Commission income is earned as a fixed percentage or fee for facilitating sales or services, directly tied to individual transactions. Revenue share income represents a portion of overall profits or earnings from a business or platform, often linked to long-term partnerships or investments. Professional earnings from commission income tend to fluctuate based on performance, while revenue share income provides a more consistent, passive income stream.
Table of Comparison
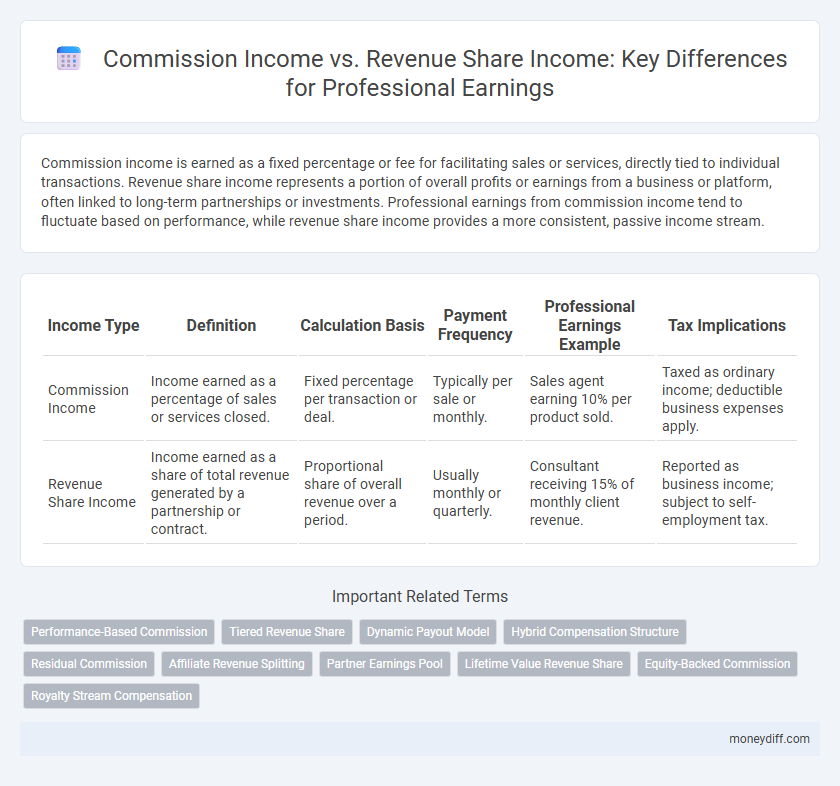
| Income Type | Definition | Calculation Basis | Payment Frequency | Professional Earnings Example | Tax Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commission Income | Income earned as a percentage of sales or services closed. | Fixed percentage per transaction or deal. | Typically per sale or monthly. | Sales agent earning 10% per product sold. | Taxed as ordinary income; deductible business expenses apply. |
| Revenue Share Income | Income earned as a share of total revenue generated by a partnership or contract. | Proportional share of overall revenue over a period. | Usually monthly or quarterly. | Consultant receiving 15% of monthly client revenue. | Reported as business income; subject to self-employment tax. |
Understanding Commission Income in Professional Earnings
Commission income in professional earnings refers to the payments received as a percentage of sales or services facilitated, directly tied to performance metrics such as total sales value or client transactions. This income type is distinct from revenue share income, which typically involves ongoing profits shared from business operations or partnerships rather than direct sales outcomes. Understanding the nuances of commission income helps professionals optimize earnings by focusing on measurable sales targets and transaction volumes.
Defining Revenue Share Income for Professionals
Revenue share income for professionals refers to earnings derived from a predetermined percentage of the profits or sales generated by a business or project they contribute to. Unlike commission income, which is typically a fixed percentage per transaction or sale, revenue share income fluctuates based on overall business performance and profitability. This model incentivizes professionals to enhance the value and success of the enterprise, aligning their financial rewards with long-term growth.
Key Differences Between Commission and Revenue Share Income
Commission income is earned based on a fixed percentage or flat fee for each sale or transaction completed, providing direct compensation for individual performance. Revenue share income involves receiving a portion of the overall revenue generated by a business or product, typically reflecting ongoing earnings tied to the company's success. The key difference lies in commission being transaction-specific and immediate, while revenue share represents a continuous income stream dependent on total revenue growth.
Pros and Cons of Commission-Based Earnings
Commission income provides professionals with the advantage of direct correlation between effort and earnings, motivating increased productivity and performance. However, this model entails income variability and dependence on sales success, which can lead to financial instability and stress. Unlike fixed revenue share income, commissions lack predictability but offer potential for higher earnings during peak performance periods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Revenue Share Models
Revenue share models offer the advantage of aligning incentives between professionals and partners by distributing earnings based on actual sales performance, promoting sustained collaboration and scalable income potential. However, these models may present disadvantages such as variability in income due to market fluctuations and the complexity of tracking accurate revenue attribution, which can lead to disputes or delayed payments. Unlike fixed commission income, revenue share demands ongoing engagement and transparency, making it crucial for professionals to evaluate partnership terms carefully before committing.
Impact on Long-Term Financial Stability
Commission income provides immediate earnings based on sales or services rendered, offering short-term financial boosts but often fluctuating with market demand. Revenue share income generates ongoing returns tied to the performance of a business or investment, contributing to sustained cash flow and enhancing long-term financial stability. Professionals relying on revenue share income benefit from a more predictable and scalable financial foundation compared to the variability of commission-based earnings.
Income Predictability: Commission vs Revenue Share
Commission income offers greater predictability with fixed rates tied directly to sales volume, allowing professionals to estimate earnings more accurately. Revenue share income fluctuates based on overall business performance and profit margins, making it less consistent but potentially more lucrative during growth periods. Understanding these differences helps professionals balance stable income streams with variable earning opportunities.
Tax Implications of Each Income Type
Commission income is typically classified as earned income and is subject to ordinary income tax rates and payroll taxes, including Social Security and Medicare. Revenue share income may sometimes be treated as passive income, potentially qualifying for different tax treatment such as lower capital gains rates or exemption from self-employment taxes, depending on the structure of the agreement. Understanding the IRS classification of each income type is crucial for accurate tax reporting and optimizing professional earnings.
Which Model Best Suits Your Professional Goals?
Commission income provides a fixed percentage of sales or transactions, ideal for professionals seeking predictable earnings tied to individual performance. Revenue share income offers a variable portion of overall profits, benefiting those aiming for long-term growth and aligned interests with a business or platform. Assess your goal for stability or scalable rewards to determine which income model best suits your professional objectives.
Strategies to Maximize Earnings from Both Income Streams
Maximizing earnings from commission income involves targeting high-margin sales and negotiating higher commission rates with partners, while revenue share income benefits from expanding client networks and fostering long-term partnerships. Leveraging data analytics to identify top-performing products can optimize both streams by focusing efforts where returns are highest. Diversifying income sources and maintaining transparent accounting practices ensure sustainable growth in professional earnings.
Related Important Terms
Performance-Based Commission
Performance-based commission income directly correlates with individual sales or client acquisitions, ensuring earnings fluctuate based on measurable achievements. Revenue share income represents a proportional stake in ongoing business profits, providing a steady, often passive, income stream linked to company-wide performance.
Tiered Revenue Share
Tiered revenue share income provides professionals with escalating earnings percentages based on performance milestones, offering a scalable advantage over fixed commission income. This model incentivizes higher productivity by aligning income growth directly with measurable revenue tiers, optimizing professional earnings potential.
Dynamic Payout Model
Commission income is typically a fixed percentage earned from individual sales or services rendered, whereas revenue share income involves receiving a proportionate slice of overall business revenue, often fluctuating with total earnings. The dynamic payout model adjusts these incomes in real-time, aligning professional earnings with performance metrics and business growth trends to maximize profitability.
Hybrid Compensation Structure
Commission income is earned based on individual sales performance, typically representing a fixed percentage of each transaction, while revenue share income derives from a proportion of total business profits or earnings, reflecting collective success. A hybrid compensation structure combines both models, providing professionals with a balanced income stream that incentivizes personal achievement and aligns with overall company growth.
Residual Commission
Residual commission income generates ongoing earnings from repeat sales or services, creating a stable, passive income stream for professionals beyond initial transactions. Commission income typically represents a one-time payment, while revenue share income involves continuous financial benefits tied to long-term business performance or client retention.
Affiliate Revenue Splitting
Commission income represents a fixed percentage paid to affiliates based on each individual sale, ensuring predictable earnings per transaction. Revenue share income, often used in affiliate revenue splitting, allocates a portion of the overall profits or sales generated over time, incentivizing affiliates to drive sustained performance and growth.
Partner Earnings Pool
Commission income represents direct payments earned from sales or services rendered, while revenue share income involves a percentage of overall profits generated by collaborative efforts. In the Partner Earnings Pool, revenue share maximizes long-term value by aligning partner incentives with collective business growth and profitability.
Lifetime Value Revenue Share
Commission income is typically a one-time payment based on individual sales or transactions, while revenue share income, especially Lifetime Value Revenue Share, provides ongoing earnings derived from a client's long-term spending and engagement. Focusing on Lifetime Value Revenue Share maximizes professional earnings by leveraging continuous income streams tied to the total future value generated by the customer relationship.
Equity-Backed Commission
Equity-backed commission income combines traditional sales commissions with ownership stakes, aligning professional earnings with long-term company performance and value appreciation. Unlike standard revenue share income, which provides a percentage of ongoing sales, equity-backed commissions incentivize sustained growth and offer potential capital gains beyond immediate cash flow.
Royalty Stream Compensation
Commission income is earned as a fixed percentage or fee based on sales or services rendered, providing predictable cash flow for professionals. Revenue share income, often linked to royalty stream compensation, involves receiving a portion of ongoing earnings from intellectual property or business profits, aligning long-term incentives with the success of the underlying asset.
Commission income vs Revenue share income for professional earnings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com