships and effective online marketing. Choosing between freelancing and dropshipping depends on individual expertise, risk tolerance, and long-term income goals.
Income Potential in Freelancing
Freelancing offers significant income potential through diverse skill-based projects and the ability to set competitive rates directly with clients. Income can scale rapidly as freelancers gain expertise, build a strong portfolio, and secure repeat contracts in high-demand fields like software development, graphic design, and digital marketing. Consistent client acquisition and specialization in lucrative niches enhance freelancers' earning capacity compared to the variable profits seen in dropshipping.
Earnings Overview: Dropshipping Profits
Dropshipping profits vary widely depending on product selection, supplier reliability, and market demand, often yielding initial profit margins between 10% to 30%. Successful dropshippers can scale income by leveraging high-demand niches and optimizing marketing strategies, with top performers earning thousands monthly. However, competition and fluctuating costs such as advertising can impact net earnings, requiring continuous adaptation to maintain profitability.
Upfront Costs and Investment Comparison
Freelancing requires minimal upfront costs, often limited to a computer and internet access, making it a low-investment option to start generating income quickly. Dropshipping demands a higher initial investment, including expenses for setting up an e-commerce store, marketing, and supplier partnerships. Comparing investment levels, freelancing offers a low-barrier entry with faster returns, whereas dropshipping involves more upfront financial commitment but has the potential for scalable income.
Consistency and Reliability of Income
Freelancing often results in inconsistent income due to fluctuating client demand and project availability, making financial planning challenging. Dropshipping can generate more consistent revenue streams by leveraging automated sales processes and scalable marketing strategies, though it requires significant upfront effort to establish reliable supplier relationships. Both models carry income variability risks, but dropshipping tends to offer more predictable earnings once the business is optimized.
Skill Requirements and Learning Curve
Freelancing demands specialized skills such as writing, coding, or graphic design, with a moderate learning curve depending on the profession and market competitiveness. Dropshipping requires knowledge of e-commerce platforms, digital marketing, and supply chain management, often involving a steeper learning curve to master inventory sourcing and customer acquisition. Skill acquisition in freelancing is more focused and task-specific, whereas dropshipping necessitates broader business and technical expertise for sustainable income generation.
Scaling Opportunities in Freelancing and Dropshipping
Freelancing offers scalable income through expanding client bases, increasing project complexity, and diversifying skill sets, enabling professionals to command higher rates and long-term contracts. Dropshipping scales by leveraging automation, broadening product ranges, and optimizing marketing strategies, allowing entrepreneurs to increase order volumes without significant inventory investment. Both models benefit from digital tools and platforms but require strategic growth management to maximize income potential.
Time Commitment and Flexibility
Freelancing offers high flexibility with control over working hours, enabling professionals to scale income by taking on multiple projects simultaneously. Dropshipping requires significant initial setup time and ongoing management but allows automation of sales processes, providing more passive income opportunities with less daily time commitment. Both income streams demand consistent effort, yet freelancing suits those prioritizing flexible schedules, while dropshipping appeals to entrepreneurs seeking scalable, low-time-intensive business models.
Financial Risks and Challenges
Freelancing income faces financial risks such as inconsistent payment schedules and client dependence, making cash flow unpredictable. Dropshipping carries challenges including inventory mismanagement, supplier reliability issues, and thin profit margins that can lead to losses. Both models require careful financial planning to mitigate risks and ensure sustainable earnings.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Money Goals
Freelancing offers flexible income opportunities based on individual skills and client demand, providing steady cash flow with lower startup costs, while dropshipping demands upfront investment in marketing and inventory management but can scale rapidly with effective e-commerce strategies. Assessing your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time commitment is crucial when choosing between freelancing's service-based earnings and dropshipping's product-focused revenue streams. Maximizing income potential depends on aligning your strengths with market demand and understanding the long-term scalability of each business model.
Related Important Terms
Passion-to-Profit Pivot
Freelancing allows individuals to leverage specific skills and passions, converting expertise directly into income through personalized client projects, fostering a sustainable passion-to-profit pivot. Dropshipping involves managing e-commerce sales without inventory, offering scalable income potential but requires strategic marketing and niche selection to successfully monetize passion-driven products.
Micro-Niche Dropshipping
Micro-niche dropshipping targets specific, high-demand product segments with low competition, resulting in higher profit margins and streamlined inventory management compared to general freelancing income streams. Freelancers rely on skill-based service fees, which can be variable and limited by time, whereas micro-niche dropshipping leverages automated sales channels for scalable and passive income growth.
Freelance Service Stacking
Freelance service stacking multiplies income streams by combining skills like content writing, graphic design, and digital marketing, creating higher-value packages for clients compared to relying solely on dropshipping profit margins. This approach leverages diverse expertise, resulting in consistent, scalable revenue and greater control over pricing and client acquisition.
Print-on-Demand Arbitrage
Freelancing offers direct skill-based income with minimal upfront costs, whereas dropshipping requires inventory management and customer service but enables scalable revenue through product arbitrage like print-on-demand. Print-on-demand arbitrage leverages customized designs on demand, reducing risk while maximizing profit margins through automated order fulfillment and targeted marketing strategies.
Skillset Monetization Funnel
Freelancing leverages specialized skillsets directly monetized through client projects, enabling precise control over income streams and scalability via diversified services. Dropshipping focuses on product sourcing and marketing skills, funneling income through automated sales processes but often requires significant investment in advertising and customer acquisition to maintain profitability.
Virtual Assistant Dropshipping
Virtual Assistant dropshipping generates income by managing online store operations, customer service, and product sourcing, allowing freelancers to earn through service fees and commissions without inventory risk. This model offers scalable revenue potential and flexible work hours compared to traditional freelancing roles that rely solely on hourly or project-based payments.
Earning Scalability Index
Freelancing offers a moderate Earning Scalability Index with income typically tied to billable hours or project rates, limiting exponential growth without proportional time investment. Dropshipping presents a higher scalability potential as it enables leveraging automated sales funnels and global market reach, allowing for passive income streams and rapid revenue expansion without direct proportional labor increase.
Creator Commerce Hybrid
Freelancing offers direct income through personalized services while dropshipping provides scalable product sales with low upfront costs; combining both in a Creator Commerce Hybrid model maximizes revenue by leveraging audience trust and diverse monetization channels. This hybrid approach enhances cash flow stability and growth potential by integrating content creation, personalized offerings, and automated e-commerce systems.
Low-Code Side Hustling
Freelancing offers immediate income generation through low-code platforms like Webflow and Airtable, enabling quick project delivery without extensive coding knowledge, while dropshipping requires setting up automated e-commerce stores via Shopify or WooCommerce low-code tools that scale with passive income potential. Leveraging low-code side hustling in freelancing tends to provide faster cash flow and client diversification, whereas dropshipping demands upfront marketing investment but can yield higher long-term revenue with optimized product sourcing and order fulfillment.
Subscription-Based Freelancing
Subscription-based freelancing offers a steady and predictable income stream by charging clients recurring fees for ongoing services, contrasting with dropshipping's income variability tied to product sales and market demand fluctuations. This model enhances financial stability and client retention, making it a preferable choice for freelancers seeking consistent revenue growth.
Freelancing vs Dropshipping for Income. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com