Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month, providing predictable costs that help stabilize budgeting. Flexible expenses, including groceries and entertainment, vary based on lifestyle choices and can be adjusted to control spending. Balancing fixed and flexible expenses is essential for effective money management and achieving financial goals.
Table of Comparison
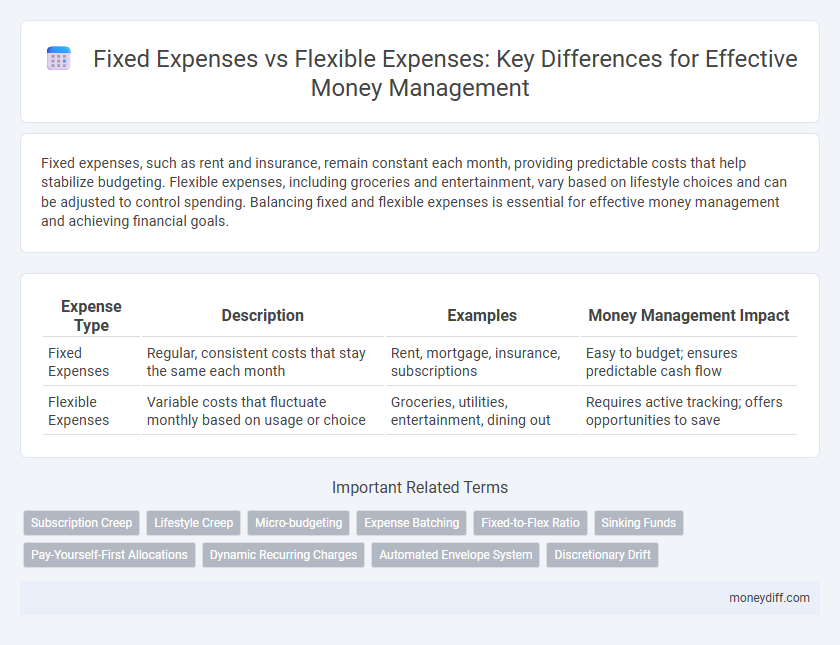
| Expense Type | Description | Examples | Money Management Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Expenses | Regular, consistent costs that stay the same each month | Rent, mortgage, insurance, subscriptions | Easy to budget; ensures predictable cash flow |
| Flexible Expenses | Variable costs that fluctuate monthly based on usage or choice | Groceries, utilities, entertainment, dining out | Requires active tracking; offers opportunities to save |
Understanding Fixed and Flexible Expenses
Fixed expenses, such as rent, insurance premiums, and loan payments, remain constant each month and are essential for stable budget planning. Flexible expenses, including groceries, entertainment, and utility bills, fluctuate based on consumption and lifestyle choices, requiring regular adjustment to avoid overspending. Understanding the distinction between fixed and flexible expenses enables effective money management by helping prioritize essential costs while controlling discretionary spending.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Flexible Expenses
Fixed expenses, such as rent, car payments, and insurance premiums, remain constant each month and are essential for budgeting stability, while flexible expenses like groceries, entertainment, and utility bills can vary significantly based on lifestyle choices and consumption. Fixed expenses provide predictability, making it easier to plan long-term financial goals, whereas flexible expenses offer opportunities for adjustment to manage cash flow during financial fluctuations. Understanding the key differences between these expenses allows for more effective money management by balancing consistent obligations with adaptable spending.
Common Examples of Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses typically include rent or mortgage payments, car loans, and insurance premiums, which remain consistent each month. These predictable costs are essential for creating a stable budget and ensuring financial obligations are met on time. Managing fixed expenses effectively helps maintain long-term financial stability and prevents unexpected budget shortfalls.
Typical Flexible Expenses in Every Budget
Typical flexible expenses in every budget include groceries, utilities, entertainment, and dining out, which vary monthly based on lifestyle and usage. These expenses offer adaptability for money management, allowing adjustments according to income fluctuations or saving goals. Tracking flexible expenses is essential for effective budgeting and identifying opportunities to reduce discretionary spending.
Why Distinguishing Expenses Matters in Money Management
Distinguishing fixed expenses like rent, utilities, and loan payments from flexible expenses such as entertainment, dining out, and hobbies is crucial for effective money management. Understanding these categories helps in budgeting accurately, ensuring essential costs are covered before allocating funds to discretionary spending. This distinction enables better financial planning, prevents overspending, and supports achieving long-term financial goals.
Strategies to Manage Fixed Expenses Effectively
Strategies to manage fixed expenses effectively include negotiating lower rates on recurring bills such as rent, insurance, and subscriptions, and opting for automatic payments to avoid late fees and maintain financial discipline. Tracking fixed expenses monthly helps identify opportunities for cost-cutting and ensures alignment with budget goals. Prioritizing fixed expense management stabilizes cash flow, enabling better allocation toward savings and flexible spending.
Tips for Controlling Flexible Expenses
Track flexible expenses monthly to identify spending patterns and potential areas for reduction. Set realistic budgets for categories like dining out, entertainment, and shopping to avoid overspending. Use apps or tools to monitor variable costs in real time, ensuring better control over discretionary spending and improving overall money management.
Balancing Fixed and Flexible Expenses for Financial Stability
Balancing fixed and flexible expenses is crucial for maintaining financial stability, as fixed costs such as rent and insurance provide predictable monthly obligations, while flexible expenses like dining out and entertainment offer adjustable spending based on available income. Allocating a consistent budget to fixed expenses ensures essential bills are covered, whereas managing flexible expenses with discretion allows for savings growth and emergency fund contributions. Effective money management hinges on optimizing this balance to prevent overspending and promote long-term financial health.
The Role of Expense Tracking in Budget Optimization
Expense tracking differentiates fixed expenses--such as rent, insurance, and loan payments--that remain constant monthly, from flexible expenses like groceries, entertainment, and utilities that vary based on consumption. By accurately monitoring and categorizing these expenses, individuals can identify spending patterns and make informed adjustments to optimize their budgets. This strategic approach enhances cash flow management, ensuring financial stability and goal achievement.
Adjusting Your Budget: Fixed vs Flexible Expense Considerations
Adjusting your budget requires a clear distinction between fixed expenses, such as rent and loan payments, which remain constant monthly, and flexible expenses, like dining out or entertainment, which vary based on lifestyle choices. Prioritizing reductions in flexible expenses provides greater control over discretionary spending without disrupting essential financial obligations. Tracking spending patterns monthly enables timely adjustments to maintain a balanced budget and optimize cash flow management.
Related Important Terms
Subscription Creep
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month, while flexible expenses fluctuate based on usage and choices, with subscription creep highlighting the unnoticed accumulation of recurring payments for services. Monitoring and regularly auditing subscriptions is crucial to prevent overspending and maintain effective money management.
Lifestyle Creep
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant and predictable, providing a stable foundation for budgeting, while flexible expenses, like dining out and entertainment, vary and can increase unnoticed, contributing significantly to lifestyle creep. Managing lifestyle creep requires closely monitoring flexible expenses to prevent gradual increases that undermine financial goals and savings.
Micro-budgeting
Fixed expenses such as rent and insurance remain constant each month, providing a stable baseline for micro-budgeting, while flexible expenses like groceries and entertainment fluctuate, allowing adjustments to optimize cash flow. Effective money management in micro-budgeting involves prioritizing fixed costs to ensure essentials are covered and dynamically controlling flexible spending to maintain financial balance.
Expense Batching
Expense batching optimizes money management by grouping fixed expenses such as rent and subscriptions separately from flexible expenses like dining or entertainment, enhancing tracking and budgeting accuracy. This approach reduces cognitive load, prevents overspending on variable costs, and ensures timely payments for recurring obligations.
Fixed-to-Flex Ratio
The Fixed-to-Flex Ratio measures the proportion of fixed expenses, such as rent and loan payments, to flexible expenses like entertainment and dining out, providing a clear framework for budgeting and cash flow management. Maintaining an optimal ratio, typically around 60:40, helps ensure financial stability by balancing essential obligations with discretionary spending.
Sinking Funds
Fixed expenses such as rent and insurance require consistent budgeting, while flexible expenses like entertainment fluctuate monthly, making sinking funds essential for proactive money management. Sinking funds allocate specific amounts over time to cover upcoming irregular costs within flexible expenses, reducing financial stress and avoiding debt.
Pay-Yourself-First Allocations
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, require consistent monthly payments, allowing for predictable budgeting, while flexible expenses like dining out and entertainment vary and need careful tracking to avoid overspending. Prioritizing pay-yourself-first allocations ensures savings and investments are funded before discretionary spending, strengthening long-term financial stability.
Dynamic Recurring Charges
Dynamic recurring charges, often classified under flexible expenses, fluctuate monthly based on usage or service adjustments, contrasting with fixed expenses that remain constant and predictable. Properly managing dynamic recurring charges through detailed tracking enhances budget accuracy and financial control in money management.
Automated Envelope System
Automated Envelope Systems categorize fixed expenses such as rent and utilities separately from flexible expenses like groceries and entertainment, enabling precise budgeting and real-time tracking. This digital method ensures timely allocation of funds, reduces overspending, and enhances overall financial discipline by automating reminders and adjustments based on spending patterns.
Discretionary Drift
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month, while flexible expenses, like dining out and entertainment, fluctuate based on lifestyle choices, often leading to discretionary drift where small increases in variable spending gradually erode budget goals. Monitoring discretionary drift is essential for effective money management, ensuring that non-essential spending does not unintentionally inflate flexible expenses and disrupt financial stability.
Fixed expenses vs Flexible expenses for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com