Withholding tax applies to digital asset earnings by automatically deducting a portion of income at the source, ensuring compliance and timely revenue collection for tax authorities. Crypto tax, however, requires individuals to report gains and losses from cryptocurrency transactions, which can be complex due to volatility and varying asset classifications. Understanding the distinctions between withholding tax and crypto tax is crucial for accurately managing tax obligations and avoiding penalties in digital asset investments.
Table of Comparison
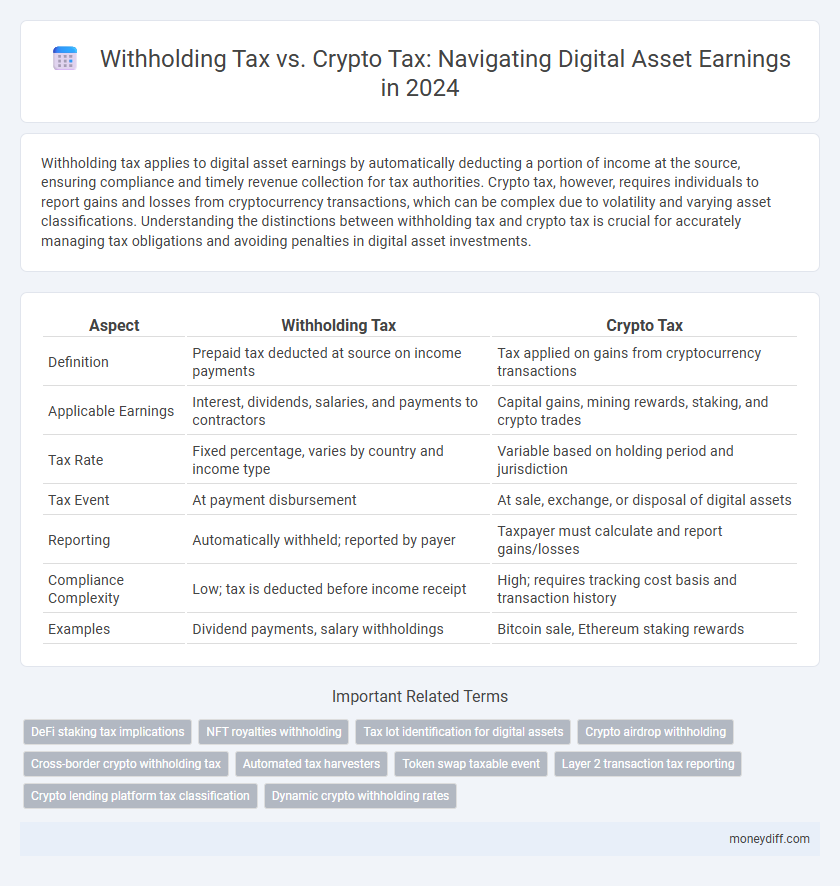
| Aspect | Withholding Tax | Crypto Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prepaid tax deducted at source on income payments | Tax applied on gains from cryptocurrency transactions |
| Applicable Earnings | Interest, dividends, salaries, and payments to contractors | Capital gains, mining rewards, staking, and crypto trades |
| Tax Rate | Fixed percentage, varies by country and income type | Variable based on holding period and jurisdiction |
| Tax Event | At payment disbursement | At sale, exchange, or disposal of digital assets |
| Reporting | Automatically withheld; reported by payer | Taxpayer must calculate and report gains/losses |
| Compliance Complexity | Low; tax is deducted before income receipt | High; requires tracking cost basis and transaction history |
| Examples | Dividend payments, salary withholdings | Bitcoin sale, Ethereum staking rewards |
Understanding Withholding Tax and Crypto Tax
Withholding tax on digital asset earnings involves the automatic deduction of a percentage of income at the source by a payer, which is then remitted to tax authorities to ensure compliance and simplify tax collection. Crypto tax, on the other hand, is a broader tax obligation where individuals or entities report profits or losses from cryptocurrency transactions, including trading, mining, and staking, based on capital gains or income tax rules. Understanding the distinction clarifies that withholding tax is a pre-collection mechanism, while crypto tax requires comprehensive self-reporting of all digital asset activities.
Key Differences Between Withholding Tax and Crypto Tax
Withholding tax applies to income sources where a portion is deducted at the source by the payer before the recipient receives the payment, commonly used in salaries, dividends, and interest income. Crypto tax specifically targets gains from digital asset transactions, including trading, mining, and staking, with reporting obligations based on realized capital gains or income. The key differences lie in the tax collection mechanism--automatic deduction versus self-reporting--and the asset types covered, where withholding tax is broader and crypto tax is specialized for digital currencies.
Scope of Application: Which Digital Assets Are Affected?
Withholding tax primarily applies to payments made to non-residents for digital asset transactions such as cryptocurrency sales, staking rewards, and airdrops, ensuring tax compliance at the source. Crypto tax covers a broader scope, including capital gains, income from mining, trading profits, and decentralized finance (DeFi) rewards across various digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, stablecoins, and NFTs. Understanding the scope of application clarifies that withholding tax targets cross-border transfers, while crypto tax regulations encompass all taxable events involving digital assets regardless of residency.
Taxation Process: Withholding vs Crypto Earnings
Withholding tax on digital asset earnings involves deducting a fixed percentage at the source before payment reaches the taxpayer, ensuring immediate tax collection and reducing evasion risks. In contrast, crypto tax requires individuals to self-report capital gains or income from cryptocurrency transactions based on fair market value at the time of each event, often subject to varying tax rates depending on jurisdiction and holding period. The taxation process for withholding tax is more automated and predictable, while crypto tax demands detailed record-keeping and compliance with complex reporting requirements to determine accurate tax liabilities.
Who Is Liable: Taxpayer Responsibilities Explained
Taxpayers earning from digital assets must understand that withholding tax applies when a third party deducts tax at the source during a transaction, whereas crypto tax requires individuals to self-report gains from cryptocurrency trading or mining. The responsibility lies with the taxpayer to accurately declare income, calculate taxes owed, and comply with local tax regulations governing digital asset earnings. Failure to fulfill these obligations can result in penalties, making awareness of withholding and crypto tax rules critical for lawful and efficient tax management.
Reporting Requirements for Digital Asset Holders
Digital asset holders must adhere to specific reporting requirements for withholding tax and crypto tax on digital asset earnings, including declaring all transactions and income from digital currencies to tax authorities. Withholding tax often requires payers to deduct tax at the source on certain crypto payments, while crypto tax mandates individuals report gains and losses on digital asset transactions in their annual tax returns. Accurate reporting involves detailed records of transaction dates, amounts, wallet addresses, and fair market values to ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid penalties.
Compliance Challenges in Digital Asset Taxation
Withholding tax on digital asset earnings requires accurate identification and reporting of payees to ensure regulatory compliance, while crypto tax presents challenges due to the decentralized and pseudonymous nature of transactions. Tax authorities face difficulties in tracking crypto asset gains, calculating fair market values, and enforcing tax obligations amidst evolving digital asset regulations. Effective compliance demands robust blockchain analytics and clear guidelines to mitigate risks of underreporting and tax evasion in the digital asset ecosystem.
International Regulations: Crypto vs Withholding Tax
International regulations on withholding tax and crypto tax for digital asset earnings vary significantly, with many countries implementing distinct frameworks to address the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies. While withholding tax is commonly applied to cross-border payments and is well-established in international tax treaties, crypto tax regulations often require reporting of capital gains, income from mining, staking, and transactions, reflecting the unique attributes of digital assets. Compliance challenges arise from inconsistent definitions, valuation complexities, and evolving regulatory approaches, necessitating careful consideration by taxpayers and multinational businesses dealing with digital currencies.
Penalties for Non-Compliance in Digital Asset Taxation
Penalties for non-compliance in digital asset taxation can be severe, with withholding tax violations leading to fines ranging from 10% to 50% of the unpaid tax amount, depending on jurisdiction. Failure to report crypto earnings accurately may result in additional interest charges and, in some cases, criminal prosecution. Tax authorities increasingly use blockchain analytics to enforce compliance and detect underreported digital asset income.
Future Trends in Withholding and Crypto Taxation
Future trends in withholding and crypto taxation indicate increased regulatory scrutiny and integration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency and compliance. Governments worldwide are likely to implement automated withholding mechanisms specifically tailored for digital asset transactions to ensure accurate tax collection. Advancements in tax reporting infrastructure will facilitate real-time tracking of crypto earnings, reducing tax evasion and promoting global tax harmonization.
Related Important Terms
DeFi staking tax implications
Withholding tax on digital asset earnings typically applies to centralized platforms where taxes are automatically deducted, whereas crypto tax for DeFi staking requires self-reporting of income earned from decentralized finance protocols, often classified as ordinary income or capital gains. Staking rewards in DeFi are subject to specific tax implications, including their fair market value at the time of receipt and potential taxable events upon withdrawal or conversion, making accurate record-keeping essential for compliance.
NFT royalties withholding
Withholding tax on NFT royalties requires platforms to deduct a percentage of earnings before payment to creators, ensuring compliance with tax authorities and timely revenue collection. Crypto tax on digital asset earnings includes reporting NFT royalties as taxable income, subject to capital gains or ordinary income tax depending on jurisdiction and transaction nature.
Tax lot identification for digital assets
Tax lot identification plays a crucial role in accurately calculating withholding tax and crypto tax on digital asset earnings by determining the cost basis of each asset acquired. Proper tax lot tracking enables taxpayers to minimize taxable gains and optimize reporting by selecting specific identification, FIFO, or LIFO methods aligned with IRS guidelines.
Crypto airdrop withholding
Crypto airdrop withholding tax applies when digital assets received are considered taxable income, requiring entities to withhold a percentage of the value at distribution to comply with local tax regulations. Unlike traditional withholding tax on income, crypto tax reporting demands tracking of airdrop fair market value at the time of receipt for accurate capital gains or income tax calculations.
Cross-border crypto withholding tax
Cross-border crypto withholding tax applies to digital asset earnings transferred across international borders, requiring accurate classification of income types to ensure compliance with differing national tax regulations. Digital asset earnings are often subject to withholding tax rates that vary by jurisdiction, necessitating thorough understanding of bilateral tax treaties to optimize tax liabilities on cross-border crypto transactions.
Automated tax harvesters
Automated tax harvesters streamline the calculation of withholding tax and crypto tax on digital asset earnings by accurately tracking transaction history and identifying taxable events. These tools optimize tax compliance by minimizing errors and maximizing deductions related to withholding obligations and digital asset capital gains.
Token swap taxable event
Withholding tax on digital assets generally applies to cross-border payments and is withheld at the source, while crypto tax encompasses broader obligations including capital gains and income from token swaps, which are considered taxable events triggering recognition of gains or losses. Token swaps specifically qualify as taxable events because exchanging one cryptocurrency for another is treated as a disposal, requiring accurate reporting of fair market value at the time of the swap to compute taxable income.
Layer 2 transaction tax reporting
Withholding tax on digital asset earnings requires reporting Layer 2 transaction details, including gas fees and transaction values, to accurately calculate taxable income. Crypto tax regulations mandate detailed disclosures of Layer 2 network activities to ensure compliance and avoid underreporting taxable gains from digital asset transactions.
Crypto lending platform tax classification
Crypto lending platform earnings are subject to crypto tax regulations, where income from interest or rewards is classified as taxable income rather than withholding tax, which typically applies to traditional financial dividends or payments to non-residents. Accurate tax classification on crypto lending platforms requires reporting gains and interest as ordinary income under cryptocurrency tax laws, ensuring compliance with digital asset taxation frameworks.
Dynamic crypto withholding rates
Dynamic crypto withholding rates adjust in real-time based on transaction size and jurisdiction, optimizing tax compliance for digital asset earnings. Unlike fixed withholding tax, these rates provide tailored taxation that accounts for market volatility and asset-specific regulations, enhancing transparency and accuracy in crypto tax reporting.
Withholding tax vs Crypto tax for digital asset earnings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com