Disability insurance provides a monthly benefit if you become unable to work due to illness or injury, covering both short-term and long-term disabilities. Income protection insurance offers a broader safety net by replacing a portion of your income during temporary or permanent inability to work, often including rehabilitation and recovery support. Understanding the specific terms, waiting periods, and coverage limits is essential to choose the right policy for protecting your financial stability against income loss.
Table of Comparison
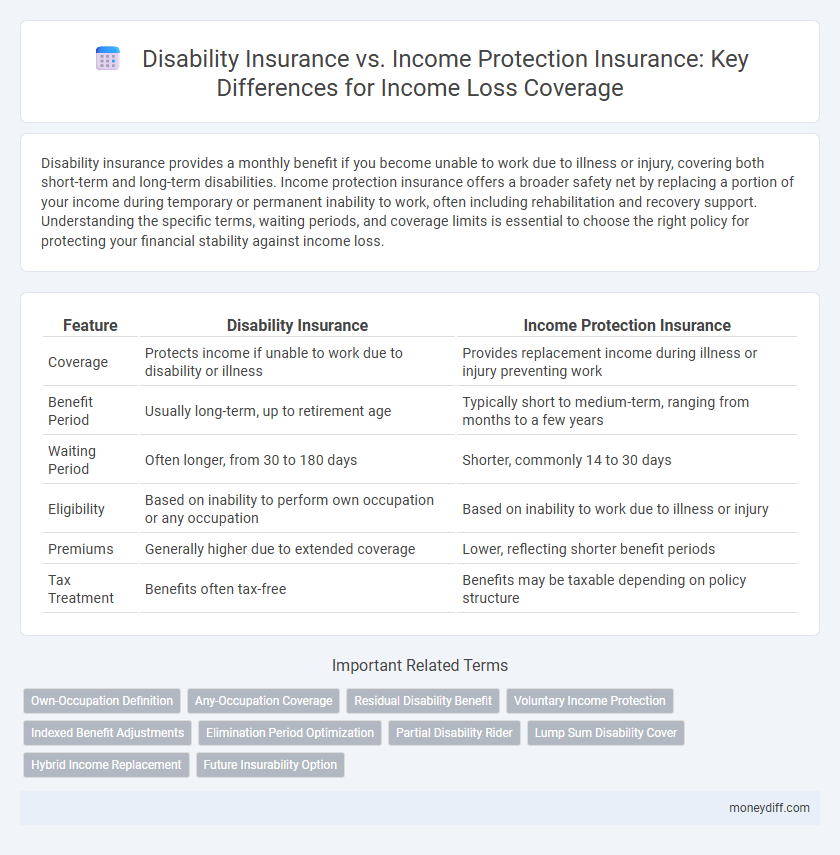
| Feature | Disability Insurance | Income Protection Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Protects income if unable to work due to disability or illness | Provides replacement income during illness or injury preventing work |
| Benefit Period | Usually long-term, up to retirement age | Typically short to medium-term, ranging from months to a few years |
| Waiting Period | Often longer, from 30 to 180 days | Shorter, commonly 14 to 30 days |
| Eligibility | Based on inability to perform own occupation or any occupation | Based on inability to work due to illness or injury |
| Premiums | Generally higher due to extended coverage | Lower, reflecting shorter benefit periods |
| Tax Treatment | Benefits often tax-free | Benefits may be taxable depending on policy structure |
Understanding Disability Insurance: Key Features
Disability insurance provides crucial financial support by replacing a portion of your income if an illness or injury prevents you from working, typically covering both short-term and long-term disabilities. It usually includes features such as elimination periods, benefit duration, and definition of disability, which determine when and how benefits are paid. Understanding these key elements ensures that policyholders receive adequate protection tailored to their specific income loss risks.
What is Income Protection Insurance?
Income Protection Insurance provides a regular income replacement if you are unable to work due to illness or injury, covering a percentage of your salary typically between 50% and 70%. Unlike Disability Insurance, which often pays a lump sum upon diagnosis of a specific condition, Income Protection Insurance supports ongoing financial stability by covering daily living expenses during extended periods of incapacity. This policy usually includes benefits such as waiting periods, benefit periods, and options for premium adjustments to align with your income needs.
Differences Between Disability and Income Protection Insurance
Disability insurance specifically covers loss of income due to injury or illness that prevents the insured from performing their job, often providing benefits based on a percentage of prior earnings. Income protection insurance offers broader coverage by supplementing lost income from various causes of incapacity, sometimes including unemployment or non-medical reasons. Unlike disability insurance, income protection policies tend to have more flexible payout periods and may cover partial disabilities or reduced work capacity.
Coverage Scope: Disability vs Income Protection
Disability insurance primarily provides coverage for income loss resulting from physical or mental disabilities that prevent you from performing your job functions, often requiring strict medical proof. Income protection insurance offers broader financial security by covering a wider range of circumstances, including illness or injury that reduces your ability to work, with more flexible payout periods tailored to individual needs. Understanding the coverage scope is essential to selecting the right policy for comprehensive income loss protection.
Eligibility Criteria Comparison
Disability Insurance typically requires applicants to meet strict medical and occupational criteria, focusing on the inability to perform their specific job, while Income Protection Insurance often provides broader eligibility by covering partial disabilities and alternative job roles. Income Protection policies may also accept applicants with pre-existing conditions under certain conditions, unlike traditional Disability Insurance which generally excludes these cases. Understanding the specific eligibility requirements, including waiting periods, income thresholds, and occupational classifications, is crucial for selecting the appropriate coverage.
Policy Exclusions and Limitations
Disability insurance often excludes coverage for pre-existing conditions, self-inflicted injuries, and injuries sustained during illegal activities, limiting the scope of income replacement. Income protection insurance typically imposes waiting periods before benefits begin and may exclude certain occupational hazards or mental health conditions. Understanding these policy exclusions and limitations is crucial for ensuring adequate financial protection during periods of income loss.
Benefit Payout Structures
Disability Insurance typically provides a fixed monthly benefit based on a percentage of your pre-disability income and continues until full recovery or policy expiration. Income Protection Insurance often offers more flexible payout structures, allowing benefits to be tailored according to the level and duration of income loss, sometimes including partial disability cover. Both policies require careful assessment of waiting periods, benefit caps, and term lengths to maximize financial security during income loss due to disability.
Cost and Premium Factors
Disability insurance premiums are often higher than income protection insurance due to broader coverage and longer benefit periods. Income protection insurance typically offers more flexible premium structures, influenced by factors such as occupation, age, and waiting periods. Cost differences also arise from varying definitions of disability and policy terms, affecting monthly premiums and overall affordability.
Claim Process: Disability vs Income Protection
Disability insurance claim process typically involves medical documentation and proof of total or partial disability verified by a licensed physician, often requiring ongoing validation of the claimant's inability to work. Income protection insurance claims focus on providing evidence of reduced income due to illness or injury, emphasizing partial loss rather than complete disability, with assessments that may include financial statements and employment verification. Both processes require thorough documentation but differ in criteria and evaluation periods based on the extent and nature of income loss.
Choosing the Right Insurance for Income Loss
Disability Insurance provides financial support when you are unable to work due to illness or injury, typically covering a percentage of your salary for long-term disabilities. Income Protection Insurance offers broader coverage, often including short-term benefits, partial disabilities, and a wider range of medical conditions affecting your ability to earn. Evaluating policy terms, benefit periods, waiting times, and coverage limits is crucial to choosing the right insurance for effective income loss protection.
Related Important Terms
Own-Occupation Definition
Disability insurance with an Own-Occupation definition provides benefits if you cannot work in your specific profession due to illness or injury, offering broader protection compared to Income Protection Insurance which often requires inability to perform any job. This distinction is critical for professionals like doctors or lawyers whose specialized skills may prevent them from working in their own occupation but allow employment in another capacity.
Any-Occupation Coverage
Disability insurance with any-occupation coverage offers benefits only if the insured cannot perform any job suited to their education, experience, or training, providing broader protection than income protection insurance, which typically covers loss of income due to inability to perform your own occupation. Any-occupation coverage ensures financial security in severe disability cases by restricting benefit eligibility to total inability to work in any capacity, making it a critical factor for comprehensive income loss protection.
Residual Disability Benefit
Residual Disability Benefit in Disability Insurance provides partial income replacement when policyholders can work but earn less due to their disability, ensuring ongoing financial support proportional to reduced earnings. Income Protection Insurance also offers this benefit, often with more flexible claim criteria and broader coverage, making it crucial for maintaining stable cash flow during partial work capacity.
Voluntary Income Protection
Voluntary Income Protection insurance offers tailored coverage for wage earners facing temporary or permanent disability, providing a percentage of income replacement based on policy terms and minimizing financial disruption during recovery. Unlike traditional Disability Insurance that often targets long-term disabilities, Voluntary Income Protection emphasizes flexible benefits and shorter waiting periods, catering specifically to unexpected income loss in workforce participation.
Indexed Benefit Adjustments
Disability Insurance with indexed benefit adjustments ensures your income replacement keeps pace with inflation, preserving your purchasing power during long-term disability periods. Income Protection Insurance often lacks automatic inflation adjustments, potentially reducing the real value of your benefits over time.
Elimination Period Optimization
Disability insurance elimination periods typically range from 30 to 90 days, balancing premium costs with income gap coverage during initial disability. Income protection insurance allows customized elimination periods, optimizing cash flow by aligning benefit payouts with personal financial reserves and recovery timelines.
Partial Disability Rider
Disability Insurance with a Partial Disability Rider offers benefits when policyholders can work reduced hours but suffer a loss of income, bridging gaps in earnings more precisely than standard Income Protection Insurance. This rider enhances financial security by providing partial income replacement specifically tailored for partial disabilities, ensuring continuous support during recovery periods.
Lump Sum Disability Cover
Lump Sum Disability Cover under Disability Insurance provides a one-time payment upon diagnosis of a specified disability, offering immediate financial support to cover significant expenses or debt, unlike Income Protection Insurance which delivers ongoing monthly income replacement. This lump sum can be crucial for managing large medical costs or modifying living arrangements, whereas Income Protection focuses on maintaining day-to-day household cash flow during prolonged income loss.
Hybrid Income Replacement
Hybrid Income Replacement combines features of Disability Insurance and Income Protection Insurance to provide comprehensive coverage for income loss due to illness or injury. This approach ensures partial income replacement by integrating short-term disability benefits with long-term income protection, offering enhanced financial security and flexibility tailored to individual risk profiles.
Future Insurability Option
Future Insurability Option in Disability Insurance allows policyholders to increase coverage without new medical exams when significant life events occur, preserving long-term protection against income loss. Income Protection Insurance typically lacks this feature, making Disability Insurance more adaptable for evolving financial needs and income stability.
Disability Insurance vs Income Protection Insurance for income loss. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com