Paper ledgers offer a tangible and straightforward method for expense recording but are prone to human error and limited accessibility. Blockchain ledgers enhance transparency and security by providing immutable, decentralized records that can be audited in real time. Choosing blockchain over paper ledgers streamlines expense tracking, reduces fraud, and improves financial accountability.
Table of Comparison
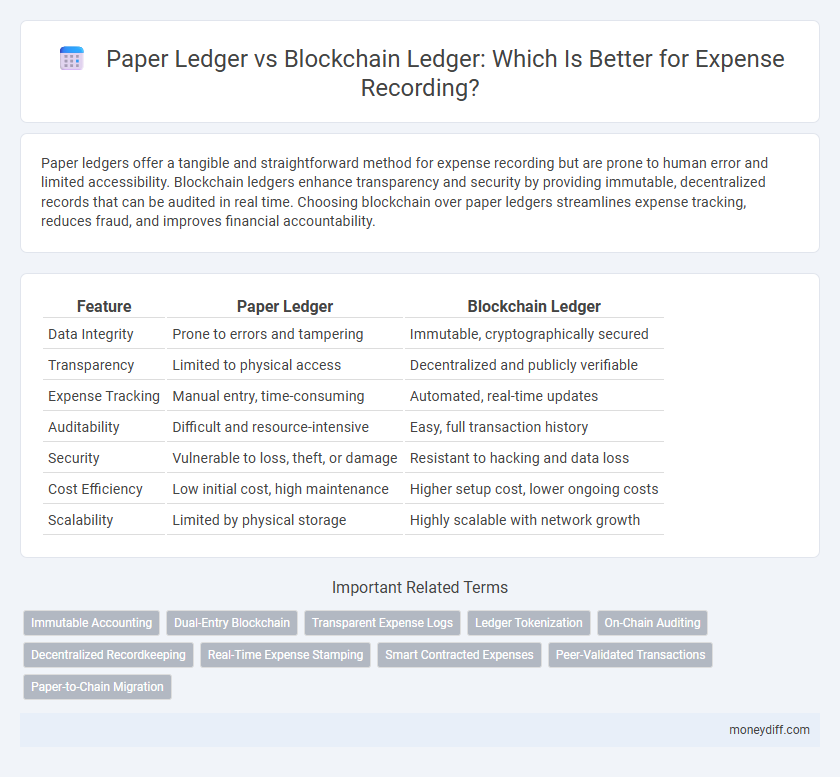
| Feature | Paper Ledger | Blockchain Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Prone to errors and tampering | Immutable, cryptographically secured |
| Transparency | Limited to physical access | Decentralized and publicly verifiable |
| Expense Tracking | Manual entry, time-consuming | Automated, real-time updates |
| Auditability | Difficult and resource-intensive | Easy, full transaction history |
| Security | Vulnerable to loss, theft, or damage | Resistant to hacking and data loss |
| Cost Efficiency | Low initial cost, high maintenance | Higher setup cost, lower ongoing costs |
| Scalability | Limited by physical storage | Highly scalable with network growth |
Introduction to Expense Recording Methods
Traditional expense recording relies on paper ledgers, providing a tangible, manual method for tracking financial transactions but prone to errors and limited accessibility. Blockchain ledgers offer a decentralized, immutable digital alternative that enhances transparency, security, and real-time expense verification through cryptographic validation. Businesses increasingly adopt blockchain technology to streamline expense management, reduce fraud, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
What is a Paper Ledger?
A paper ledger is a traditional method of recording expenses by manually writing financial transactions in a physical book or ledger. It offers a tangible, straightforward way to track income and expenses but lacks real-time updates and secure access controls. Compared to blockchain ledgers, paper ledgers are more vulnerable to errors, loss, and fraud due to their reliance on manual entry and physical storage.
Understanding Blockchain Ledgers
Blockchain ledgers provide a decentralized, immutable record of expenses that enhances transparency and reduces the risk of fraud compared to traditional paper ledgers. Each transaction is cryptographically secured and time-stamped, enabling real-time auditing and accurate tracking across multiple parties without a central authority. This system improves data integrity and operational efficiency for expense recording by eliminating manual errors and ensuring consistent, tamper-proof records.
Accuracy and Transparency in Record-Keeping
Blockchain ledger offers superior accuracy in expense recording by utilizing decentralized verification and cryptographic security, minimizing errors and tampering compared to traditional paper ledgers. The transparent nature of blockchain permits real-time auditing and traceability of transactions, enhancing accountability and reducing the risk of fraud. In contrast, paper ledgers are prone to human error, manipulation, and delayed reconciliation, making them less reliable for maintaining precise and transparent financial records.
Security Features: Paper vs Blockchain
Paper ledgers rely on physical security measures such as locked storage and restricted access, but they remain vulnerable to theft, damage, and forgery. Blockchain ledgers utilize cryptographic encryption, decentralized consensus mechanisms, and immutability to ensure tamper-proof and transparent expense recording. The inherent security features of blockchain significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized alterations compared to traditional paper-based expense tracking.
Accessibility and Ease of Use
Paper ledgers offer straightforward accessibility with tangible record-keeping, requiring minimal technical skills that accommodate users unfamiliar with digital tools. Blockchain ledgers provide enhanced accessibility through decentralized platforms accessible globally via smartphones or computers, while offering automated data validation for accuracy. Ease of use favors paper for simple manual entries but blockchain excels in preventing errors and enabling real-time expense tracking through user-friendly interfaces.
Cost Implications of Each Method
Paper ledgers for expense recording incur costs related to physical storage, printing supplies, and manual labor for data entry and reconciliation, often leading to higher ongoing operational expenses. Blockchain ledgers reduce these costs by automating transaction verification and eliminating the need for physical materials, but they require investment in digital infrastructure and energy consumption for network maintenance. Over time, blockchain ledgers offer greater cost efficiency due to enhanced transparency, reduced errors, and improved auditability, which can significantly lower compliance and fraud-related expenses.
Auditability and Fraud Prevention
Paper ledgers offer limited auditability and are susceptible to human error and tampering, increasing the risk of fraud in expense recording. Blockchain ledgers provide enhanced auditability through immutable, time-stamped records and decentralized verification, significantly reducing opportunities for fraudulent activities. The cryptographic security and transparency of blockchain ledgers ensure a robust and reliable system for expense tracking and fraud prevention.
Suitability for Personal vs Business Expenses
Paper ledgers remain suitable for personal expenses due to their simplicity, low cost, and ease of use without technological barriers. Blockchain ledgers offer enhanced security, transparency, and immutability, making them ideal for business expenses requiring audit trails and fraud prevention. For businesses, blockchain's decentralized nature supports real-time expense tracking and efficient financial reporting, surpassing traditional paper methods.
Future Trends in Expense Recording Technologies
Blockchain ledger technology is rapidly transforming expense recording by enhancing transparency, security, and real-time verification compared to traditional paper ledgers. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of decentralized expense tracking systems integrated with AI-driven analytics to automate reconciliation and fraud detection. These innovations promise increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved compliance in corporate financial management.
Related Important Terms
Immutable Accounting
Paper ledgers offer a physical record of expenses but are susceptible to errors, tampering, and loss, compromising the integrity of financial data. Blockchain ledgers provide immutable accounting by securely recording expense transactions on a decentralized, tamper-proof digital ledger, ensuring transparent and auditable financial records.
Dual-Entry Blockchain
Dual-entry blockchain ledgers offer enhanced transparency and immutability for expense recording compared to traditional paper ledgers, reducing errors and fraud through cryptographic verification of each transaction. This system inherently supports real-time auditing and seamless reconciliation, streamlining expense management processes for businesses.
Transparent Expense Logs
Blockchain ledgers offer transparent expense logs by providing immutable, timestamped records accessible to all authorized parties, eliminating discrepancies common in paper ledgers. Unlike traditional paper ledger entries susceptible to tampering and loss, blockchain ensures secure, auditable expense tracking with real-time updates.
Ledger Tokenization
Ledger tokenization in blockchain transforms traditional paper ledger expenses into secure, tamper-proof digital assets, enabling real-time tracking and automated auditing. This enhances transparency, reduces fraud risks, and streamlines expense reconciliation compared to manual, error-prone paper ledgers.
On-Chain Auditing
Paper ledgers lack real-time transparency and are prone to human error, making expense tracking less reliable compared to blockchain ledgers; blockchain enables on-chain auditing by providing immutable, time-stamped records that enhance accuracy and fraud detection. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures expense transactions are securely verifiable and accessible for continuous auditing without manual reconciliation delays.
Decentralized Recordkeeping
Paper ledgers rely on centralized, physical recordkeeping, which increases risks of data loss, tampering, and limited accessibility, whereas blockchain ledgers offer decentralized recordkeeping, ensuring secure, immutable, and transparent expense tracking across multiple nodes. This decentralized architecture enhances trust in expense records by preventing single points of failure and enabling real-time verification and auditability.
Real-Time Expense Stamping
Blockchain ledgers enable real-time expense stamping by instantly recording transactions with immutable timestamps, ensuring accuracy and transparency. In contrast, paper ledgers rely on manual entry, causing delays and increasing the risk of errors in expense tracking.
Smart Contracted Expenses
Smart contracted expenses recorded on blockchain ledgers ensure real-time, tamper-proof verification and automated execution of expense agreements, enhancing transparency and reducing reconciliation errors compared to traditional paper ledgers. Blockchain's immutable ledger and programmable smart contracts streamline expense tracking and validation, minimizing fraud and administrative overhead in corporate financial management.
Peer-Validated Transactions
Paper ledgers lack the capability for peer-validated transactions, relying solely on centralized manual entry prone to errors and fraud. Blockchain ledgers enable decentralized peer validation, ensuring transparent, immutable records for accurate and trustworthy expense tracking.
Paper-to-Chain Migration
Migrating expense records from paper ledgers to blockchain ledgers enhances accuracy, security, and transparency by leveraging immutable, time-stamped entries that eliminate manual errors and fraud risks inherent in traditional bookkeeping. Blockchain integration streamlines audit processes and real-time expense tracking, significantly improving financial accountability and operational efficiency for organizations transitioning from outdated paper systems.
Paper Ledger vs Blockchain Ledger for expense recording. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com