Trading income generates returns through buying and selling assets, often benefiting from market volatility and short-term price movements. Yield farming income derives from lending or staking cryptocurrencies in decentralized finance protocols, typically offering passive returns based on interest or reward tokens. While trading income can be higher but more volatile, yield farming provides consistent, albeit usually lower, returns with lower active management requirements.
Table of Comparison
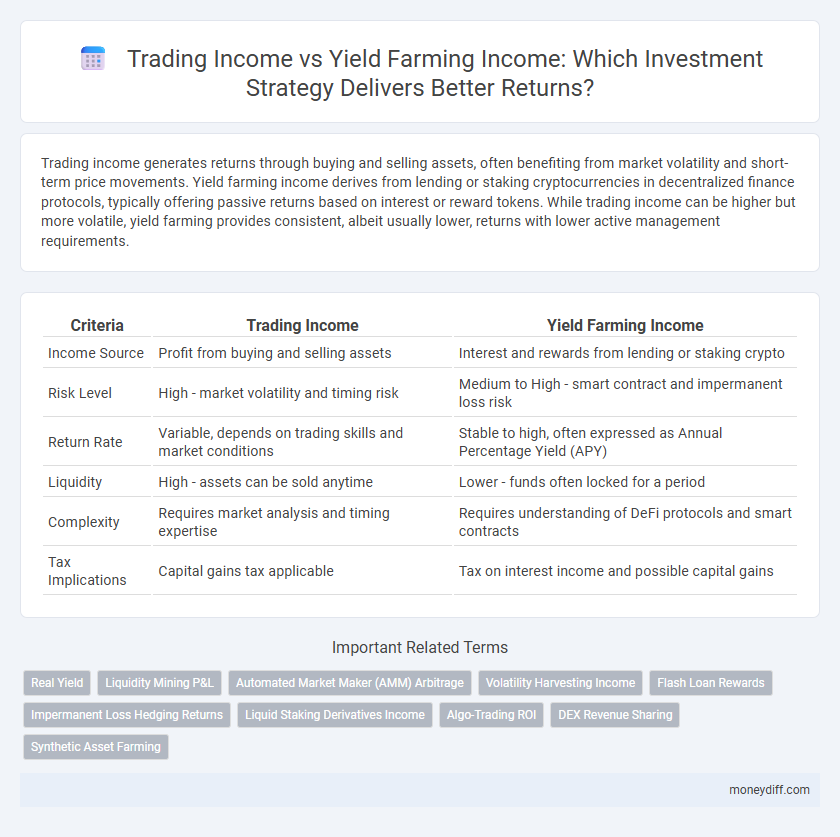
| Criteria | Trading Income | Yield Farming Income |
|---|---|---|
| Income Source | Profit from buying and selling assets | Interest and rewards from lending or staking crypto |
| Risk Level | High - market volatility and timing risk | Medium to High - smart contract and impermanent loss risk |
| Return Rate | Variable, depends on trading skills and market conditions | Stable to high, often expressed as Annual Percentage Yield (APY) |
| Liquidity | High - assets can be sold anytime | Lower - funds often locked for a period |
| Complexity | Requires market analysis and timing expertise | Requires understanding of DeFi protocols and smart contracts |
| Tax Implications | Capital gains tax applicable | Tax on interest income and possible capital gains |
Overview: Trading Income vs Yield Farming Income
Trading income generates returns through buying and selling assets frequently, capturing short-term price fluctuations, while yield farming income is earned by providing liquidity to decentralized finance protocols and receiving interest or token rewards. Trading income is typically more volatile and requires active management, whereas yield farming income tends to be more passive but can involve risks like smart contract vulnerabilities. Investors comparing these income sources should consider factors such as liquidity, risk tolerance, tax implications, and expected return stability.
Defining Trading Income in Investment Portfolios
Trading income in investment portfolios refers to profits generated from the frequent buying and selling of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, aiming to capitalize on short-term price movements. This income contrasts with yield farming income, which derives from providing liquidity to decentralized finance protocols and earning interest or rewards. Trading income is typically characterized by higher volatility and potential tax implications due to the active management and short holding periods of the traded assets.
Understanding Yield Farming Income in DeFi
Yield farming income in DeFi involves earning returns by providing liquidity or staking assets on decentralized platforms, often generating rewards in the form of native tokens. Unlike traditional trading income derived from buying low and selling high, yield farming offers passive income through interest, fees, or token incentives based on the amount and duration of liquidity provided. Understanding yield farming requires analyzing risks such as impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, and market volatility, which directly impact net returns compared to trading profits.
Risk Profiles: Trading versus Yield Farming
Trading income involves high volatility with rapid price fluctuations, exposing investors to market risks and potential significant losses, whereas yield farming income typically offers more stable, predictable returns through interest or rewards on crypto deposits but carries risks like smart contract vulnerabilities and liquidity shocks. Traders face short-term market timing risks that require active management, while yield farmers encounter protocol-specific risks and impermanent loss due to token price changes. Understanding these distinct risk profiles helps investors align their risk tolerance with either the aggressive nature of trading or the comparatively steady, yet technical, challenges of yield farming.
Return Potential: Comparing Gains Over Time
Trading income offers potential for high short-term gains through market volatility, while yield farming income provides more stable, passive returns by locking assets in decentralized finance protocols. Historical data shows trading can generate significant profits quickly but carries higher risk and requires active management, whereas yield farming yields consistent, compounding interest over longer periods with moderate risk. Investors seeking rapid capital appreciation may prefer trading, but those prioritizing steady, predictable income often benefit more from yield farming strategies.
Liquidity Considerations for Investors
Trading income often provides higher liquidity as assets can be quickly bought or sold on exchanges, enabling investors to access funds rapidly. Yield farming income, while potentially offering higher returns through staking or liquidity pools, typically involves locking assets for fixed periods, reducing immediate liquidity. Investors must weigh the balance between accessible cash flow from trading and the longer-term commitment inherent in yield farming to optimize their portfolio's liquidity needs.
Volatility: Managing Market Fluctuations
Trading income experiences higher volatility due to rapid market price changes, resulting in unpredictable short-term gains or losses. Yield farming income offers relatively stable returns by leveraging liquidity pools and protocol incentives, but it remains susceptible to impermanent loss and smart contract risks. Effective management of market fluctuations requires balancing active trading strategies with yield farming's passive income potential to optimize overall portfolio stability.
Capital Requirements and Entry Barriers
Trading income typically demands higher capital requirements and faces significant entry barriers due to the need for advanced market knowledge, sophisticated tools, and regulatory compliance. Yield farming income often requires lower initial investment and easier access, leveraging decentralized finance platforms with fewer restrictions, though it involves risks like smart contract vulnerabilities. Investors should evaluate their capital availability and risk tolerance when choosing between trading and yield farming for optimal returns.
Regulatory and Security Factors
Trading income is subject to established financial regulations and often involves centralized platforms with stringent compliance standards, enhancing investor protection. Yield farming income, while potentially higher, operates in decentralized protocols that face regulatory uncertainty and elevated risks of smart contract vulnerabilities. Investors must weigh the security protocols and evolving legal landscape when choosing between trading and yield farming for sustainable returns.
Optimal Strategies for Maximizing Investment Returns
Trading income generates returns through active asset buying and selling, capitalizing on market volatility and price fluctuations to maximize short-term profits. Yield farming income, derived from cryptocurrency staking and liquidity provision, offers passive, steady returns by leveraging decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and interest rewards. Combining active trading strategies with yield farming diversification optimizes investment returns by balancing risk exposure and consistent income streams.
Related Important Terms
Real Yield
Trading income generates returns through short-term asset price fluctuations, often incurring higher fees and taxes, whereas yield farming income stems from providing liquidity in decentralized finance protocols, producing real yield via interest and reward tokens. Real yield in yield farming reflects actual economic profit derived from protocol revenue and asset appreciation, offering more sustainable and predictable investment returns compared to trading income's speculative nature.
Liquidity Mining P&L
Trading income generates returns through the active buying and selling of assets, often subject to market volatility and short-term price fluctuations impacting profit and loss (P&L) margins. Yield farming income, particularly from liquidity mining, offers passive rewards by providing asset liquidity to DeFi protocols, earning fees and token incentives that contribute to a steady P&L stream, though risks include impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities.
Automated Market Maker (AMM) Arbitrage
Trading income from Automated Market Maker (AMM) arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, generating consistent profits through low-latency, high-frequency transactions. Yield farming income, while rewarding liquidity provision with interest and tokens, typically involves higher risk and impermanent loss compared to the strategic precision of AMM arbitrage trading.
Volatility Harvesting Income
Trading income fluctuates significantly due to market volatility, providing opportunities for volatility harvesting through frequent asset repositioning. Yield farming income generates relatively stable returns by leveraging decentralized finance protocols, but its volatility harvesting potential is limited compared to active trading strategies.
Flash Loan Rewards
Trading income generates profits through asset price fluctuations, while yield farming income derives from providing liquidity to decentralized finance protocols. Flash loan rewards, a high-frequency DeFi strategy, offer unique arbitrage opportunities by exploiting instantaneous uncollateralized loans, potentially maximizing yield farming returns beyond typical trading strategies.
Impermanent Loss Hedging Returns
Trading income generates returns through buying low and selling high in volatile markets, often exposing investors to price fluctuations, while yield farming income derives from providing liquidity and earning fees and rewards, but is subject to impermanent loss risks. Hedging impermanent loss in yield farming can enhance net returns by offsetting price divergence between pooled assets, improving overall investment performance compared to pure trading strategies.
Liquid Staking Derivatives Income
Trading income from liquid staking derivatives offers higher short-term gains through active market participation, while yield farming income provides more stable and predictable returns by locking assets in DeFi protocols. Investors in liquid staking derivatives benefit from both staking rewards and derivative trading opportunities, enhancing overall portfolio diversification and income potential.
Algo-Trading ROI
Trading income from algorithmic strategies typically offers higher short-term ROI due to rapid market executions and data-driven decisions, whereas yield farming income provides more stable but variable returns based on liquidity provision and DeFi protocols' interest rates. ALGO-based trading leverages predictive models and backtested signals to maximize returns, often outperforming yield farming yields which depend heavily on platform rewards and token price volatility.
DEX Revenue Sharing
Trading income from decentralized exchanges (DEXs) relies on fees generated through active asset swaps, offering variable returns based on market volatility and trading volume. Yield farming income, derived from providing liquidity to DEX pools, earns proportional DEX revenue sharing and additional token incentives, typically resulting in more stable, passive investment returns compared to trading profits.
Synthetic Asset Farming
Trading income generates returns through the buying and selling of assets, relying heavily on market volatility and timing, while yield farming income, particularly from synthetic asset farming, derives from providing liquidity and collateral to decentralized protocols that mint synthetic derivatives, offering more predictable and often compounded returns. Synthetic asset farming leverages synthetic tokens pegged to real-world assets, enabling investors to earn yield without direct exposure to the underlying asset's price fluctuations.
Trading Income vs Yield Farming Income for investment returns. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com