Investment returns typically focus on maximizing financial gains through assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, emphasizing growth and capital appreciation. Social investing profits prioritize generating positive social or environmental impact alongside financial income, often balancing ethical considerations with sustainable returns. Both approaches influence overall investment income but differ in their core objectives and risk-reward profiles.
Table of Comparison
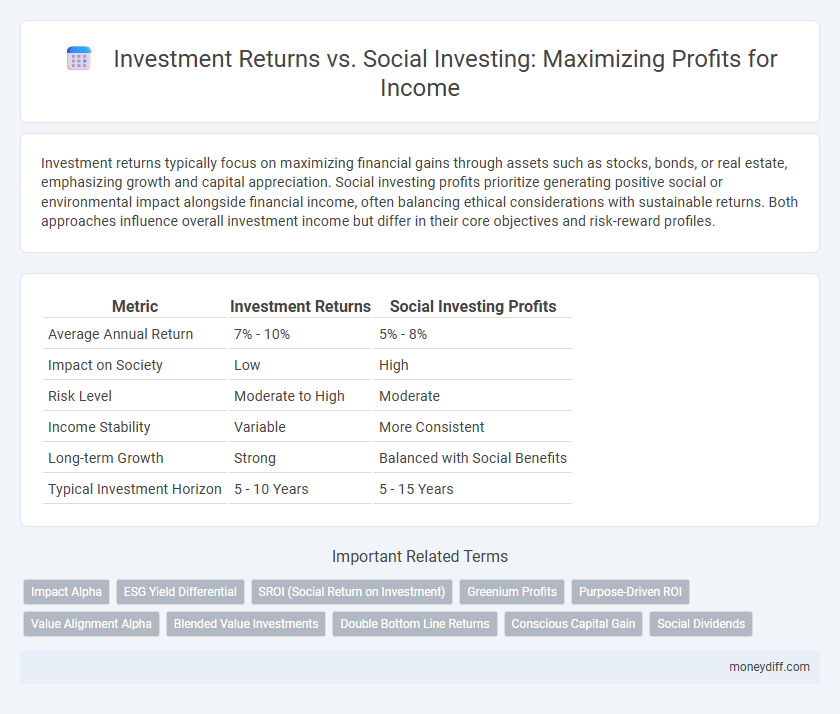
| Metric | Investment Returns | Social Investing Profits |
|---|---|---|
| Average Annual Return | 7% - 10% | 5% - 8% |
| Impact on Society | Low | High |
| Risk Level | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Income Stability | Variable | More Consistent |
| Long-term Growth | Strong | Balanced with Social Benefits |
| Typical Investment Horizon | 5 - 10 Years | 5 - 15 Years |
Comparing Investment Returns and Social Investing Profits
Traditional investment returns typically emphasize maximizing financial gain through stocks, bonds, or real estate appreciation, often yielding higher short-term profits. Social investing profits prioritize measurable social impact alongside financial income, potentially resulting in modest but sustainable returns tied to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Balancing these approaches involves evaluating the trade-offs between pure financial growth and the broader societal benefits embedded in social investment portfolios.
Understanding Investment Income: Traditional vs. Social Approaches
Investment income from traditional investments primarily comes from dividends, interest, and capital gains, focusing on financial returns. Social investing profits integrate financial performance with social impact metrics, aiming for positive environmental or social outcomes alongside monetary gains. Comparing these approaches highlights the balance between maximizing financial returns and generating measurable social value in income portfolios.
Evaluating Profitability in Social Investing
Evaluating profitability in social investing requires analyzing both traditional investment returns and the broader impact on social outcomes. Investment returns focus on financial gains measured by metrics like ROI and annual yield, while social investing profits incorporate social value creation alongside monetary income. Balancing these factors involves integrating financial performance with impact assessments to optimize overall income and community benefits.
Financial Returns: Mainstream Investments vs. Social Investments
Mainstream investments typically deliver higher financial returns due to their focus on profit maximization and market-driven growth, often yielding average annual returns of 7-10%. Social investments prioritize social impact alongside financial performance, resulting in moderately lower returns, generally around 4-6%, but with added benefits like community development and environmental sustainability. Investors balancing income goals may consider diversified portfolios combining both approaches to achieve a blend of robust financial returns and positive social outcomes.
Measuring Income Performance: Social Impact vs. Traditional Assets
Measuring income performance requires comparing traditional investment returns with social investing profits, where social impact metrics often complement financial outcomes. Traditional assets prioritize numerical returns such as ROI and yield, whereas social investing integrates social and environmental benefits alongside income generation. Investors increasingly use hybrid performance indicators to assess both monetary gains and positive societal contributions, achieving balanced income performance analysis.
Risk and Reward Factors in Social vs. Conventional Investing
Investment returns in conventional investing typically offer higher predictability and potential for financial gains, driven by market trends and economic indicators. Social investing prioritizes ethical impact and sustainability, often accepting lower or variable profits in exchange for positive social outcomes. Risk factors in social investing include regulatory changes and market volatility in emerging sectors, while conventional investing risks center on economic downturns and asset depreciation.
The Role of ESG in Investment Income Generation
ESG factors significantly influence investment income by driving sustainable long-term returns and mitigating risks associated with environmental, social, and governance issues. Investment returns increasingly reflect the financial performance of companies committed to responsible practices, attracting capital from socially focused investors. Social investing profits often stem from aligning portfolios with ESG criteria, which enhances both financial gains and positive societal impact.
Balancing Profit and Purpose in Investment Strategies
Balancing investment returns with social investing profits requires a strategic approach that integrates financial gains and positive societal impact. Prioritizing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria alongside traditional financial metrics enhances portfolio resilience and long-term growth. Investors who align profit motives with social responsibility often experience sustainable income streams and improved risk-adjusted returns.
Long-Term Income Growth: Social Investing Compared to Traditional Investments
Long-term income growth from social investing often targets sustainable, ethical companies that prioritize environmental and social governance (ESG) factors, potentially delivering competitive returns alongside positive societal impact. Traditional investments may offer higher immediate financial returns but can lack the resilience and reputation benefits associated with socially responsible portfolios. Over time, research shows that portfolios integrating ESG criteria tend to experience lower volatility and more stable income streams, enhancing overall investment income growth.
Key Metrics for Assessing Social Investing Returns
Key metrics for assessing social investing returns include financial yield, social impact measurement, and risk-adjusted returns, which help quantify both monetary gains and positive societal outcomes. Tools such as the Social Return on Investment (SROI) ratio and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) scores provide critical insights into performance beyond traditional investment returns. Comparing these metrics to conventional investment returns enables investors to balance income goals with mission-driven impact effectively.
Related Important Terms
Impact Alpha
Investment returns typically prioritize financial gains, whereas social investing profits emphasize measurable positive social or environmental impact alongside financial performance. Impact Alpha highlights that blending traditional investment returns with social impact metrics attracts investors seeking both sustainable financial growth and meaningful societal change.
ESG Yield Differential
Investment returns in traditional portfolios often outperform social investing profits, yet ESG yield differentials demonstrate that companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices can achieve competitive or superior long-term income growth. Studies reveal ESG-integrated investments deliver resilience and risk-adjusted returns, narrowing the yield gap while promoting sustainable value creation.
SROI (Social Return on Investment)
Investment returns traditionally measure financial gains from assets, whereas Social Return on Investment (SROI) quantifies the broader social, environmental, and economic value generated alongside financial profits. Integrating SROI into investment income analysis highlights the impact-driven benefits, offering a comprehensive perspective that aligns profitability with positive societal outcomes.
Greenium Profits
Investment returns driven by Greenium profits highlight the premium investors receive for supporting environmentally sustainable projects, often outperforming traditional investments in terms of long-term income growth. Social investing profits capitalize on combining financial gain with positive environmental impact, leveraging market demand for green assets to enhance portfolio resilience and generate sustainable income streams.
Purpose-Driven ROI
Purpose-driven ROI prioritizes measurable social impact alongside financial gains, blending traditional investment returns with intentional social investing profits. This approach optimizes income by aligning capital growth with ethical values, attracting investors seeking both economic and societal benefits.
Value Alignment Alpha
Investment returns primarily focus on maximizing financial gains, whereas social investing profits emphasize generating positive societal impact alongside economic benefits. Value Alignment Alpha represents the value created when investment strategies integrate social and environmental goals with financial performance, leading to sustainable income streams aligned with investor ethics.
Blended Value Investments
Blended value investments combine financial returns with social impact, offering investors both competitive investment returns and measurable social investing profits. This approach maximizes income by aligning financial gains with positive community and environmental outcomes, creating a sustainable impact-driven revenue model.
Double Bottom Line Returns
Investment returns traditionally emphasize maximizing financial gains, while social investing profits integrate measurable social impact alongside monetary growth, achieving double bottom line returns that balance economic value with positive societal outcomes. This dual-focused approach attracts investors seeking sustainable income streams that contribute to both wealth accumulation and meaningful community development.
Conscious Capital Gain
Conscious capital gains prioritize ethical and sustainable investments, balancing financial returns with positive social impact to generate meaningful investment income. This approach contrasts traditional investment returns by integrating social investing profits, fostering long-term value creation for both investors and communities.
Social Dividends
Social investing profits generate social dividends that align financial returns with positive societal impact, often resulting in stable income streams alongside measurable community benefits. Compared to traditional investment returns, social dividends emphasize sustainable growth and long-term value creation that supports environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
Investment Returns vs Social Investing Profits for investment income. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com