Bonus pay provides immediate, taxable income based on performance metrics, offering employees a direct financial reward without ownership rights. Phantom stock simulates equity ownership by granting employees cash bonuses tied to stock value, aligning income with company success while deferring actual share issuance. Choosing between bonus pay and phantom stock depends on preferences for immediate income versus potential long-term gains linked to company performance.
Table of Comparison
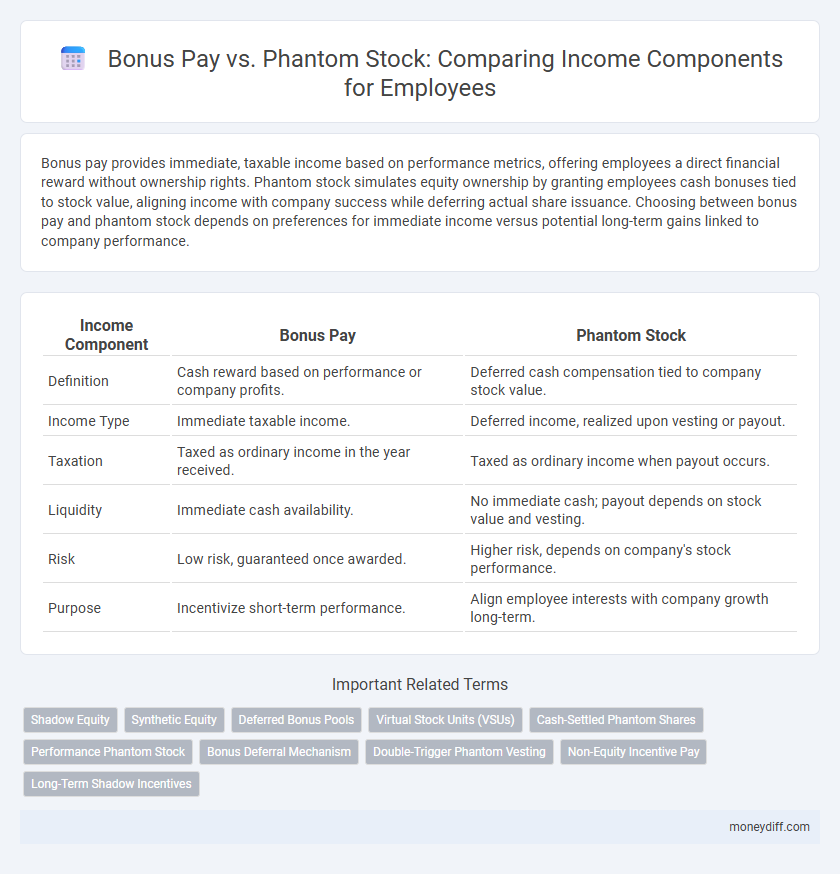
| Income Component | Bonus Pay | Phantom Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cash reward based on performance or company profits. | Deferred cash compensation tied to company stock value. |
| Income Type | Immediate taxable income. | Deferred income, realized upon vesting or payout. |
| Taxation | Taxed as ordinary income in the year received. | Taxed as ordinary income when payout occurs. |
| Liquidity | Immediate cash availability. | No immediate cash; payout depends on stock value and vesting. |
| Risk | Low risk, guaranteed once awarded. | Higher risk, depends on company's stock performance. |
| Purpose | Incentivize short-term performance. | Align employee interests with company growth long-term. |
Understanding Bonus Pay and Phantom Stock
Bonus pay offers immediate cash compensation based on individual or company performance, providing clear and direct income benefits. Phantom stock mimics real stock ownership by granting employees the right to receive cash equivalents tied to stock value, aligning employee incentives with long-term company success. Understanding the distinct income timing and tax implications of bonus pay and phantom stock helps optimize compensation strategies for sustained financial growth.
Core Differences Between Bonus Pay and Phantom Stock
Bonus pay is a direct cash reward based on individual or company performance, offering immediate income and no future obligations. Phantom stock represents a contractual right to receive a cash payment equivalent to company stock value appreciation, aligning employee interests with long-term company growth without granting actual shares. While bonus pay impacts short-term cash flow, phantom stock provides deferred income tied to stock value, often with vesting periods and tax advantages.
How Bonus Pay Contributes to Income
Bonus pay directly increases an employee's total income by providing immediate monetary rewards based on performance or company profitability. Unlike phantom stock, which offers potential future value, bonus pay enhances cash flow and financial liquidity in the short term. This form of income incentivizes productivity and can significantly boost annual earnings without affecting equity ownership.
Phantom Stock as an Income Component
Phantom stock serves as a valuable income component by providing employees with the economic benefits of stock ownership without actual equity issuance, often tied to company performance metrics. Unlike traditional bonus pay, phantom stock aligns employee incentives with long-term company growth, delivering potential financial gains through stock value appreciation and dividends. This form of compensation enhances income stability and tax deferral opportunities, making it a strategic tool for wealth accumulation.
Tax Implications of Bonus Pay vs Phantom Stock
Bonus pay is typically taxed as ordinary income in the year it is received, resulting in immediate tax liability for employees. Phantom stock, on the other hand, generally defers tax until the stock vests or is paid out, allowing potential tax deferral benefits. The timing and nature of taxation for phantom stock can provide strategic planning advantages compared to the immediate taxation of bonus pay.
Liquidity: Immediate vs Deferred Income Benefits
Bonus pay provides immediate liquidity by delivering cash directly to employees, enhancing short-term income and spending capacity. Phantom stock, on the other hand, offers deferred income benefits by mimicking stock ownership value without granting actual equity, potentially leading to significant payouts aligned with company performance over time. This deferred structure can increase long-term financial gains but lacks the immediate cash flow advantages of bonus pay.
Aligning Incentives: Performance Bonuses vs Stock-Based Compensation
Performance bonuses provide immediate financial rewards tied directly to individual or company achievements, fostering short-term motivation and goal attainment. Phantom stock offers long-term incentives by simulating equity ownership without actual stock issuance, aligning employee interests with company growth and shareholder value. Combining these compensation components effectively balances short-term performance incentives with sustainable wealth accumulation, optimizing overall income alignment.
Risk Factors: Bonus Pay Stability vs Phantom Stock Volatility
Bonus pay offers more stable income as it is typically tied to short-term performance metrics and company profitability, providing predictable cash flow to employees. Phantom stock, however, carries greater risk due to its dependency on the company's long-term stock performance and market volatility, potentially resulting in fluctuating or delayed compensation. Employees seeking consistent income might favor bonus pay, while those willing to accept volatility for potential higher returns may consider phantom stock.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Financial Impact
Bonus pay provides immediate cash flow, enhancing short-term income with direct tax implications in the current fiscal year. Phantom stock offers potential long-term financial benefits by mimicking equity gains without ownership, allowing deferred taxation until payout. Choosing between bonus pay and phantom stock depends on prioritizing immediate liquidity versus long-term wealth accumulation and tax planning strategies.
Choosing the Right Income Component for Financial Planning
Bonus pay offers immediate taxable income and enhances short-term cash flow, making it suitable for meeting current financial needs or debt repayment. Phantom stock provides deferred compensation linked to company performance, benefiting long-term wealth accumulation and tax planning by aligning income with equity growth. Selecting between these income components depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax considerations to optimize overall financial planning.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Equity
Bonus pay provides immediate cash income, while phantom stock functions as shadow equity, offering deferred compensation linked to company valuation without granting actual shares. Shadow equity through phantom stock aligns employee incentives with long-term corporate growth, enhancing income potential beyond traditional bonus structures.
Synthetic Equity
Bonus pay provides immediate cash income as a reward for performance, while phantom stock offers synthetic equity that mirrors actual stock value appreciation without granting true ownership, aligning employee incentives with company growth over time. Phantom stock serves as a deferred compensation tool that can enhance long-term income potential by simulating equity benefits without diluting shareholder equity.
Deferred Bonus Pools
Deferred bonus pools allocate income by postponing bonus pay distribution, enhancing tax efficiency and aligning employee incentives with long-term company performance. Phantom stock components provide a simulated equity value increase without actual share transfer, offering deferred income benefits tied to company valuation growth.
Virtual Stock Units (VSUs)
Bonus pay provides immediate cash income based on performance metrics, while Phantom Stock, specifically Virtual Stock Units (VSUs), offers long-term income potential tied to company stock value without actual equity ownership. VSUs align employee incentives with shareholder interests by granting value appreciation benefits, typically payable at vesting or liquidity events.
Cash-Settled Phantom Shares
Cash-settled phantom shares provide income through cash payments based on the company's stock value without granting actual equity, offering employees a performance-linked bonus that mimics stock appreciation. Unlike traditional bonus pay, phantom stock aligns employee income with long-term company success, potentially delivering higher financial rewards tied directly to market performance.
Performance Phantom Stock
Performance Phantom Stock incentivizes employees by granting cash bonuses tied directly to company performance metrics, offering a stock-simulated income without equity dilution. Unlike traditional bonus pay, which is a one-time cash reward, Performance Phantom Stock aligns long-term employee income with shareholder value, enhancing retention and motivation.
Bonus Deferral Mechanism
Bonus pay provides immediate income, whereas phantom stock offers deferred compensation tied to company performance, allowing employees to benefit from equity value growth without actual stock ownership. The bonus deferral mechanism enhances tax efficiency and aligns employee incentives with long-term corporate goals by postponing taxable income until vesting or payout.
Double-Trigger Phantom Vesting
Bonus pay provides immediate income but lacks long-term wealth-building potential, whereas double-trigger phantom stock combines income with equity-mimicking benefits by vesting only upon company performance and a qualifying event such as a sale or IPO. This structure aligns employee incentives with shareholder value while offering tax deferral advantages and potential significant financial upside.
Non-Equity Incentive Pay
Bonus pay offers immediate cash rewards based on performance metrics, providing direct income benefits without affecting equity ownership. Phantom stock simulates equity value increases, delivering long-term non-equity incentive pay through cash payouts tied to company stock performance without granting actual shares.
Long-Term Shadow Incentives
Bonus pay provides immediate income boosts tied to short-term performance metrics, while phantom stock serves as a long-term shadow incentive aligning employee interests with company equity appreciation without actual stock issuance. Phantom stock enhances retention by offering deferred compensation that mirrors stock value growth, thereby optimizing income components for sustained financial motivation.
Bonus pay vs Phantom stock for income components. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com