Salary income is earned through employment, providing a fixed and predictable earnings stream based on work performed or hours worked. Royalty income, on the other hand, originates from intellectual property rights or natural resources, generating variable earnings depending on usage or sales. Understanding the tax implications and consistency of these income types is essential for effective financial planning and maximizing overall income.
Table of Comparison
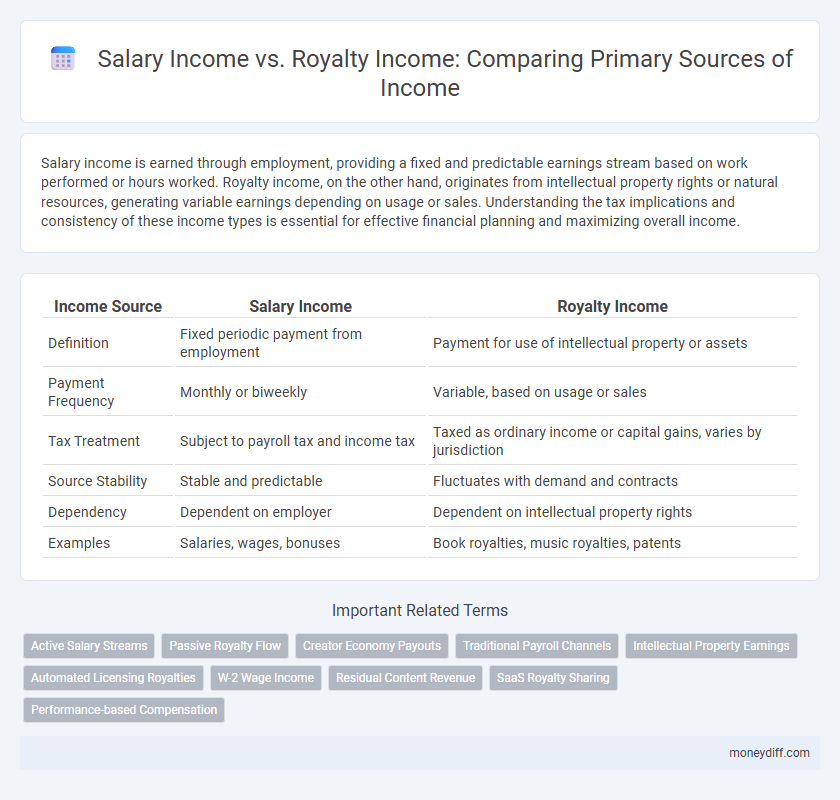
| Income Source | Salary Income | Royalty Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed periodic payment from employment | Payment for use of intellectual property or assets |
| Payment Frequency | Monthly or biweekly | Variable, based on usage or sales |
| Tax Treatment | Subject to payroll tax and income tax | Taxed as ordinary income or capital gains, varies by jurisdiction |
| Source Stability | Stable and predictable | Fluctuates with demand and contracts |
| Dependency | Dependent on employer | Dependent on intellectual property rights |
| Examples | Salaries, wages, bonuses | Book royalties, music royalties, patents |
Understanding Salary Income: Definition and Characteristics
Salary income refers to the fixed regular payment received by an employee from an employer, typically expressed as an annual or monthly amount. It is characterized by consistency, tax withholding at source, and dependency on employment tenure and position. Unlike royalty income, which is earned from intellectual property or asset licensing, salary income arises solely from active work or services rendered under an employment contract.
What Is Royalty Income? Key Features Explained
Royalty income is earnings received from granting others the right to use intellectual property such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, or natural resources. This type of income is typically recurring and based on agreements specifying payments as a percentage of revenue or a fixed amount per use. Key features include passive income nature, dependency on asset utilization, and tax treatment distinct from salary income.
Salary vs Royalty: Core Differences in Earning Methods
Salary income is earned through regular employment where an individual receives a fixed or variable amount based on agreed terms with an employer, typically paid monthly or biweekly. Royalty income arises from intellectual property rights, such as patents, copyrights, or natural resources, and is generated through ongoing payments linked to usage, sales, or production volume. The key difference lies in salary being a direct compensation for labor, while royalty income is derived from ownership and licensing agreements.
Stability and Predictability: Salary Income Compared to Royalties
Salary income offers greater stability and predictability as it is usually fixed, paid on a regular basis, and not directly influenced by market fluctuations. Royalty income, derived from intellectual property or natural resources, can vary significantly depending on sales performance, market demand, or resource availability, making it less consistent. Consequently, individuals relying on salary income often experience steady cash flow, while those dependent on royalties may face income variability.
Flexibility of Income: Royalty Streams vs Fixed Salaries
Royalty income offers greater flexibility by providing ongoing payments that fluctuate based on usage or sales, allowing income growth potential tied to the asset's performance. Salary income remains fixed and predictable, ensuring consistent monthly earnings but lacking scalability. For individuals seeking adaptable cash flow with long-term upside, royalties present a dynamic alternative to the stability of fixed salaries.
Risk and Security Factors: Salary Income vs Royalty Earnings
Salary income offers a stable and predictable cash flow with employer-backed benefits and legal protections, minimizing financial risk for employees. Royalty income, while potentially higher, is subject to market fluctuations and intellectual property performance, increasing variability and uncertainty. Evaluating the balance between guaranteed security and variable earnings is essential when comparing these income sources.
Tax Implications: Salaries Versus Royalty Payments
Salary income is typically subject to standard income tax rates with regular withholding by employers and mandatory contributions to social security and pension funds. Royalty income, often arising from intellectual property rights, may be taxed as ordinary income or under special regimes with possible withholding tax, and can be subject to different reporting requirements depending on jurisdiction. Tax planning must consider the classification of income as salary or royalty, as it impacts tax rates, deductions, and compliance obligations.
Passive Income Potential: The Royalty Advantage
Salary income provides a steady stream of earnings based on fixed compensation for services rendered, limiting the scope for growth beyond periodic raises or promotions. Royalty income, derived from intellectual property like books, patents, or music, offers significant passive income potential as it generates earnings continuously without ongoing active work. This royalty advantage enables individuals to build long-term wealth by leveraging creative assets that produce sustained cash flow over time.
Career Growth: Advancing Through Salary or Royalty Opportunities
Salary income provides a stable cash flow essential for consistent career growth and predictable financial planning. Royalty income, often tied to intellectual property or creative works, can offer scalable earnings that grow with the success and market reach of the asset. Career advancement strategies should weigh the security of salary against the potential for exponential growth through royalties in relevant industries.
Which is Better for Wealth Building: Salary or Royalty Income?
Salary income provides stability and predictable cash flow, essential for meeting regular financial obligations and building a foundation for savings and investments. Royalty income, derived from intellectual property or creative works, offers the potential for passive earnings and long-term wealth growth with minimal ongoing effort. For sustainable wealth building, combining a reliable salary with royalty income streams can maximize financial security and wealth accumulation.
Related Important Terms
Active Salary Streams
Salary income represents active earnings derived from employment, characterized by fixed periodic payments and consistent tax withholdings. Royalty income, while potentially recurring, stems from intellectual property rights and is considered passive, often subject to different tax treatments and lacking the regularity of active salary streams.
Passive Royalty Flow
Salary income is earned from active employment and is subject to regular tax withholding, while royalty income represents passive earnings derived from intellectual property rights, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks. Royalty income provides a sustainable passive flow that can continue without direct involvement, often yielding higher long-term returns compared to fixed salary payments.
Creator Economy Payouts
Salary income provides a fixed, predictable paycheck based on employment agreements, while royalty income in the creator economy varies depending on content performance, licensing deals, and platform monetization models. Creators leveraging royalty income benefit from scalable earnings tied to audience engagement, often surpassing traditional salary limits through digital distribution and intellectual property rights.
Traditional Payroll Channels
Salary income is earned through traditional payroll channels where employers withhold taxes and contribute to social security on behalf of employees, ensuring regular and stable payments. Royalty income, in contrast, originates from intellectual property rights and is typically received directly by individuals without payroll deductions, often subject to different tax treatments and reporting requirements.
Intellectual Property Earnings
Salary income derives from employment contracts and is subject to regular tax withholding, whereas royalty income originates from licensing intellectual property rights such as copyrights, patents, or trademarks and is taxed based on the net earnings from these assets. Intellectual property earnings from royalties often provide passive income streams with variable taxation depending on jurisdiction-specific regulations and the nature of the licensed rights.
Automated Licensing Royalties
Automated licensing royalties generate passive income through systematic distribution of intellectual property, often yielding higher returns compared to traditional salary income due to scalability and reduced active involvement. Unlike fixed salary income, royalty income fluctuates based on usage, sales, or licenses granted, offering potential exponential growth tied to the value and reach of the licensed assets.
W-2 Wage Income
W-2 wage income represents earnings from employment reported on a W-2 form, reflecting consistent salary or hourly wages subject to payroll taxes and withholding, while royalty income derives from intellectual property rights like patents, copyrights, or natural resources, often reported on Schedule E. Salary income provides steady, predictable cash flow with standard tax treatment, whereas royalty income can vary greatly and may qualify for different tax deductions and credits.
Residual Content Revenue
Salary income is a fixed amount earned regularly from employment, while royalty income generates residual revenue from intellectual property or content usage rights. Residual content revenue from royalties offers ongoing passive income streams, often scaling with the distribution and popularity of the content.
SaaS Royalty Sharing
Salary income is a fixed compensation earned by employees for their services, subject to standard tax withholding, while royalty income from SaaS royalty sharing involves ongoing earnings based on licensing or usage of software services, often requiring specialized tax treatment for digital assets and intellectual property rights. SaaS royalty sharing models generate passive income streams tied to subscription revenues, incentivizing stakeholders to optimize platform adoption and usage metrics to maximize royalty distributions.
Performance-based Compensation
Performance-based compensation in salary income is typically structured through bonuses, commissions, or incentives directly tied to an employee's measurable achievements or company performance metrics. Royalty income, however, arises from intellectual property rights or asset usage and does not fluctuate based on personal performance but rather on usage rates or sales volumes of the underlying asset.
Salary Income vs Royalty Income for income sources. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com