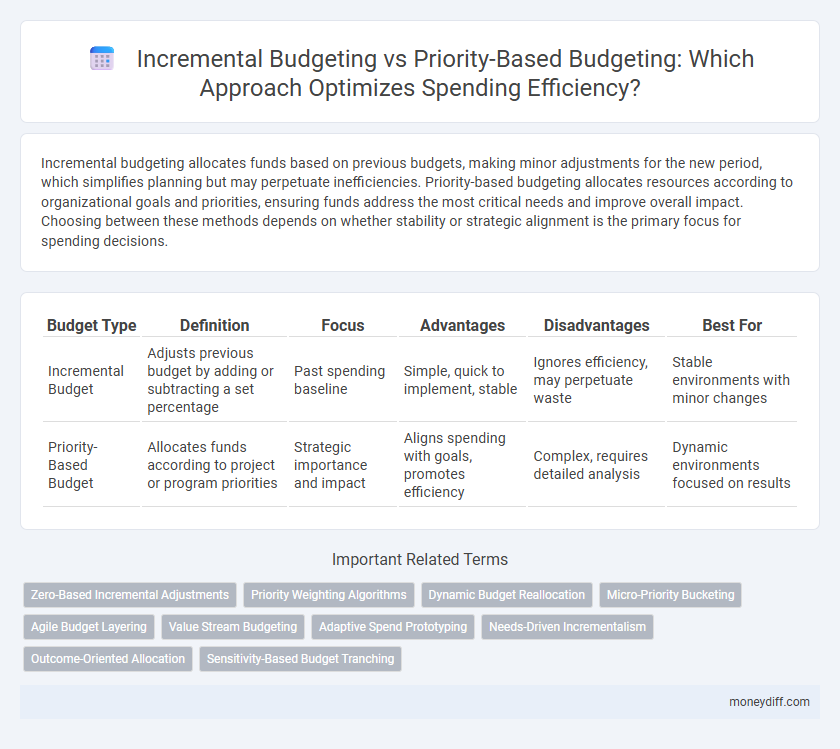
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on previous budgets, making minor adjustments for the new period, which simplifies planning but may perpetuate inefficiencies. Priority-based budgeting allocates resources according to organizational goals and priorities, ensuring funds address the most critical needs and improve overall impact. Choosing between these methods depends on whether stability or strategic alignment is the primary focus for spending decisions.
Table of Comparison
| Budget Type | Definition | Focus | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incremental Budget | Adjusts previous budget by adding or subtracting a set percentage | Past spending baseline | Simple, quick to implement, stable | Ignores efficiency, may perpetuate waste | Stable environments with minor changes |
| Priority-Based Budget | Allocates funds according to project or program priorities | Strategic importance and impact | Aligns spending with goals, promotes efficiency | Complex, requires detailed analysis | Dynamic environments focused on results |
Understanding Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting allocates funds by making adjustments based on the previous period's budget, typically increasing or decreasing by a set percentage. This method simplifies budget preparation but can perpetuate inefficiencies by assuming past allocations are appropriate without comprehensive review. Understanding incremental budgeting is essential for organizations aiming to balance fiscal stability with operational flexibility in their spending plans.
What is Priority-Based Budgeting?
Priority-Based Budgeting allocates resources according to the strategic importance and outcomes of programs rather than historical spending levels. This approach helps identify which activities deliver the highest value and ensures funds are directed towards priorities that align with organizational goals. Unlike Incremental Budgeting, it fosters efficient resource use by focusing on impactful initiatives rather than incremental adjustments.
Key Differences Between Incremental and Priority-Based Budgets
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on previous budgets, adjusting amounts by a fixed percentage, which often leads to perpetuating past inefficiencies and limited alignment with strategic goals. Priority-based budgeting allocates resources according to the importance and impact of activities, promoting efficient spending that aligns with organizational priorities and objectives. This approach enhances transparency and accountability, ensuring funds target high-value programs rather than uniformly increasing or decreasing all expenditures.
Pros and Cons of Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting simplifies financial planning by using the previous year's budget as a baseline, allowing for easy adjustments and predictability in spending. However, it may perpetuate inefficiencies by allocating funds without critically evaluating program effectiveness or changing organizational priorities. This approach often limits flexibility, making it difficult to respond to new opportunities or challenges compared to priority-based budgeting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Priority-Based Budgeting
Priority-based budgeting allocates funds according to the importance of projects, ensuring resources target high-impact initiatives and improving strategic alignment. This approach enhances transparency and accountability by linking expenditures to organizational goals but can be time-consuming and complex to implement due to the need for detailed prioritization criteria and stakeholder consensus. However, it may also lead to underfunding essential but less visible functions, presenting a challenge in balancing innovation with core operational needs.
Impact on Organizational Financial Planning
Incremental budgeting relies on past expenditures as a baseline, which can limit financial agility and hinder strategic reallocation of resources during organizational financial planning. Priority-based budgeting allocates funds according to the importance of projects, improving alignment with strategic goals and enhancing the organization's capability to respond to changing financial conditions. This approach fosters more efficient resource distribution, driving better financial outcomes and supporting long-term sustainability.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method for Your Needs
Incremental budgeting adjusts previous period expenditures by a fixed percentage, making it straightforward but often perpetuating inefficiencies. Priority-based budgeting allocates funds based on program importance and impact, promoting optimal resource use aligned with strategic goals. Selecting the right budgeting method depends on organizational priorities, transparency needs, and the desire for flexibility in managing financial resources effectively.
Steps to Transition from Incremental to Priority-Based Budgeting
Transitioning from incremental budgeting to priority-based budgeting involves first conducting a thorough review of existing expenditures to identify non-essential costs and reallocate funds toward high-impact programs. Next, stakeholders must establish clear organizational goals and criteria to rank projects based on strategic priorities and potential outcomes. Finally, implement a transparent decision-making process with regular monitoring and adjustments to ensure resources align with evolving priorities and maximize overall budget efficiency.
Common Challenges in Budget Implementation
Incremental budgeting often leads to the perpetuation of past inefficiencies and limits flexibility in adapting to changing priorities, causing resource misallocation. Priority-based budgeting requires accurate data and stakeholder consensus, which can be difficult to achieve, resulting in delays and resistance during implementation. Both approaches face challenges such as inadequate communication, limited training, and lack of clear performance metrics that hinder effective budget execution.
Best Practices for Effective Money Management
Incremental budgeting adjusts the previous period's budget by a fixed percentage, favoring stability but risking inefficiency by perpetuating outdated allocations. Priority-based budgeting allocates funds based on the strategic importance and expected outcomes of programs, enhancing resource effectiveness and alignment with organizational goals. Implement best practices by regularly reviewing budget priorities, incorporating data-driven analysis, and engaging stakeholders to ensure transparent, flexible, and goal-oriented financial planning.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Incremental Adjustments
Zero-Based Incremental Adjustments in budgeting involve reviewing and justifying expenditures from a zero base, ensuring each cost item is necessary, unlike traditional incremental budgets that adjust prior allocations by a fixed percentage. Priority-Based Budgeting allocates resources according to strategic importance, but combining it with zero-based incremental adjustments enhances financial efficiency by continuously reassessing priorities and eliminating outdated or low-value expenses.
Priority Weighting Algorithms
Priority weighting algorithms enhance priority-based budgeting by systematically assigning weights to spending categories based on strategic goals and impact metrics, improving resource allocation effectiveness compared to incremental budgeting, which adjusts previous budgets by fixed increments without reevaluating priorities. These algorithms dynamically analyze stakeholder inputs, historical data, and performance indicators to optimize budget distribution toward high-impact initiatives, driving more efficient fiscal outcomes and aligning expenditures with organizational objectives.
Dynamic Budget Reallocation
Incremental budgeting adjusts previous budgets with slight increases or decreases, often leading to less flexibility in reallocating funds, whereas priority-based budgeting allocates resources dynamically based on program importance and performance metrics. Dynamic budget reallocation enhances fiscal efficiency by continuously shifting funds toward high-impact initiatives, promoting adaptive spending aligned with strategic priorities.
Micro-Priority Bucketing
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on previous expenditures with minor adjustments, which often leads to inefficiencies, whereas priority-based budgeting, especially through micro-priority bucketing, strategically categorizes spending into granular priority groups to optimize resource allocation and enhance fiscal discipline. Micro-priority bucketing enables organizations to align budgetary decisions closely with specific goals by assigning clear priority levels to individual projects or expenses, improving transparency and maximizing the impact of each dollar spent.
Agile Budget Layering
Incremental Budget allocates funds based on previous spending patterns with minor adjustments, supporting stability but often limiting flexibility, while Priority-Based Budget prioritizes resource allocation aligned with strategic goals and outcomes, enhancing responsiveness and value delivery. Agile Budget Layering integrates both approaches by layering fixed baseline costs with dynamic priority-driven increments, enabling adaptive spending that balances consistency and strategic agility.
Value Stream Budgeting
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on previous periods, often perpetuating inefficiencies, while priority-based budgeting allocates resources according to strategic goals and value streams, enhancing spending effectiveness. Value stream budgeting aligns financial commitments with the delivery of customer value, driving continuous improvement and optimal resource utilization across business processes.
Adaptive Spend Prototyping
Incremental Budget allocates funds based on previous expenditures, often reinforcing existing priorities without accommodating significant changes, while Priority-Based Budget aligns spending with strategic goals by evaluating program importance and impact. Adaptive Spend Prototyping enhances decision-making by iteratively testing budget scenarios, enabling dynamic adjustments to better match organizational priorities and optimize resource allocation.
Needs-Driven Incrementalism
Needs-driven incrementalism in budgeting focuses on adjusting funds based on evolving organizational requirements, contrasting with priority-based budgeting which allocates resources according to strategic importance and outcomes. This approach ensures flexible allocation that addresses immediate operational demands while maintaining fiscal discipline through gradual budget increments.
Outcome-Oriented Allocation
Incremental budgeting increases existing budget allocations based on previous expenditures, often neglecting outcome-based performance metrics, whereas priority-based budgeting allocates funds by evaluating programs' effectiveness and strategic importance to maximize impact. Outcome-oriented allocation in priority-based budgeting ensures resources directly support high-priority goals, improving efficiency and accountability in public and organizational spending.
Sensitivity-Based Budget Tranching
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on prior expenditure with minor adjustments, whereas priority-based budgeting focuses on funding programs aligned with strategic goals and performance outcomes. Sensitivity-based budget tranching enhances decision accuracy by segmenting budgets according to spending sensitivity, enabling more precise resource distribution and risk management within both incremental and priority-based frameworks.
Incremental Budget vs Priority-Based Budget for Spending Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com